Antibodies (Exosome)
Tetraspanin family proteins, including CD9, CD63, and CD81, presented on the surfaces of exosomes are used as exosome markers. Fujifilm Wako offers a line-up of various exosome marker antibodies prepared using a DNA immunization method. Our antibodies are more sensitive than those prepared by conventional methods.
Product Line-up
More Information
Marker Proteins of Extracellular Vesicles (Including Exosomes)
Extracellular vesicles (EVs), such as exosomes, are known to contain marker proteins, including the tetraspanin family (CD9, CD63, CD81), integrin family (ITGA, ITGB), ESCRT complex-binding proteins (TSG101, ALIX), lipid raft markers (Flotillin-1/2), and heat shock proteins (HSP70). The expression levels of these marker proteins vary depending on the cell of origin; in some cases, certain marker proteins may be minimally expressed.
In this context, the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles (ISEV) published a position paper, MISEV2018, in 20181), proposing proteins useful for demonstrating the presence and purity of EVs (Table 1). The paper highlights the importance of confirming not only the presence of EV proteins (Categories 1a or 1b, 2a, and optionally 2b in Table 1*) but also, at a minimum, any impurities such as lipoproteins and albumin (Categories 3a or 3b in Table 1). Category 4 pertains to proteins specific to certain small EVs, and Category 5 includes proteins required for analyzing the functions of EVs.
Table 1: Examples of Marker Proteins Used for Characterizing EVs by Protein Constituents (Partial excerpt from MISEV2018)
Category 1
Transmembrane or GPI-anchored proteins associated to plasma membrane and/or endosomes
1a: non-tissue specific
Tetraspanins (CD63, CD81, CD82), other multi-pass membrane proteins (CD47), MHC class I (HLA-A/B/C), Integrins (ITGA, ITGB) etc.
1b: cell/tissue specific
Tetraspanins (TSPAN8, CD37, CD53, CD9), EPCAM, CD90, CD45 etc.
Category 2
Cytosolic proteins recovered in EVs
2a: with lipid or membrane protein-binding ability
ESCRT-I/II/III (TSG101, CHMP) and accessory proteins(ALIX), Flotillins-1 /2, Caveolins, Annexins etc.
2b: promiscuous incorporation in EVs (and possibly exomeres)
Heat shock proteins (HSP70), Actin, Tubulin, GAPDH
Category 3
Major components of non-EV co-isolated structures
3a: lipoproteins (produced by liver, abundant in plasma, serum)
Apolipoproteins A1/2 (APOA1/2), Apolipoproteins B (APOB, APOB100), Albumin (ALB)
3b: protein and protein/nucleic acid aggregates
Tamm-Horsfall protein, Ribosomal proteins
Category 4
Transmembrane, lipid-bound and soluble proteins associated to other intracellular compartments than plasma membrane(PM)/endosomes
4a: nucleus
Histones, Lamin A/C
4b: mitochondria
cytochrome C (CYC1), TOMM20
4c: secretory pathway (endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus)
calnexin (CANX), Grp94, BIP, GM130
4d: others (autophagosomes, cytoskeleton…)
Actinin1/4 (ACTN1/4), cytokeratin18 (KRT18)
Category 5
Secreted proteins recovered with EVs
5a: Cytokines and growth factors
TGFB1/2, IFNG, VEGFA, FGF1/2, PDGF, EGF, interleukins etc.
5b: adhesion and extracellular matrix proteins
Fibronectin (FN1), Collagen, MFGE8 etc.
Production of Antibodies Against EV Markers
Among the marker proteins of EVs, membrane proteins such as CD9, CD63, and CD81 are challenging targets for producing high-quality antibodies using conventional methods due to their complex tertiary structures. To address this issue, Fujifilm Wako produces anti-CD9, CD63, and CD81 antibodies using the “DNA immunization” method.
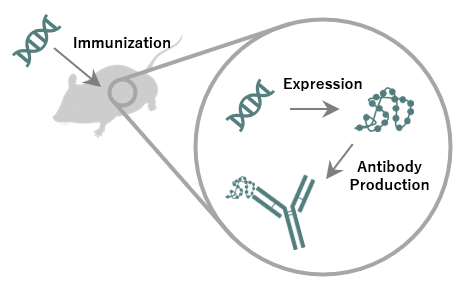
Figure 1. DNA immunization
DNA immunization involves the administration of an expression vector containing the cDNA of the target antigen for animal immunization, rather than using peptide or protein antigens. The administered cDNA of the target antigen is transcribed under the control of a promoter in the vector and expressed within the animal's body, producing an antigen. Antibodies produced by this method primarily recognize antigens in their native form, enabling the production of antibodies with high affinity even against membrane proteins with complex tertiary structures (Figure 1).
In practice, using Fujifilm Wako’s “Anti CD9, Monoclonal Antibody (1K)” (Product Number: 014-27763), CD9 in EVs purified from COLO201 cell culture supernatant was detected by Western Blotting under non-reducing conditions. This antibody demonstrated a higher sensitivity in detecting CD9 compared to conventional products (Figure 2). Similar results were obtained with Fujifilm Wako’s anti-CD63 and anti-CD81 antibodies, further indicating their value as research tools for EVs, including exosomes.
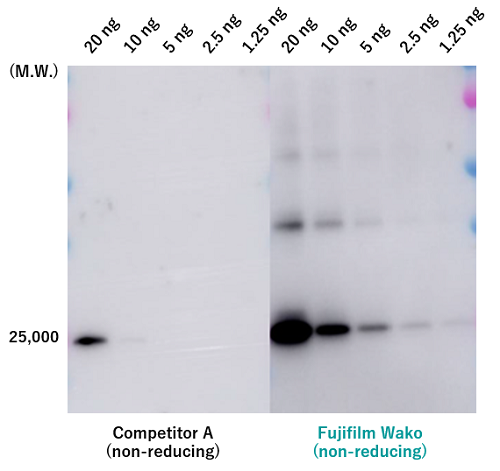
Figure 2. Performance Comparison of Anti-CD9 Antibodies by Western Blotting
EVs were purified from COLO201 cell culture supernatant using the PS affinity method, followed by analysis of CD9 by Western blotting.
Primary Antibody: Anti CD9, Monoclonal Antibody (1K)
Secondary Antibody: Anti Mouse IgG (H+L), Peroxidase-conjugated
Detection Reagent: ImmunoStar® Zeta (Product Number: 291-72401)
References
- Théry, C. et al.: J. Extracell. Vesicles, 7(1), 1535750(2018).
Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines
Product Line-up
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.








