Alzheimer's Disease Research
Alzheimer's disease is characterized pathologically by senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in postmortem brains and accounts for the largest proportion of the causes of dementia. Although the molecular mechanism of the onset of Alzheimer's disease has not yet been elucidated, an amyloid cascade hypothesis has been proposed in which amyloid-β (Aβ) gradually accumulates in the brain over several decades before the onset of the disease, abnormally phosphorylated tau protein and the like causes neurofibrillary tangles, and finally neuronopathy occurs and causes symptoms. Fujifilm Wako offers a line-up of reagents that can detect and measure important factors in Alzheimer's disease, including high-performance anti amyloid β antibodies and ELISA kits using these antibodies, as well as Aβ oligomers, tau protein, and phosphorylated tau protein.
Product Line-up
More Information
What is Alzheimer's Disease?
Alzheimer's Disease (AD) is a neurological disorder characterized primarily by cognitive impairments, such as memory loss. First reported by Alois Alzheimer in 1906, AD is estimated to account for 60-70% of dementia cases1). While most patients are aged 65 or older, some may develop the disease before the age of 65 due to certain genetic risk factors.
The pathological hallmarks of AD include senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs). Research has revealed that senile plaques are primarily extracellular deposits of a protein called amyloid β (Aβ), while NFTs are intracellular accumulations of hyperphosphorylated tau protein2). The accumulation of Aβ and tau is believed to lead to the progressive loss of neurons, contributing to the worsening of cognitive impairments such as memory loss.
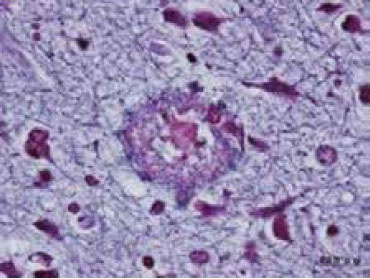
Senile plaque
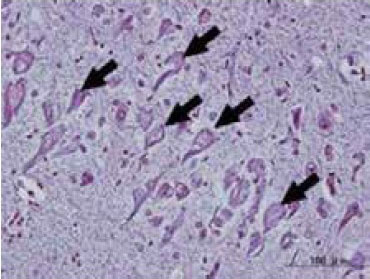
NFTs
The Mechanism of Development of Alzheimer's Disease - Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis -
The deposition of Aβ and the accumulation of tau are the main characteristics of AD, and how these molecules contribute to the onset and progression of the disease has long been a central topic of discussion. Various hypotheses have been proposed, among which the amyloid cascade hypothesis is one of the most widely supported. This hypothesis suggests that Aβ, particularly the highly toxic Aβ42, acts as the starting point of AD. It proposes that Aβ affects neurons, leading to the formation of NFTs, neuronal dysfunction, and subsequent neuronal death, ultimately resulting in dementia (Figure 1) 3).
Causative genes for familial AD, such as the Amyloid precursor protein (APP), a precursor of Aβ 4-5), and Presenilins (PSEN1/PSEN2), which are involved in the cleavage and production of Aβ 6), have been identified. These findings continue to support the amyloid cascade hypothesis. However, many treatments developed based on this hypothesis have failed in clinical trials due to safety issues or lack of efficacy, leading to most being discontinued. As a result, while the amyloid cascade hypothesis remains the dominant theory, its specifics are currently being reexamined.
More recently, the " Aβ oligomer hypothesis," which suggests that intracellular Aβ oligomers have a toxic effect on neurons, has gained attention 7). However, it is still unclear which specific oligomers contribute to the onset of AD, and further research is needed.
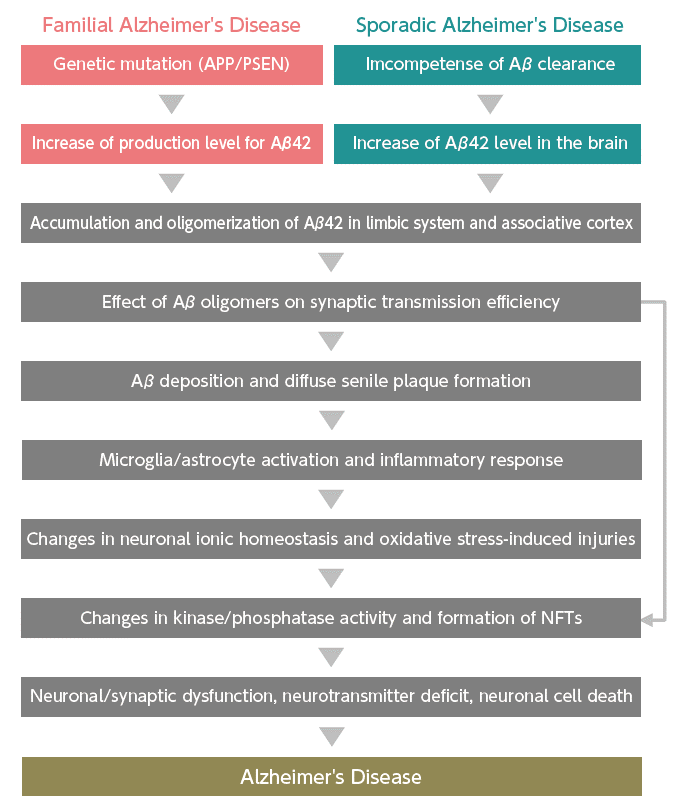
The Development of Alzheimer's Disease in the Context of the Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis
This figure is adapted from reference 3 and incorporates elements of the Aβ oligomer hypothesis.
References
- World Health Organization:
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia (Accessed 25 Apr. 2024) - Ihara, Y. et al.: J. Biochem., 99(6), 1807(1986).
Phosphorylated tau protein is integrated into paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease - Selkoe, D. J. and Hardy, J.: EMBO Mol. Med., 8(6), 595(2016).
The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease at 25 years - Goate, A. et al.: Nature, 349(6311), 704(1991).
Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer's disease - Chartier-Harlin et al.: Nature, 353(6347), 844(1991).
Early-onset Alzheimer's disease caused by mutations at codon 717 of the beta-amyloid precursor protein gene - Rogaev, E. I. et al.: Nature, 376(6543), 775(1995).
Familial Alzheimer's disease in kindreds with missense mutations in a gene on chromosome 1 related to the Alzheimer’s disease type 3 gene - Selkoe, D. J.: Science, 298(5594), 789(2002).
Alzheimer's disease is a synaptic failure
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.