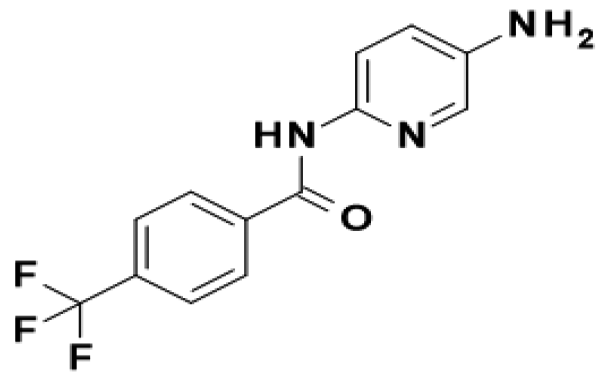
TFAP
- for Cellbiology
- Specification Assay :
- 97.0+% (HPLC)
- Manufacturer :
- FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation
- Storage Condition :
- Keep at -20 degrees C.
- Molecular Formula :
- C13H10F3N3O
- Molecular Weight :
- 281.23
- Structural Formula
- Label
- Packing
- SDS
|
Comparison
|
Product Number
|
Package Size
|
Price
|
Availability
|
Certificate of Analysis
|
Purchase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
10mg
|
|
Out of Stock |
※Check availability in the US with the distributor.
Document
Applications
Gastric ulcer formation test in rats
TTFAP, IMN (indomethacin), and aspirin were administered at 300, 10, and 30 mg/kg, respectively; mean + SEM; n = 4/group; ** p < 0.01 versus vehicle.
Gastric damage score was calculated by measuring the lengths, and summing the values for each rat at 4 h after oral administration of each compound. Indomethacin and aspirin induced gastric ulcer formation at 10 and 30 mg/kg, respectively (white arrow in panels c and d), while TFAP did not induce gastric ulcer formation even at 300 mg/kg.
Data was provided by Dr. Hiroki Kakuta, Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Okayama University.
Analgesic effect test
After oral administration of each compound, acetic acid aqueous solution was intraperitoneally injected or formalin was injected into the plantar surface of the hind paw. Then, analgesic effect was evaluated by counting the number of writhes, bites, and licks and so on. The results indicate that TFAP has an analgesic effect.
Data was provided by Dr. Hiroki Kakuta, Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Okayama University.
Chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay
The angiogenesis activity of TFAP was evaluated by the assay of chick chorioallantoic membrane (CAM). TFAP inhibited CAM angiogenesis at 300 ng/CAM.
Data was provided by Dr. Hiroki Kakuta, Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Okayama University.
References
- Kakuta, H., Zheng, X., Oda, H., Harada, S., Sugimoto, Y., Sasaki, K., Tai, A. : J. Med. Chem., 51, 2400(2008).
- Wako JIHO, 77(1), 6(2009).
Overview / Applications
| Outline | This product is for research use only. Do not administer it to human. Although cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) inhibition is thought to be a major mechanism of gastric damage by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), some COX-1-selective inhibitors exhibit strong analgesic effects without causing gastric damage. However, it is not clear whether their analgesic effects are attributable to COX-1-inhibitory activity or other bioactivities. We have launched N-(5-amino-2-pyridinyl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide (TFAP), which has a structure clearly different from those of currently available COX-1-selective inhibitors, is a potent COX-1-selective inhibitor (COX-1 IC50 = 0.80 +/- 0.05 um, COX-2 IC50 = 210 +/- 10 um). TFAP causes little gastric damage in rats even at an oral dose of 300 mg/kg, though it has an analgesic effect at as low a dose as 10 mg/kg. This shows that COX-1-selective inhibitors can be analgesic agents without causing gastric damage. Reference: |
|---|---|
| Precautions for Use | Packed on inactive gas |
Property
| Appearance | White - pale brown, crystals - powder |
|---|
Manufacturer Information
Alias
- N-(5-Amino-2-pyridinyl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.