[Technical Report] Development of HPLC column eligible for measurements of 6 aldehydes specified in the Japanese Offensive Odor Control Law and multicomponent analysis
This article was written by Mamoru Kubota, FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation, for Vol. 87, No.3 (July 2019) of Wako Junyaku Jiho.
The content of this article is from the time of publication. It is not the latest information due to new knowledge and changes in regulatory rules after original publication.
-
Offensive odor is a general term of odor that makes people unpleasant and annoyed and classified into sensory pollution as with noise and vibration. The Japanese Offensive Odor Control Low has identified (currently 22 substances) as the specified offensive odor substances and restricted the emission by setting odor index. Some aldehydes emit a pungent and burnt odor, and 6 substances are identified as specified offensive odor substances.1,2 In the Low, gas chromatography (GC) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC/MS) methods have been specified for measurement of these 6 substances (Table 1), and in September 2018, the high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method was added.3
-
• Table 1. Aldehydes (6 substances) identified as specified offensive odor substances
1. Acetaldehyde
2. Propionaldehyde
3. n-Butyraldehyde
4. Isobutyraldehyde
5. n-Valeraldehyde
6. Isovaleraldehyde
Advantages of the HPLC method over the GC and GC/MS methods are that the analytical procedure from the sample pre-treatment to measurement can be performed without the following 2 matters:
- Ion-exchange solid-phase extraction (SPE) column
- Solvent exchange of final eluate
The HPLC method in the Japanese Offensive Odor Control Low, however, does not specify the analytical column in details such as type of the packing material and column size and only requires the column that has resolution performance appropriate for assay of the 6 substances. Many applications offered by HPLC manufacturers use reverse-phase ODS (C18) columns, but such columns are said to have difficulty in separating n-butyraldehyde and isobutyraldehyde.
Wakopak® Wakosil®-DNPH column is dedicated to separation and analysis of aldehydes derivatized with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH). Our column's features and specification are as follows:
Features
- The column packing material is spherical silica gel (particle size of 5 µm) chemically modified with triacontyl groups.
- Effective in separating DNPH-n-butyraldehyde and DNPH-iso-butyraldehyde
- Capable of performing simultaneous multicomponent analysis on aldehydes other than the 6 specified offensive odor substances: capable of performing simultaneous analysis on 16 substances*
(*The 16 substances include DNPH-acetone)
Specification
- Column size 4.6 × 250 mm (D), (W)
- Customized column size also available
- Measurement with gradient elution using 2 special eluents A and B
The special eluents A and B facilitate smooth elution without baseline variations and interfering peaks.
Figures 1 and 2 show examples of measurement of the 6- and 16-substance mixture standard solutions with Wakopak® Wakosil®-DNPH column, and Table 2 shows reproducibility (n = 10) of measurement results on 16 substances and their detection limits. To generate the calibration curves, 10 µL each of dilutions of the 16-substance mixture standard solution was injected. For each substance, a curve with the correlation coefficient (r) of 0.999, which indicated a linear relationship, was obtained in a range from 0 to 50 ng. In addition, a correlation of the analysis results between the gradient elution method with Wakopak® Wakosil®-DNPH column and the isocratic elution method with an ODS column was investigated. When (1) formaldehyde and (2) acetaldehyde in the outdoor air were captured and derivatized with DNPH, and analyses were performed by these methods, the analysis results on both substances showed favorable correlation with (1) r = 0.999 and (2) r = 0.99.
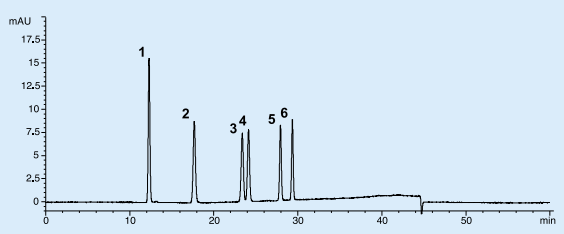
Figure 1. Chromatogram of 6-substance mixture standard solution
HPLC Conditions
Column: Wakopak® Wakosil®-DNPH, Column size: 4.6 mmφ x 250 mm, Instruments: Agilent 1100, Eluent: A ; Wakosil®-DNPH Eluent A, B ; Wakosil®-DNPH Eluent B, Gradient: High Press, gradient mode, 0-16 min. B 10%, 16-35 min. B 10-90%, 35-40 min. B 90%, Flow Rate: 0.8 mL/min at 35℃, Detector: UV 360 nm, Inj Vol.: 10 µL, Sample: -2,4-DNPH / 1. Acetaldehyde, 2. Propionaldehyde, 3. iso-Butyraldehyde, 4. n-Butyraldehyde, 5. iso-Valeraldehyde. 6. n-Valeraldehyde (each 0.625 µg/mL as aldehyde)
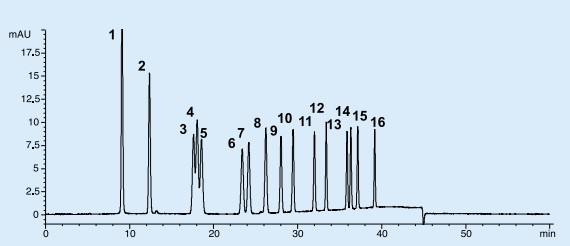
Figure 2. Chromatogram of 16-substance mixture standard solution]
HPLC Conditions
Column: Wakopak® Wakosil®-DNPH, Column size: 4.6 mmφ x 250 mm, Instruments: Agilent 1100, Eluent: A ; Wakosil®-DNPH Eluent A, B ; Wakosil®-DNPH Eluent B, Gradient: High Press, gradient mode, 0-16 min. B 10%, 16-35 min. B 10-90%, 35-40 min. B 90%, Flow Rate: 0.8 mL/min at 35℃, Detector: UV 360 nm, Inj Vol.: 10 µL, Sample: -2,4-DNPH / 1. Formaldehyde, 2. Acetaldehyde, 3. Propionaldehyde, 4. Acrolein, 5. Acetone, 6. iso-Butyraldehyde, 7. n-Butyraldehyde, 8. Crotonaldehyde, 9. iso-Valeraldehyde, 10. n-Valeraldehyde, 11. Benzaldehyde, 12. Hexaldehyde, 13. o-Tolualdehyde, 14. m-Tolualdehyde, 15. p-Tolualdehyde, 16. 2,5-Dimethylbenzaldehyde (each 0.625 µg/mL as aldehyde, ketone)
Table 2. Reproducibility of measurement results on 16 substances with Wakopak® Wakosil®-DNPH column and their detection limits
| Substance name | Coefficient of variation (CV%*, n = 10) |
Detection limit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.781 ng** | 6.250 ng** | 50.000 ng** | pg (S/N = 2) | |
| 1. Formaldehyde | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 7.0 |
| 2. Acetaldehyde | 1.8 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 9.8 |
| 3. Propionaldehyde | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 15.6 |
| 4. Acrolein | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.7 | 14.2 |
| 5. Acetone | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 16.3 |
| 6. iso-Butyraldehyde | 2.1 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 19.5 |
| 7. n-Butyraldehyde | 1.9 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 18.6 |
| 8. Crotonaldehyde | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 13.9 |
| 9. iso-Valeraldehyde | 2.1 | 1.2 | 1.7 | 17.0 |
| 10. n-Valeraldehyde | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 19.5 |
| 11. Benzaldehyde | 1.6 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 15.0 |
| 12. Hexaldehyde | 2.1 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 15.6 |
| 13. o-Tolualdehyde | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.8 | 17.7 |
| 14. m-Tolualdehyde | 1.9 | 1.4 | 2.0 | 21.7 |
| 15. p-Tolualdehyde | 1.8 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 21.2 |
| 16. 2,5-Dimethylbenzaldehyde | 1.8 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 17.0 |
*: CV% calculated from peak areas. Measurement condition is the same as that for chromatography of the 16-substance mixture standard solution.
**: Amount of each substance in 10 µL of a dilution sample of the 16-substance mixture standard solution
In addition to the above, FUJIFILM Wako offers DNPH-aldehyde mixture standard solutions (6 and 16 substances) for measurement of aldehydes, Presep®-C DNPH, Presep®-C DNPH (Short), a sample capture SPE cartridge column with lure slip connector capable of capturing aldehydes and derivatizing these with DNPH, Presep®-C Ozone Scrubber, an ozone removing cartridge column with lure slip connector and an extraction solvent (acetonitrile) for the sample capture SPE cartridge column, making your aldehyde measurement easy.
Back issues of Wako Junyaku Jiho also present tips in operations from capture to HPLC run to ensure accurate measurement of aldehydes. Please refer to these issues as well.
References
- Notice No. 9 Measurement Method of Specified Offensive Odor Substances: Japanese Ministry of the Environment, May 30, 1972.
- Outline of Offensive Odor Regulations: Water and Air Environment Section, Tottori Prefectural Life Environment Department, July 2015.
- Notice No. 78 Measurement Method of Specified Offensive Odor Substances Attached 4: Japanese Ministry of the Environment, September 21, 2018.




