ELISA / Assay Kits (Neuroscience)
Fujifilm Wako offers ELISA kits for use in research on neurological diseases, including kits for measurement of amyloid β (Aβ) and tau accumulation in the brain of patients with Alzheimer's disease, which is the most frequent cause of dementia, and for orexin, which is said to be the cause of narcolepsy. An ELISA kit for measuring brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a candidate marker of psychiatric disorders, is also available.
More Information
As for the difference between neurological and psychiatric disorders, those pathologically diagnosed in postmortem brains are called neurological disorders and other than these are called psychiatric disorders. Many studies on these diseases have been actively carried out, from basic research for elucidation of disease mechanisms to applied research for diagnosis and treatment. However, currently no established effective diagnosis or treatment method is available for most of these disorders, despite their high prevalence and great influence on quality of life (QOL).
Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders and Their Molecular Mechanisms
Alzheimer's Disease
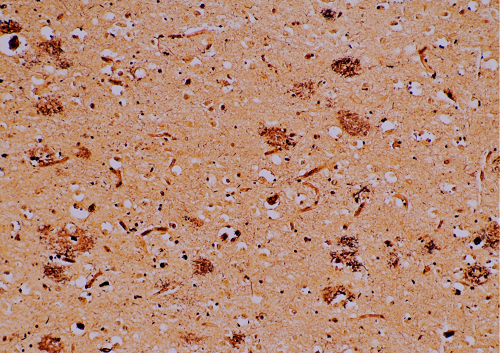
Dementia is a disorder that leads to cognitive decline, including memory loss, aphasia, apraxia, and executive dysfunction. There are several types of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, Lewy body dementia, and vascular dementia, while Alzheimer's disease is known to be the most common form. Alzheimer's disease, which was first reported by Alois Alzheimer in 1906, is characterized pathologically by senile plaques (insoluble deposit formed by aggregation and accumulation of amyloid-β) and neurofibrillary tangles in postmortem brains. Although the molecular mechanism of the onset of Alzheimer's disease has not yet been elucidated, there is a widely-accepted hypothesis in which Amyloid-β(Aβ)gradually accumulates in the brain over several decades before the onset of the disease, abnormally phosphorylated tau protein subsequently causes neurofibrillary tangles, and finally neuronopathy occurs and causes symptoms.
Aβ has long been studied as a causal factor in Alzheimer's disease. Human Aβ includes Aβ 40 and Aβ 42. Aβ 40 is said to be less cohesive, while Aβ 42 is considered to be more cohesive and more toxic. In previous research, a hypothesis was proposed in which Aβ shows higher toxicity when aggregated into aggregates that are dimers called Aβ oligomers or more complex aggregates. Various molecular species of Aβ oligomers exist, such as dimers, trimers, and 12-mers, and the size of Aβ oligomers that is important is a theme of discussion. Fujifilm Wako offers Aβ Oligomer ELISA Kit that can selectively measure 9-mer or higher Aβ oligomers.
Tau proteins control microtubule stability, as microtubule-associated proteins. Neurofibrillary tangles composed of accumulated phosphorylated tau are formed in the brain of patients with Alzheimer's disease and are reported to correlate with the severity of dementia. In addition, it has been reported that the concentrations of total tau and phosphorylated tau in the cerebrospinal fluid are higher in patients with Alzheimer's disease than in patients without dementia. Although biomarkers for diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease have not yet been established, T181, tau protein phosphorylated at threonine 181, is widely used. Fujifilm Wako provides ELISA kits that can measure total tau protein and phosphorylated tau protein (T181).
Depression
Major depressive disorder, is a type of mood disorder in which people experience depressed mood for a long period of time. Bipolar disorder (manic-depressive disorder), in which the states of mania and depression alternate cyclically, is also a type of mood disorder but is distinguished from major depression.
Sufferers of depression may have any of the following major symptoms: depressed mood (dispirited, feeling heavy), not finding fun in any activity, or lack of interest in anything (loss of pleasure or interest). At the same time, symptoms such as easily becoming tired (fatigability), being unable to sleep or always sleepy (sleep disturbance), and blaming oneself (feeling guilty) appear. Although approximately 10% of the population develops depression once in a lifetime, some patients may be forced to take a long-term absence from work or may even commit suicide, and thus various studies have been conducted to establish early diagnosis and treatment methods.
A variety of hypotheses regarding the mechanism of onset of depression have been proposed, including the monoamine hypothesis, in which the cause of depression is a decrease in the concentration of monoamines (serotonin, noradrenaline, dopamine) in the brain, and the HPA-axis hypothesis, in which the cause of depression is dysfunction of the stress response pathway, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.
Previous studies showed that serum concentration of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) was significantly lower in depression patients compared with healthy subjects, that severity of depression was correlated with serum BDNF concentration, and that the serum BDNF concentration was increased by use of an antidepressant. BDNF is also expected as a disease marker of depression. It has been clarified that precursor BDNF (ProBDNF) and mature BDNF (mBDNF) exist, and each has different physiological functions. To elucidate the mechanism of depression it is necessary to investigate the association of each molecule with depression. Fujifilm Wako developed the Mature BDNF ELISA Kit, which can specifically measure Mature BDNF.
Sleep-Wake Disorders

Throughout our lives the states of sleep and wake are repeated. The balance between these states is regulated by the brain, and any abnormality in the regulation causes trouble in switching between the sleep and wake states.
A representative disease caused by the above-mentioned abnormality is narcolepsy. Narcolepsy is a disease in which the patient shows strong daytime sleepiness and falls asleep in the daytime. In some cases, patients may fall asleep even in a tense condition, interfering with their daily activities.
One of the causes of narcolepsy is abnormal nerve activity of the orexin neuron. Orexin A is markedly decreased in the cerebrospinal fluid of narcolepsy patients, suggesting that orexin is necessary for the maintenance of arousal. Although a method requiring use of a radioisotope (RI) has been mainly used for measurement of orexin A, Fujifilm Wako offers the Orexin A ELISA Kit, which can conveniently measure orexin A without using RI.
References
- “Neuroscience Illustrated (3rd edition)” ed. by Manabe, T., Mori, H., Watanabe, M., Okano, H. and Miyakawa, T., Yodosha, Japan, (2013). (Japanese).
- “Dementia” ed. by Mori, H., Yodosha, Japan, (2017). (Japanese)
- Jeon, Sang Won, and Yong-Ku Kim.:International journal of molecular sciences, 17(3), 381(2016).
Molecular Neurobiology and Promising New Treatment in Depression
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.