Amino Acid, Peptides & Proteins
Amino acids are contained in food as nutrients and thus important chemical compounds. Approximately 20% of human body is composed of amino acids. Because amino acid concentration is strictly controlled in blood (plasma), and changes in amino acid in body fluid indicate altered metabolic and pathological conditions, it is used as an indicator of these conditions. To determination of amino acid sequence of protein or peptide in amino acid analysis, Edman method has been widely applied as a very useful method. In addition, to quantitative analysis of amino acids, derivatization methods (3-aminopyridyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate [APDS], phenylthiocarbamyl [PTC], and ninhydrin methods), by which amino acids are transformed into characteristic chemical compounds such as fluorescent substances to improve selectivity and sensitivity of measurement, have been applied.
FUJIFILM Wako has a large assortment of derivatizing reagents and standard solutions as well as buffers compatible with various automatic analyzers.
Product Line-up
More Information
Amino acids are contained in food as nutrients and thus important chemical compounds. Approximately 20% of human body is composed of amino acids.
Because amino acid concentration is strictly controlled in blood (plasma), and changes in amino acid indicate altered metabolic and pathological conditions, it is used as an indicator of these conditions.
Although amino acid analysis is important in terms of presenting physiologically significant findings, most amino acids exhibit no characteristic absorption in visible and ultraviolet range, and thus it is difficult to measure amino acids with high sensitivity.
Derivatization is a technique that can overcome the difficulty in amino acid analysis. By the derivatization technique, analytes are reacted with reagents to form characteristic chemical compounds such as fluorescent substances, which improve selectivity and sensitivity of the measurement.
FUJIFILM Wako has a large assortment of reagents, including derivatizing reagents and standard solutions, available for various amino acid analyses.
Derivatization in amino acid analysis
Amino acids are compounds that absorbs less ultraviolet. Derivatization is significant in order to detect amino acids by HPLC with high sensitivity. Typical amino acid derivatization methods include (i) pre-column derivatization method by which analytes are transformed into substances suitable for separation and detection before column separation, and (ii) post-column derivatization method by which analytes are transformed into substances suitable for detection after column separation.
[i] Pre-column derivatization method
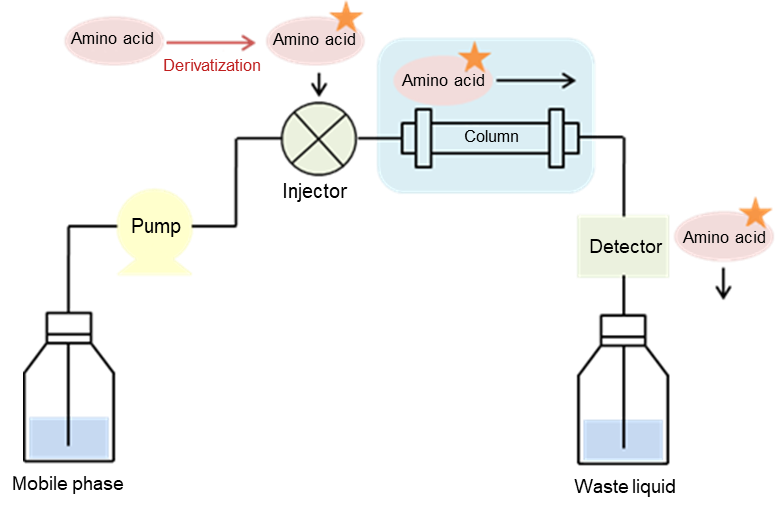
The pre-column derivatization method transforms analytes into substances that is suitable for separation and detection before column separation. As advantage of this method, consumption of reagents is less. Besides, reagents can be selected according to the type of detector and it can analyze with high sensitivity. Representative pre-column derivatization methods are APDS method and PTC method, and FUJIFILM Wako offers derivatizing reagents for these methods.
[ii] Post-column derivatization method
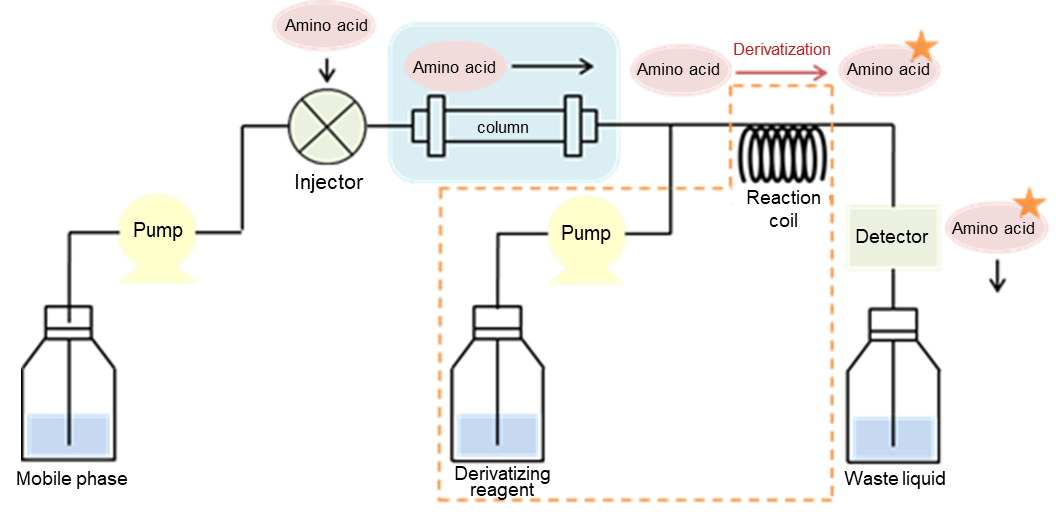
The post-column derivatization method is a method whereby the analyte is derivatized and led to the detector after column separation. It has the advantages of automated reactions, excellent quantitation and reproducibility, and does not be affected by the sample matrix since the sample components are separated by the column before the reaction. A representative post-column derivatization method employs a ninhydrin method, and FUJIFILM Wako offers ninhydrin coloring solution kits compatible with automatic analyzers manufactured by Hitachi and JEOL.
Comparison of derivatization methods
| Pre-column derivatization method | Post-column derivatization method | |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment | It can analyze with a general HPLC system but requires special equipment for automation. | Automation is simple with dedicated equipment. |
| Reagents | Consumption of reagent is small. A wide range of derivatizing reagents are available depending on detector type. |
Consumption of reagent is large. Available derivatizing reagents are limited. |
| Sensitivity and quantitativeness | Highly sensitive analysis is possible, but derivatized products, if unstable, may affect quantitative results. | Highly sensitive analysis may not be feasible, but it is favorably quantitative and reproducible. |
| Reverse-phase HPLC | Applicable | Non-applicable |
| Impact of sample matrix | Efficiency of derivatization reaction may be affected by sample matrix. | The reaction with derivatizing reagents is not affected by the sample matrix because components in the sample are separated by the column before reaction. |
Product Line-up
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.



