Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody Discovery Service
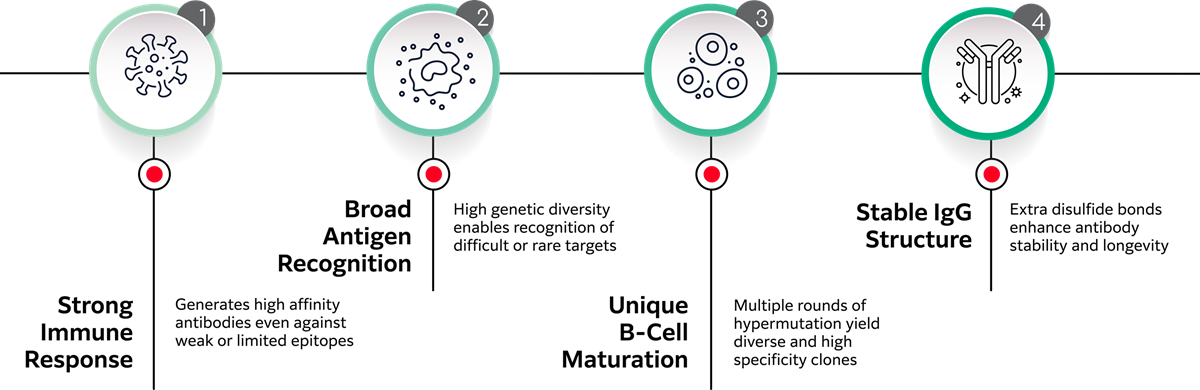
Our Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody Discovery Service leverages the benefits of the DNA Immunization method in combination with Fujifilm's proprietary single B-cell screening technology. Our experts with 20 years of experience in antibody development offer you a tailored service to discovering rabbit monoclonal antibodies. These antibodies boast 10-100x higher binding affinity than those from mice or rats, covering a wider range of epitopes. The DNA Immunization method, which involves immunization of rabbits using plasmid DNA, bypasses the need for immunization using recombinant protein/peptide, and facilitates the in vivo synthesis of proteins, leading to the generation of antibodies that recognize the native form of the antigen of interest, including challenging membrane proteins like multipass transmembrane proteins. From just the target information, we can provide the antibody gene sequence for the high performance, high affinity antibody discovered through our service.
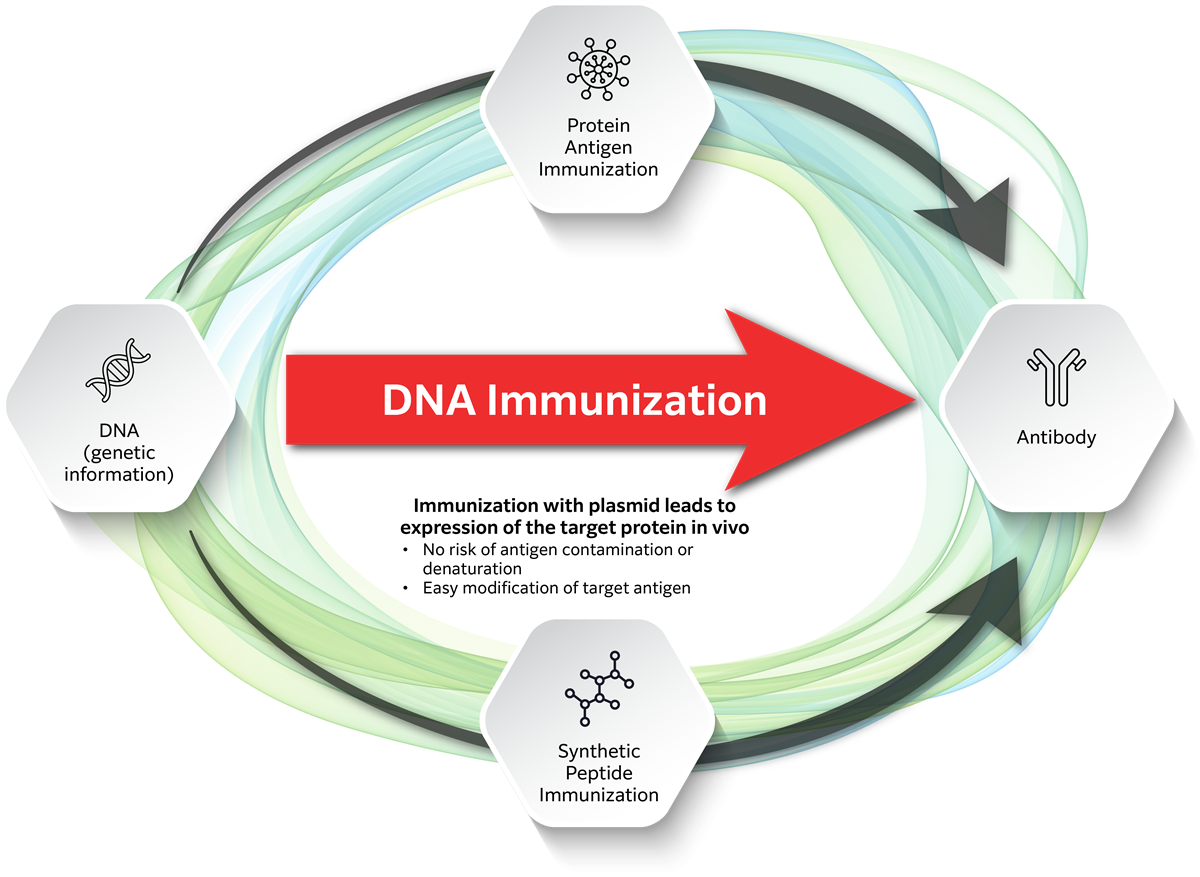
What is DNA immunization? Antibody Production Technology

DNA immunization is a method of antibody production. An expression vector containing the cDNA of the target antigen is produced, and the vector is directly administered to the immunized animal.
The cDNA of the target antigen is transcribed by the promoter of the vector and expressed in the body of the immunized animal to acquire immunogenicity.
The DNA immunization method has a high success rate for antibodies against membrane proteins, which are difficult to obtain with conventional immunization using antigens (peptides/proteins).
In the conventional method of producing monoclonal antibodies, recombinant proteins are prepared from DNA information or peptide synthesis, and these are administered as antigens to immunized animals to obtain antibodies. The DNA immunization method, on the other hand, induces immunity by injecting a plasmid directly into the immunized animal and expressing the target protein in the animal's body. Compared to the conventional protein/peptide immunization method, the DNA immunization method has the advantages of bypassing the need for the antigen protein/peptide, while avoiding antigen contamination, antigen denaturation and allowing for easy modification of the target antigen.
Another feature is that neutralizing antibodies (functional antibodies) are easily obtained.
Service Highlights
Service Highlights
DNA Immunization Method
- No need to prepare purified antigen.
- Antibodies that recognize native form of proteins can be produced.
- Antibodies against multipass transmembrane proteins and highly homologous targets can be produced.
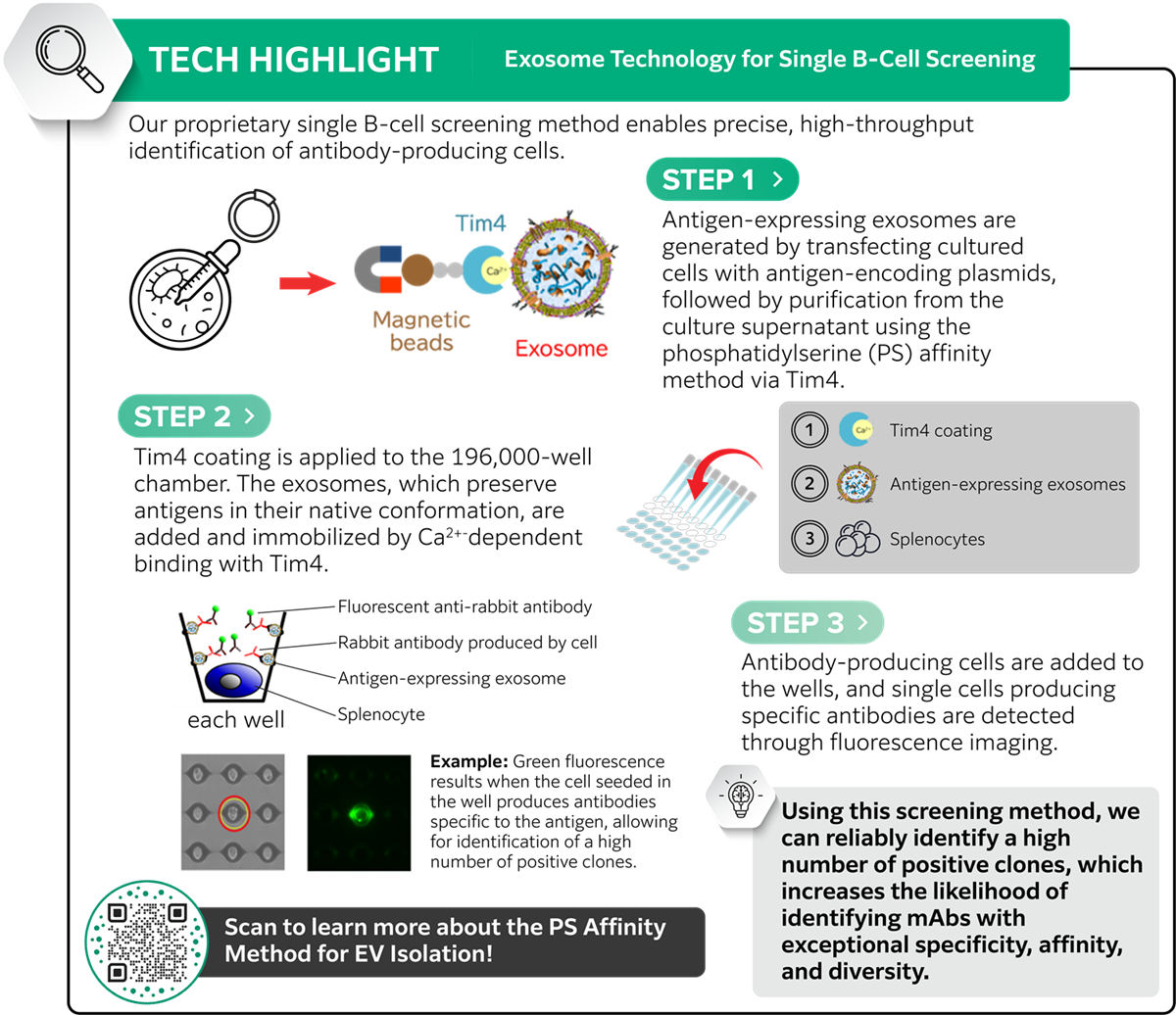
Our proprietary single B-cell screening technology ensures we can reliably identify a high number of positive clones, which increases the likelihood of identifying mAbs with exceptional specificity, affinity, and diversity
Consult with antibody experts with decades of experience in a premium, stage-gated service
Custom antibody gene sequences with strong partners for downstream antibody solutions such as antibody engineering (i.e., optimization, humanization), and manufacturing
Features of Rabbit Antibodies
FUJIFILM’s Single B-Cell Screening Technology
Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody Generation
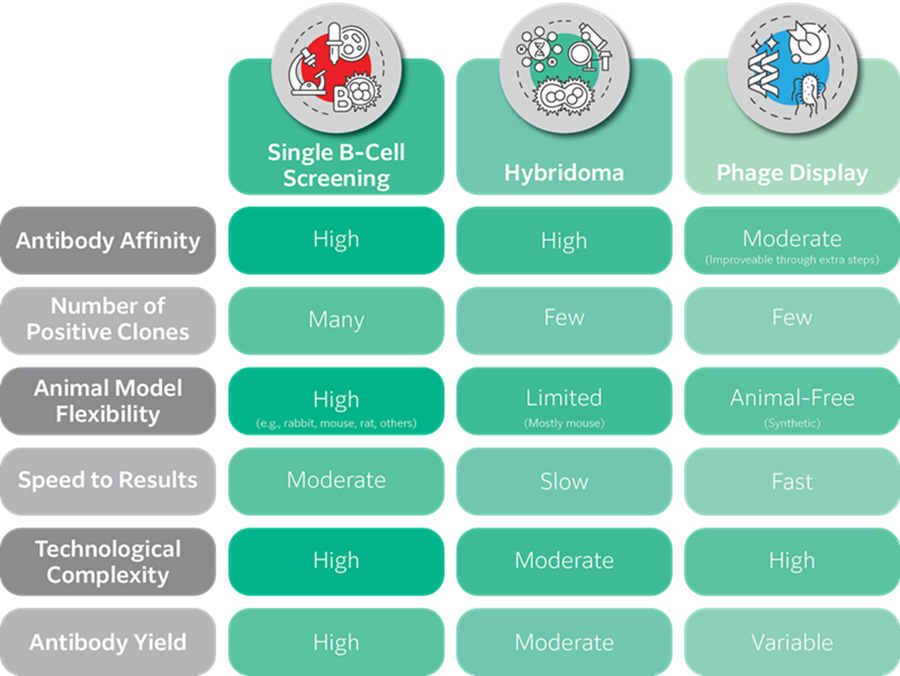
Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody Production Monoclonal rabbit antibodies have been difficult to produce for technical reasons. In particular, the inefficiency of the hybridoma method, which is the golden standard for monoclonal antibody production, has been a technical hurdle. Instead of using hybridoma technology, we have made it possible to efficiently produce rabbit monoclonal antibodies by introducing our proprietary FUJIFILM Group single B-cell screening technology.
Our single B-cell screening method pushes the boundaries of monoclonal antibody discovery by combining excellence in antibody quality, adaptability, and yield. Unlike traditional approaches such as hybridoma or phase display, single B-cell cloning delivers a broader pool of positive clones and directly obtains antibody gene sequences, paving the way for unparalleled quality and reproducibility that meets the rigorous demands of modern antibody development. While setting up such an experimental system is difficult, our extensive expertise in this technique enables us to offer you the benefits of single B-cell screening without any of the difficulty.
Stage 3 – Technology Focus
In Stage 3 of the service, we unlock the full potential of the rabbit immune system by leveraging FUJIFILM’s proprietary single B-cell screening technology (PAT.P: WO2024071374), which preserves native heavy/light chain pairing and maximizes the recovery of high-affinity clones.

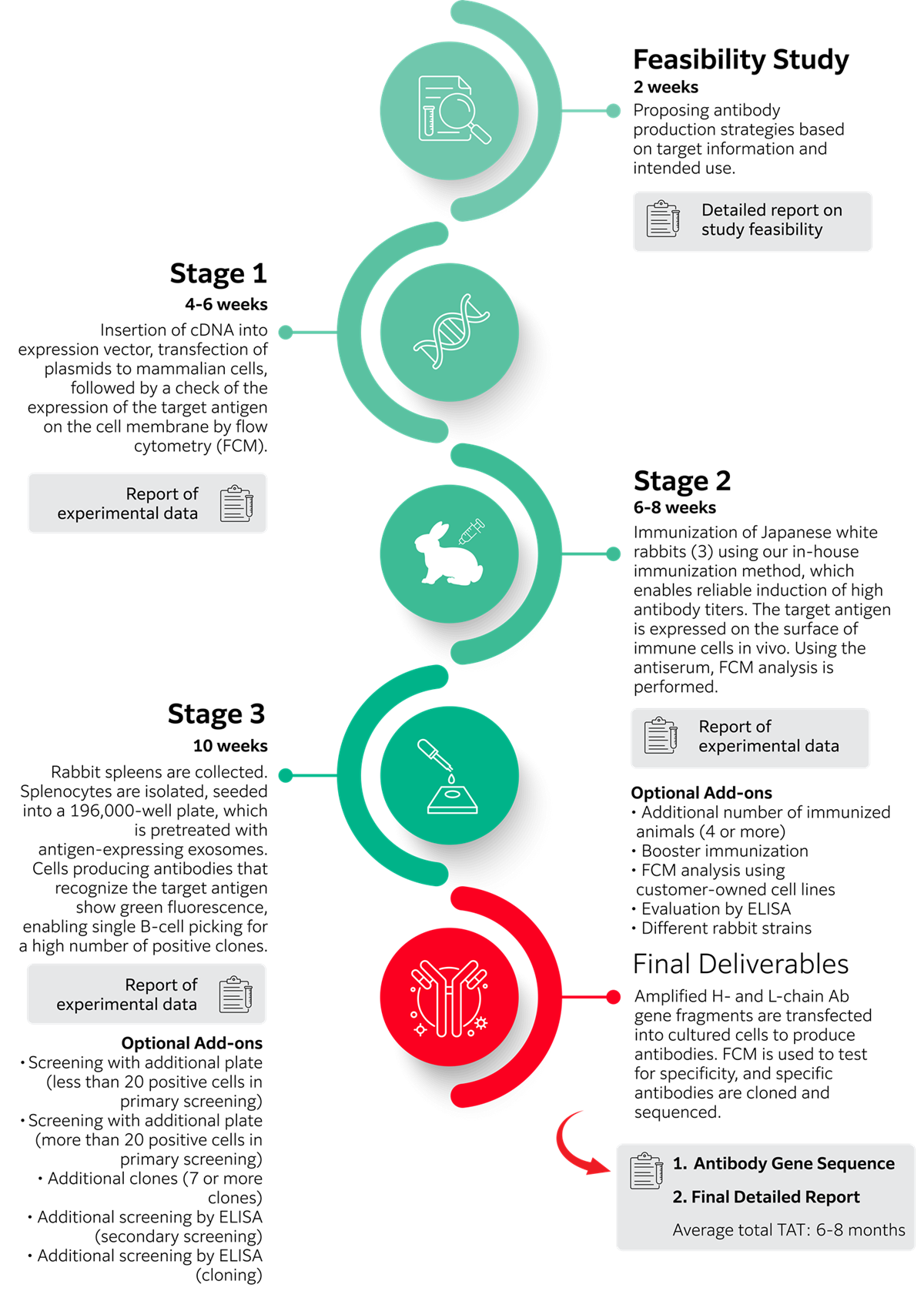
Stage-Gated mAb Discovery - Service Flow
Inquiry
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.




