Insulin ELISA Kits
Insulin is a hormone secreted by β-cells in the islets of Langerhans (pancreatic islets) within the pancreas. Its primary target tissues are the liver, muscles, and adipose tissue. When blood glucose levels increase, insulin is released, which causes blood glucose levels to decrease. The main causes of diabetes are reduced insulin secretion or impaired insulin action.
Fujifilm Wako provides a wide range of insulin ELISA kits. The most suitable kit can be selected based on several factors including the animal species, insulin concentration in the sample, specificity, and ease of use.
What is Insulin?
Insulin is a hormone secreted from β-cells of islet of Langerhans in the pancreas. Main targets of insulin are liver, muscle, and adipose tissue. Insulin actions when blood glucose level increases in these targets are as follows;
| Target | Insulin’s Action |
|---|---|
| Liver | Glycogenesis, Protein synthesis, Fatty acid synthesis, Carbohydrate utilization, and Inhibition of gluconeogenesis |
| Muscle | Membrane permeability of carbohydrates/amino acids/K ion, Glycogenesis, Protein synthesis & inhibition of protein degradation |
| Adipose tissue | Membrane permeability of glucose and fatty acid synthesis |
Diabetes is mainly caused by a decrease in insulin secretion or insulin resistance (cells do not respond well to insulin and blood glucose level can not be increased easily).
Insulin biosynthesis and structure
Molecular weight of insulin is about 5,800 and pI 5.4. It is consisted of 2 chains, A and B. It has 3 disulfide bonds formed between A6 and A11, A7 and B7, and A20 and B19. Exists as a dimer molecule in acidic to neutral water solution without Zn ion, and as a hexamer including two Zn ions in neutral solution if Zn ions are present.
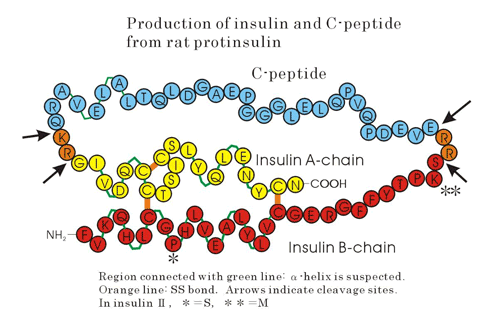
A precursor of insulin, called proinsulin with a single polypeptide chain, is first synthesized in the cell, then sulfide bonds are formed, and finally by enzymatic cutting at two sites, active insulin and c-peptide (connecting peptide) are formed as shown in below figure.
Potencies of insulin preparations of various animal species
Potency of an insulin preparation was originally determined by bioassay. For example, 1 rabbit unit is the amount of insulin which lowers the blood sugar level of 24-hours fasting rabbit by 50% within 5 hours after administration. It corresponds to about 3 IU. However, whole body bioassay inevitably shows poor precision owing to individual variation with index of precision about 0.15. From such reason international standard preparation has been used.
Rat and mouse have two molecular species of insulin, type 1 and type 2. Amino acid sequences of these molecular species are same between rat and mouse. But as their ratios are different between the two animals, it is recommended to use standard preparation derived from each animals.
Insulin is used therapeutically in humans, and its physiological effects must therefore be clearly defined. In the past, when insulin purity was lower, managing it by weight posed certain risks. To address this, international standards were established as a reference.
The 4th international standard preparation (1958) is a mixture of purified preparations of bovine (52%) and porcine (48%) insulin, and 1 mg of the standard is defined as 24 IU (=0.04167 mg/IU). Following further purification of insulin, WHO issued 1st International Standard in 1986 which has the potency of 26 IU/mg (0.038 mg/IU). In the same year, 1st International Standard of bovine insulin, the potency of which is 25.7 IU/mg, and Porcine insulin 1st International Standard, 26 IU/mg, were provided. One ampoule contains about 50 mg. Before these standards, in 1974, 1st International Reference Preparation of human insulin for immunoassay was provided as 3 IU/ampoule. As mentioned above, since insulin is used therapeutically in humans, expressing clinical measurements in IU is more practical. However, for animals, handling insulin by weight is preferred.
While it is uncertain whether the biological activity of each insulin molecule is consistent across different animal species, porcine and bovine insulin are believed to have nearly the same potency as human insulin. If conversion is needed, such as when calculating HOMA-IR, an approximation of 1 mg equaling 26 IU is recommended.
The point of insulin measurement including the above is posted on following:
Product Lineup
Fujifilm Wako has a lineup of insulin ELISA kits for various purposes.
How to Choose Kits
Measured Samples
| Samples | Points |
|---|---|
| Serum/Plasma | When experimental animals are fasted, blood insulin levels decrease. For long-term fasting, the High Sensitivity Kit is recommended. For shorter fasting periods, the Standard Kit or the Ready to Use Kit is suitable. Additionally, in diabetic or obese model mice, blood insulin levels may be elevated. The High Concentration Kit is recommended if insulin levels are expected to exceed 10 ng/mL, though the duration of fasting should also be considered. |
| Tissue Extract | The High Concentration Kit is recommended. As the extraction solvent may influence assay results, please verify the dilution linearity beforehand. |
| Cell Culture Supernatant | The High Concentration Kit is recommended when insulin concentrations in the sample are expected to be high. If insulin is present in the media additives, measuring C-peptide is advised. |
Cross-Reactivity to Proinsulin
Proinsulin is processed into insulin and C-peptide during its transport from the Golgi apparatus to secretory granules. However, some unprocessed proinsulin remains in the secretory granules and is co-released with insulin into the bloodstream during granule secretion. When measuring blood insulin using immunological methods, proinsulin is also detected, which is referred to as immunoreactive insulin (IRI) and is distinguished from insulin.
When assessing pancreatic β-cell dysfunction using the proinsulin/insulin ratio, the High Specificity Kit is recommended.
Animal Species
Fujifilm Wako can supply standards for measuring insulin in dogs, cattle, monkeys, hamsters, and pigs. By combining these standards with the LBIS™ Rat Insulin ELISA Kit (Product No. 299-94801), samples from each of these animals can be measured.
Product Lineup
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Luminescent | Luminescent | Standard | Ready to Use | High Sensitivity (Wide Range) |
High Sensitivity | High Specificity | Luminescent | Standard | High Sensitivity | |
| Product No. | 290-89201 | 296-89301 | 292-89401 | 298-89501 | 290-89701 | 296-89801 | 292-89901 | 296-89301 | 299-94801 | 293-90301 | |
| Calibration Curve Range | Concentration (pg/mL) |
||||||||||
| 100,000 | ● | ||||||||||
| 50,000 | ● | ||||||||||
| 20,000 | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 12,000 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| 10,000 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||
| 5,000 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||
| 2,500 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| 500 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| 156 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||
| 100 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||
| 78 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| 39 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| 30 | |||||||||||
| Features | Wide range measured, saving time for remeasurement | Wide range measured, saving time for remeasurement | Standard measuring range | Standard solution, Detection antibody & Avidin solution already diluted | Suitable for high concentrated samples* | Suitable for low concentrated samples** | Insulin-specific measurement by suppressing cross-reactivity for proinsulin | Wide range measured, saving time for remeasurement | ・ Standard measuring range ・ Other animals can be measured*** using each standard solution |
Suitable for low concentrated samples** | |
* Tissue extract, diabetes-model blood samples etc.
** Long-term fasting samples etc.
*** Dog, porcine, monkey, hamster, and bovine
Insulin in dog, porcine, monkey, hamster, and bovine can also be measured by combining LBIS™ Rat Insulin ELISA Kit (Product No. 299-94801) with a standard solution (be optionally available) for each animal,
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
Insulin ELISA Kit (Human)
Insulin ELISA Kits (Mouse)
Insulin ELISA Kits (Rat)
Insulin Standard Solutions
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.



