ADRA Kit
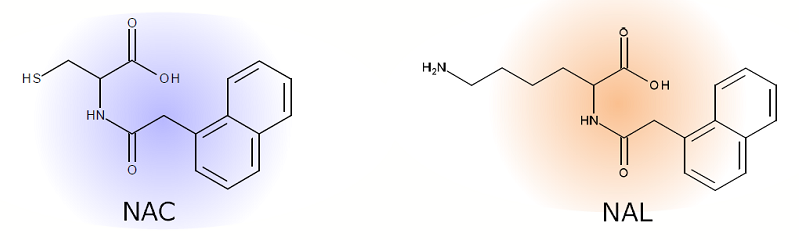
ADRA(Amino acid Derivative Reactivity Assay) is in chemico test method, representing an alternative (non-animal) method, for the evaluation of skin sensitization potential compounds. The kit comprises two amino acid derivates, NAC (N-(2-(1-naphthyl)acetyl)-L-cysteine) and NAL (α-N-(2-(1-naphthyl)acetyl)-L-lysine), which are composed out of a nucleophilic region and a detection molecule (naphthalene rings).
ADRA examination instruction video
These videos explain some of the procedures in the examination. Please check the package insert for the specific operation details.
Principle
ADRA is proposed to address the molecular initiating event of skin sensitization AOP (Adverse Outcome Pathway) by quantifying the reactivity of the test compounds against the model synthetic amino acid derivatives. The reaction is monitored by HPLC-analysis after 24 hours incubation at 25°C and 281 nm, determining the relative residual concentration of NAC and NAL in the reaction liquid.
Advantages of ADRA
- NAC and NAL are detected at a relatively long wavelength (281 nm).
・・・ Preventing co-elution of the test chemical and the nucleophilic reagent. - ADRA avoids precipitation by using only 1% of reactants of the existing method.
- Variability of result values are very low.
・・・ In ADRA, the reaction is stopped by the addition of a fixing solution (2.5%TFA) before analyzing. - Multiple test chemicals can be assayed in a short period of time.
・・・ The test procedure is performed using a single 96-well plate and a multichannel pipette.
Kit Components
-
Components Amount Qty NAC for 10 mL 2 vials NAL for 10 mL 2 vials NAC Buffer (pH 8.0) premixed for 300 mL 2 vials NAL Buffer (pH 10.2) premixed for 300 mL 2 vials 0.01 mol/L EDTA Solution for 1 mL 2 vials 
How to use
- Dissolve and prepare the buffer premix in water
- Dissolve NAC and NAL
- React the test compounds with 96-well plate for 24 hours
- Analyze it by HPLC
※Buffer premix, NAC, and NAL are subdivided into small amounts for reaction. It can be used for ADRA just by dissolving it.
96-well plate layout, HPLC condition, data analysis method, and data analysis sheet can be downloaded from here.
Required reagents & lab ware
Reagents
| Wako Cat. No. | Product Name | Grade | Package Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| 204-02743 | Trifluoroacetic Acid | Wako Special Grade | 25 mL |
| 015-08633 | Acetonitrile | for High Performance Liquid Chromatography | 3 L |
| 217-01031 | Ultrapure Water * | for Ultratrace Analysis | 1 L |
| 016-00346 | Acetone ** | Guaranteed Reagent | 500 mL |
| 043-07216 | Dimethyl Sulfoxide ** | Guaranteed Reagent | 500 mL |
* Use water with low metal content.
** Not to be used, if the test chemical dissolves in water or acetonitrile.
Phenylacetaldehyde (CAS RN® 122-78-1) is required as a positive control.
Lab ware
- Electronic balance –with a displayed precision of 0.1 mg
- Micropipette – Three micropipettes capable of distribution of 2 -10 μL, 10 - 100 μL, 100 - 1000 μL
- 12 channel pipette – capable of distribution of 50 - 150 μL
- HPLC system – equipped with a light-shielding auto-sampler for a 96-well plate capable of liquid feeding at 0.3 mL/min
- UV detector - photodiode array (PDA) detector or absorbance detector (281 nm)
- HPLC column
- pH meter – with precision of ±0.01 pH, equipped with a buffer solution for calibration
- Incubator – capable of a temperature of 25°C
- 96-well plate
- 500 mL plastic bottle
- Test tube mixer
- Plate seal*
* Use the seal having high sealability and solvent-resistant performance. - Plate shaker
- Plate centrifuge
Note: to avoid NAC/NAL dimerization upon metal ion contamination, all consumables (except for components for HPLC analysis) must be made of polypropylene or polyethylene.
References
| References | contents |
|---|---|
| Yamamoto Y et al (2015) J Appl Toxicol. 35, 1348-1360. | about prediction accuracy |
| Fujita M et al (2019) J Appl Toxicol. 39, 191-208. | |
| ADRA test guidline | about applicability limit |
| Direct Peptide Reactivity Assay (DPRA) Validation Study Report (in Japanese) | |
| Yamamoto Y et al.(2019) J Toxicol Sci. 44, 585-600. | about IATA (combination) |
| Fujita M et al.(2019) J Appl Toxicol. 39, 1492-1505. | about validation test |
| Amino acid Derivative Reactivity Assay (ADRA) JaCVAM Validation Study Report | |
| Direct Peptide Reactivity Assay (DPRA) Validation Study Report (in Japanese) | |
| Yamamoto Y et al.(2019) J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods, 97, 67-79. | about weight concentration modulation |
| Fujita M et al (2019) J Appl Toxicol. 39, 191-208. | about countermeasures for cysteine dimer |
| Fujita M et al (2019) J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 96, 95-105. | about Co-elution |
| Yamamoto Y et al.(2019) J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods, 97, 67-79. | about mixture measurement |
| Fujita M (2019) Toxicol In Vitro.59:161-178 | |
| Wanibuchi et al.(2019) J Toxicol Sci. 44, 821-832 | |
| Yamamoto Y et al. (2019) 100:106624. | about hardly soluble substance |
| ADRA SOP | about work efficiency |
| Fujita M et al (2019) J Appl Toxicol. 39, 191-208. | about variation in data (depletion) ⇒SD value fluctuation |
| ADRA SOP | about stop reaction |
| Fujita M. et al.(2014) J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods, 70, 94-105 | etc |
Application
High speed analysis (by Shimadzu Corporation)
Shimadzu Corporation showed an example of high-speed analysis of ADRA.
By using high-speed conditions, HPLC analysis can be completed in 18 hours in the test of 10 test substances, which took about 50 hours conventionally.
Please check the website of Shimadzu Corporation for the detail.
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.



