Antigen Retrieval Reagents
Reduced antigenicity in immunohistochemical staining is caused by epitope masking of the target antigen due to cross-linking by formalin during fixation. Antigen retrieval can be accomplished by heat or enzymatic treatment, but it is labor-intensive to test buffers and reaction conditions. In such cases, it is recommended to use buffers for antigen retrieval, such as ImmunoSaver, which eliminates the need for testing for conditions.
Product Line-up
More Information
Reduced Antigenicity and Antigen Retrieval Treatment
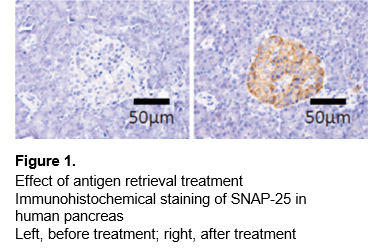
Reduced antigenicity in immunohistochemical staining is caused by epitope masking of the target antigen due to cross-linking by formalin during fixation. Antigen retrieval is the process of re-exposing epitopes, and the success or failure of antigen retrieval can make a big difference in staining (Figure 1).
Methods of Antigen Retrieval
There are several methods of antigen retrieval. The most frequently used are heat treatment and enzymatic treatment.
Heat Treatment
The cross-links are reversed by applying heat to the specimen. Heating can be accomplished using, in the order of increasing retrieval effectiveness, hot water bath, microwave, or autoclave. Several different solutions can be used, including distilled water (least effective), citrate buffer (pH 6.0), and Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0) (most effective). However, autoclaving and addition of Tris-EDTA buffer are not always the best choice. It is necessary to determine temperature, time, pH, and buffer conditions that are appropriate for each specimen, considering the antibody, fixation condition, and embedding method used. Since it is time-consuming to examine these conditions for each antigen, it is recommended to use a buffer for antigen retrieval such as ImmunoSaver, which eliminates the need for testing for conditions.
Enzymatic Treatment
Antigen retrieval is achieved by treatment with enzymes such as proteinase K, pepsin, or trypsin. Optimal enzyme concentration should be determined.
References
1) Okubo, K.: “Master of cell and tissue staining”, Yodosha, p.122(2014).
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.



