Aspartate aminotransferase (AST/GOT) Assay Kits
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) is an aminotransferase enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of L-aspartate and α-ketoglutarate into glutamate and oxaloacetate. AST is highly abundant in the liver, myocardium, and skeletal muscle and is released into the bloodstream due to increased cell permeability or cell death. Therefore, it serves as a marker for organ damage, including liver injury. AST is also useful indicators of liver fibrosis caused by conditions such as metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). LabAssay™ AST (GOT) is a kit used for the determination of AST in samples. With the use of a microplate, this kit provides a quick and convenient method for measuring AST in samples.
What is AST (GOT)?
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) is an aminotransferase enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of L-aspartate and α-ketoglutarate into glutamate and oxaloacetate. It is also known as glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT). AST is highly abundant in the liver, myocardium, and skeletal muscle and is released into the bloodstream due to increased cell permeability or cell death. Therefore, it serves as a marker for organ damage, including liver injury.
In addition to AST, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) is commonly used as a marker for liver injury. ALT is predominantly found in the liver, making it a more specific marker for liver damage. In contrast, because AST is also present in the myocardium and skeletal muscle, an elevated AST level with normal or minimally elevated ALT may indicate cardiac or muscle injury. Furthermore, AST has a shorter half-life in the bloodstream compared to ALT, which allows for the assessment of disease status, including liver injury, based on this difference.
AST and ALT are also useful indicators of liver fibrosis caused by conditions such as metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). Liver fibrosis scoring systems, including the NAFLD fibrosis score (NFS)1) and the Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4)2) index, incorporate AST and ALT as key parameters.
Methods of AST (GOT) Measurement
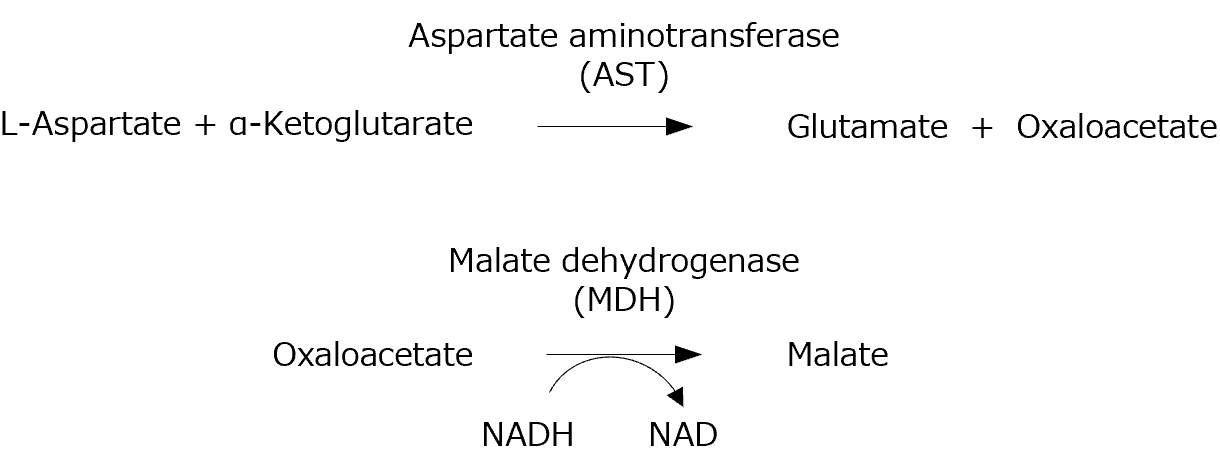
Principle of the AST (GOT) assay
When a sample is mixed with Substrate-Enzyme Solution and α-KG Solution, glutamate and oxaloacetate are formed from L-aspartate and α-ketoglutarate in a reaction catalyzed by AST in the sample. The oxaloacetate thus produced is converted to malate by malate dehydrogenase (MDH). At the same time, NADH is oxidized to NAD, and the absorbance at 340 nm decreases. Finally, the reaction is stopped using a reaction Stop Solution, and the absorbance is measured to determine the AST activity value in the sample.
LabAssay™ AST (GOT)
LabAssay™ AST (GOT) is a kit used for the determination of AST in samples. With the use of a microplate, this kit provides a quick and convenient method for measuring AST in samples.
[Note] LabAssay™ series are reagents for research purposes. They cannot be used for diagnostic purposes.
Kit Performance
| Analysis sample | Mouse Serum/Plasma Rat Serum/Plasma Dog Serum/Plasma Cat Serum/Plasma |
|---|---|
| Calibration curve range | 0-405 U/L |
| Sample volume | 7 μL |
| Measurement duration | Approx. 40 min |
| Wavelength | Primary wavelength 340 nm Reference wavelength 405 nm |
References
- Angulo, P. et al.: Hepatology, 45(4), 846(2007).
The NAFLD fibrosis score: a noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD - Shah, A. G. et al.: Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol., 7(10), 1104(2009).
Comparison of noninvasive markers of fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
Labassay™ AST (GOT)
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.



