Exosome Isolation Kits
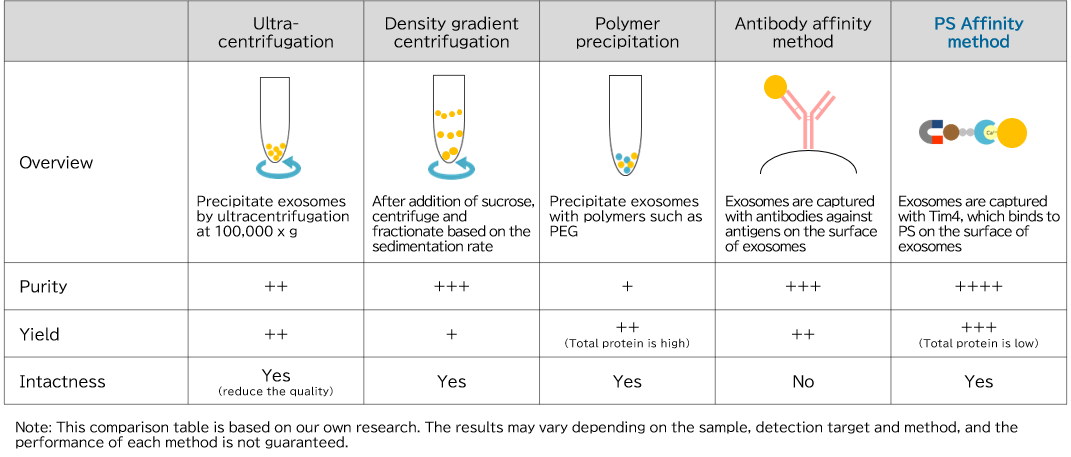
In exosome research, it is important to isolate and purify exosomes in a state close to their in vivo state with high purity and high yield. There are many methods for isolation and purification of exosomes, including ultracentrifugation and polymer precipitation, but each method has problems such as presence of many impurities, low recovery amount, and damage to recovered exosomes.
Fujifilm Wako, in collaboration with Prof. Hanayama, Department of Immunology, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kanazawa University, developed a new exosome isolation and purification technique, the "PS-affinity method", and prepared the technique into a kit using Tim4 protein, which specifically binds to phosphatidylserine (PS) on the surfaces of extracellular vesicles, including exosomes.
More Information
Novel Exosome Purification Method Using Phosphatidylserine and Tim4
Exosomal membranes contain proteins and lipids derived from secretory cells. Among them, phosphatidylserine (PS) is known to face inside the cell in living cells by the action of the enzyme flippase, whereas it is also exposed to the outside of exosomes1). The T-cell immunoglobulin domain and mucin domain-containing protein 4 (Tim4) is a phagocytic receptor of macrophages for apoptotic cells. Tim4 was found to bind to PS via the IgV domain in the extracellular region in a calcium ion-dependent manner2).
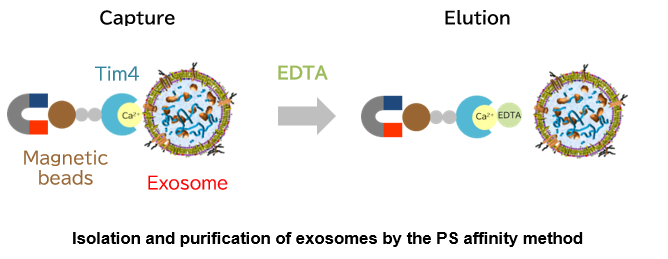
Based on the above findings, Fujifilm Wako developed a new exosome purification method distinct from existing methods in collaboration with Professor Hanayama of Department of Immunology, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kanazawa University, and successfully developed a kit. This method uses magnetic beads coated with Tim4 to capture exosomes in samples such as cell culture supernatant and serum in the presence of calcium ions, and isolate exosomes by adding chelating agents3). The PS affinity method employs a simple procedure to achieve a higher purity of intact exosomes than conventional exosome purification methods. It is being established as a new exosome purification method to replace the ultracentrifugation method that has been considered the gold standard.
Comparison of exosome isolation and purification methods
Performance Data for the PS Affinity Method
| Performance Data | Measured | Method | Comparison | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultra-centrifugation | Polymer precipitation | Antibody affinity method | |||
| Particle Analysis by NanoSight | Particles | Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis | ✔ | ✔ | - |
| Particle Analysis by Electron Microscopy | Particles | Electron Microscopy | ✔ | - | - |
| Capture Performance of Tim4 and Anti Exosome Marker Antibody | Marker Protein | ELISA | - | - | ✔ |
| Analysis of Purified Exosome in Biological Fluid by Western Blotting | Marker Protein | Western Blotting | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Comparison of Yield and Purity by Western Blotting | Marker Protein | Western Blotting | ✔ | ✔ | - |
| Comparison of Yields of microRNA and mRNA | microRNA/mRNA | real-time qPCR | ✔ | - | - |
| Determination of Total Protein by the BCA Assay | Total Protein | BCA assay | - | - | - |
| Proteomics Analysis | Proteomics | LC-MS | ✔ | ✔ | - |
| Exosome Uptake Assay with HeLa Cells | Uptake Assay | Fluorescence microscopy Flow cytometry |
- | - | - |
▼Particle Analysis by NanoSight

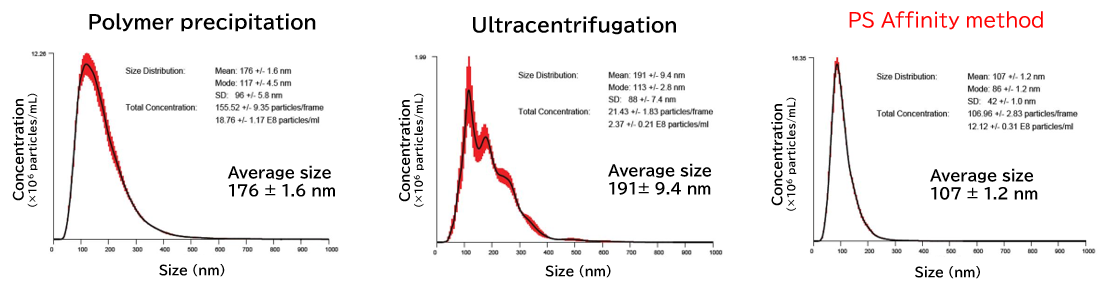
NanoSight is an analytical instrument for the analysis of size and concentration of nanoparticles that functions by visualizing the Brownian motion of nanoparticles in solvent through Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA). Even when the particles in the solvent are mixtures of various materials or polydisperse systems with varying particle sizes, the number of particles having each particle size can be counted using videos of Brownian motion of nanoparticles obtained by the visualization technique.
Exosomes isolated from cell culture supernatants by the PS affinity method, ultracentrifugation, and polymer precipitation method were diluted to appropriate concentrations in ultrapure water, and particle size and concentration were analyzed using NanoSight LM10.
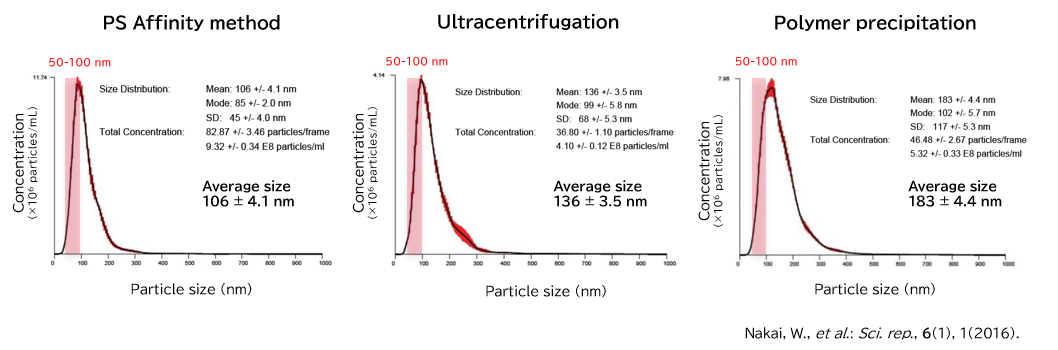
[Result]
With the PS affinity method, particles corresponding to the particle size of exosomes (50-100 nm) were more concentrated, indicating higher purity.
▼Particle Analysis by Electron Microscopy
Electron microscopy is a technique for obtaining magnified images of specimens using an electron beam. As an electromagnetic wave, an electron beam has a very short wavelength, allowing for morphological observation at a much higher magnification than with optical microscopes. Electron microscopy is used to observe and analyze all types of samples, from metals and polymers to water-containing materials such as biological tissues, plants, and foods. Below is an example of electron microscopic analysis of exosomes using a transmission electron microscope (TEM).
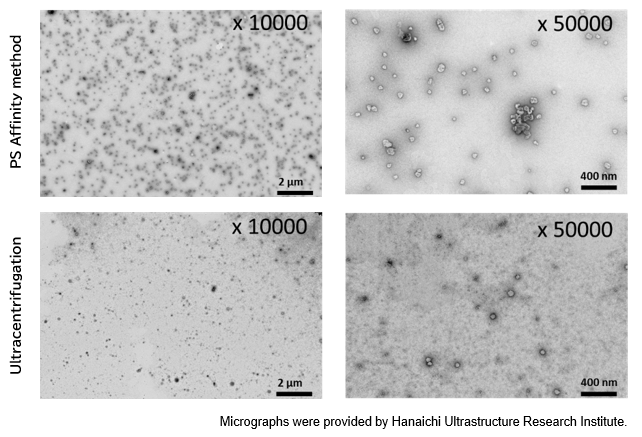
PS Affinity method
Sample: COLO201 cell culture supernatant 10 mL
Number of particles: 3.69 x 1010 particles/mL
Ultracentrifugation
Sample: COLO201 cell culture supernatant 10 mL
Number of particles: 1.68 x 1010 particles/mL
[Result]
A higher number of exosomes was isolated with high purity using the PS affinity method.
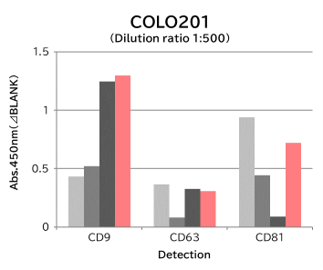
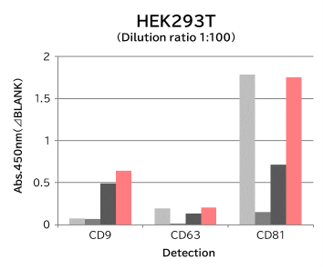
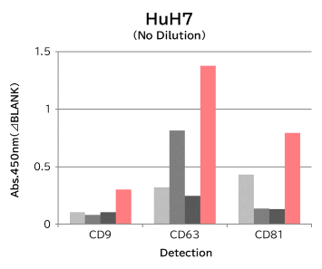
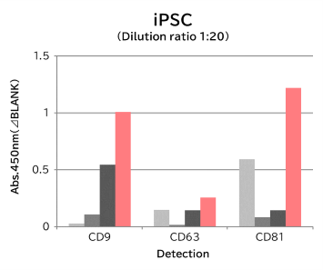
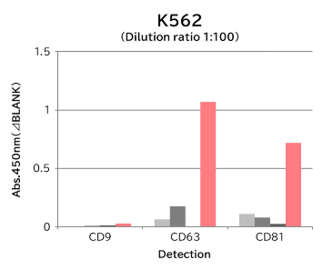
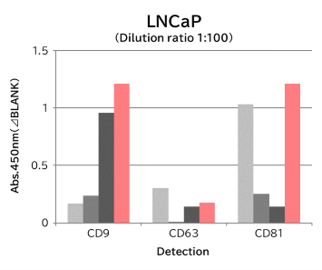
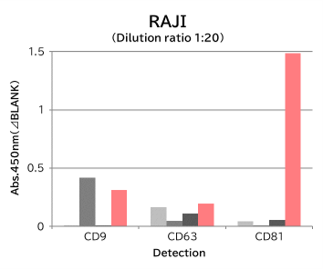
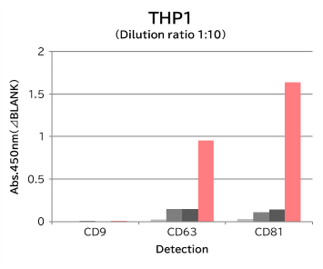
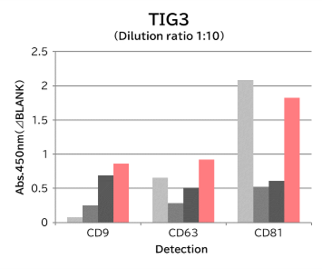
▼Capture Performance of Tim4 and Anti Exosome Marker Antibody
Using 9 types of cell culture supernatants (10,000 x g centrifugation), exosomes in the sample were captured with Tim4 or each exosome marker antibody (CD9, CD63, CD81), then biotin-labeled anti exosome marker antibody was used for detection.

[Result]
Compared with anti exosome marker antibodies, Tim4 could efficiently capture exosomes from a wide range of cell types.
▼Analysis of Purified Exosome in Biological Fluid by Western Blotting
>Human Serum
- Exosomes were isolated from normal human serum by using PS affinity methods, ultracentrifugation and antibody affinity method, followed by western blotting with the anti CD9 and anti CD63 antibodies.
Each signal corresponds to 150 μL of the serum sample. 15 μL of eluate and 5 μL of 4 x SDS sample buffer were mixed and applied all in each well. 
[Result]
Yield of exosomes by PS affinity methods is higher than ultracentrifugation and the antibody-based method.
>Human Plasma (EDTA)
- Exosomes were isolated from EDTA-plasma, EDTA-plasma (buffer-exchanged), and serum by using PS affinity method, followed by western blotting with the anti Flotillin-2 antibody.
Each signal corresponds to 150 μL of various sample. 15 μL of eluate and 5 μL of 4 x SDS sample buffer were mixed and applied all in each well. 
[Result]
Exosomes can be isolated more efficiently by exchanging buffer by ultrafiltration.
>Human Urine
- Exosomes were isolated from normal human urine by using PS affinity method, ultracentrifugation and polymer precipitation, followed by western blotting with the anti CD9 antibody.
Each signal corresponds to 150 μL of urine sample. 15 μL of eluate and 5 μL of 4 x SDS sample buffer were mixed and applied all in each well. 
[Result]
Exosomes can be isolated with high purity from urine sample.
Particle Analysis by NanoSight (Human urine sample)
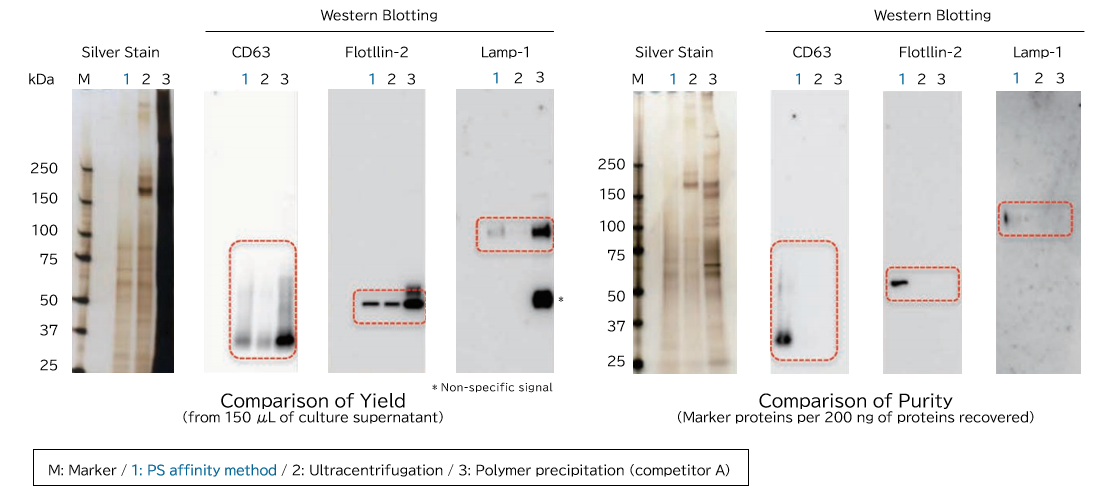
▼Comparison of Yield and Purity by Western Blotting
Samples prepared from K562 cell culture supernatant (medium supplemented with 10% Exosome-depleted FBS) using ultracentrifugation, polymer precipitation, and the PS affinity methods were subjected to electrophoresis followed by detection by silver staining and western blotting (anti CD63, anti Flotillin-2, and anti Lamp-1 antibodies). MS analysis of recovered fractions was also performed, to compare the percentage of human peptides derived from K562 cells among all identified peptides.
<Supplemental Data> Comparison of human sample-derived peptides identified by MS analysis
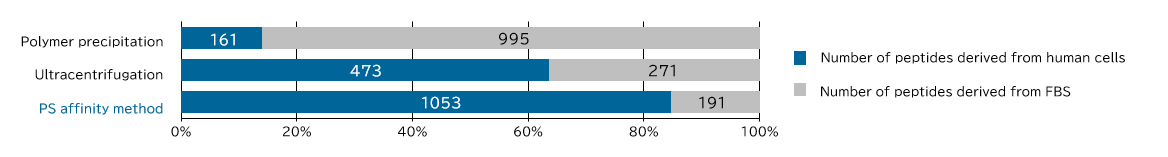
[Result]
Exosomes with high purity were recovered from FBS-containing medium as well using the PS affinity method.
▼Comparison of Yields of microRNA and mRNA
Exosomes were isolated from healthy human serum using ultracentrifugation and the PS affinity methods. RNA was recovered from the isolated exosomes using the microRNA Extractor® SP kit (Product Number: 295-71701), and microRNA (let-7a, miR-16, miR-92a, miR-142-3p) and mRNA levels (GAPDH, PIK3CB) were determined by quantitative PCR, and Ct values were compared.

[Result]
More microRNA and mRNA were recovered from exosomes isolated using the PS affinity method compared to the ultracentrifugation method.
▼Determination of Total Protein by the BCA Assay
Protein concentration in an exosome preparation purified from cell culture supernatant using PS affinity method was determined according to the high-sensitivity protocol for Protein Assay BCA Kit (Product Number: 297-73101)
- An exosome solution purified using PS affinity method pipetted into a 96 well plate in 25 μL aliquots and then 200 μL of a mixture of Reagent A and Reagent B included in Protein Assay BCA Kit was added to each well. After subsequent incubation at 60°C for 30 minutes, the absorbance was measured at 560 nm.
Protein concentration of exosomes purified from 10 mL of COLO201 cell culture supernatant (after 5-fold concentration)
Absorbance (ーBLANK) = 0.1152
BCA concentration = 49.2 μg/mL 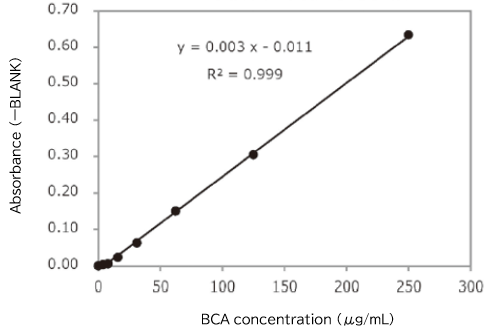
[Result]
Protein concentration in a purified exosome preparation was able to determine using the high-sensitivity protocol for Protein Assay BCA Kit.
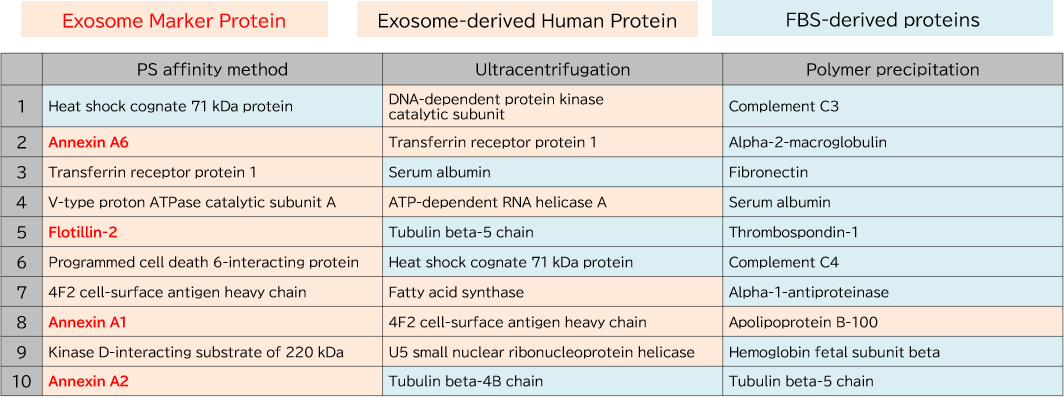
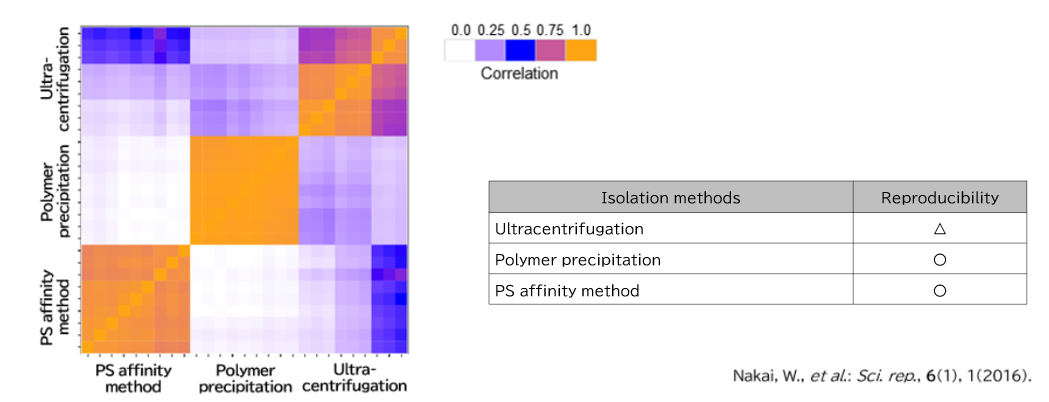
▼Proteomics Analysis
Exosomes were purified from K562 cell culture supernatant (medium supplemented with 10% Exosome-depleted FBS) using ultracentrifugation, polymer precipitation, and the PS affinity method. Purified samples were separated by 10% polyacrylamide electrophoresis, and the entire protein bands were cut out. Subsequently, in-gel digestion was performed, and proteins were identified by LC-MS. The pairwise correlation of identified proteins in exosomes (n = 3) purified by the three methods was also calculated.
1. Comparison of Top 10 Most Abundant Proteins
2. Comparison of Pair-wise correlation
▼Exosome Uptake Assay with HeLa Cells
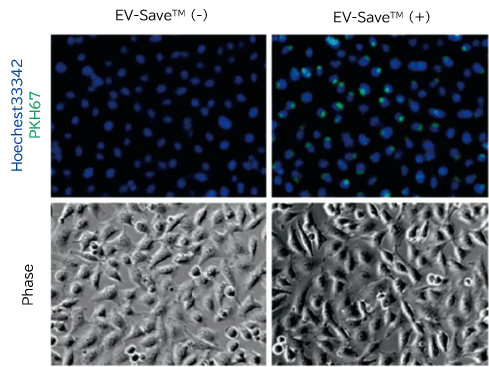
Exosomes purified by PS affinity method were labeled with PKH67 (Sigma) and confirmed their ability to be incorporated into HeLa cells.
- Purify exosomes using PS affinity method from COLO201 cell culture supernatant. *1
- Determine the protein concentration and particle concentration by BCA Assay and using NanoSight, respectively.
- Dispense the exosome sample solution in a 1.5 mL tube.*2
- Dissolve 2.0 μL PKH67 linker in 0.25 mL of Diluent C. (provided with the PKH67 kit)・・・ 4 x Dye solution*3
- Add 1/3 volume of 4 x Dye solution to the exosome sample, mix, and incubate the mixture at room temperature for 5-10 minutes.
- Equilibrate Exosome Spin Columns (MW 3000) (Thermo Fisher Scientific #4484449) with PBS according to the protocol provided with the product.
- Apply 100 μL of each sample to each spin column equilibrated as described above*4 and centrifuge at 750 x for 2 minutes.
- Add the solution containing labeled exosomes to HeLa cells seeded on a dish on a preceding day.*5 After 24 hours, perform microscopic observation or flow cytometry.
- To prevent loss of labeled samples due to adsorption in Step 6-7 Gel filtration, addition of EV-Save™ Extracellular Vesicle Blocking Reagent (Product Number: 058-09261) to the elution buffer included in the kit is recommended.
- We used exosome sample corresponding to 3 μg protein (equivalent to 1 x 1010 particles). Prepare an appropriate amount as needed for your experiment.
- Prepare an appropriate amount as needed for the experiment.
- Because the maximum loading volume is 100 μL per column, multiple columns corresponding to the sample volume are recommended to be kept on hand where the sample amount is more than 100 μL.
- Adjust the number of exosomes added.
- Fluorescence microscopy
- Flow cytometry

[Result]
PKH67-labeled exosomes are incorporated through endocytosis in both microscopy image and flow cytometry chart. In addition, EV-Save™ Extracellular Vesicle Blocking Reagent added to the sample remarkably reduced the loss due to adsorption to the gel filtration column in a dye-removal step.
References
- Trajkovic, K. et al.: Science, 319(5867), 1244(2008).
Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes - Miyanishi, M. et al.: Nature, 450(7168), 435(2007).
Identification of Tim4 as a phosphatidylserine receptor - Nakai, W., et al.: Sci. rep., 6(1), 1(2016).
A novel affinity-based method for the isolation of highly purified extracellular vesicles
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.