Autotaxin (ATX) Assay Kits
Autotaxin (ATX) is a 125-kDa glycoprotein that was isolated as a cell motility-stimulating factor from the culture supernatant of human melanoma cells. It is known that liver damage, such as fibrosis, leads to the inhibition of ATX degradation, resulting in an increase in its blood concentration. LabAssay™ ATX is a kit designed for measuring ATX levels in samples. Utilizing a microplate, ATX in the sample can be measured quickly and easily.
What is Autotaxin (ATX)?
Autotaxin (ATX) is a 125-kDa glycoprotein that was isolated as a cell motility-stimulating factor from the culture supernatant of human melanoma cells1). ATX is a phospholipid-metabolizing enzyme that hydrolyzes lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) to produce lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), which induces organ fibrosis2).
A significant correlation between the histological stages of liver fibrosis and serum ATX activity has been reported3). This correlation is thought to be due to the inhibition of ATX degradation caused by liver damage, such as fibrosis, which leads to the retention of ATX in the bloodstream and an increase in its blood concentration. As ATX levels rise, LPA levels also increase, suggesting that ATX is involved in the progression of fibrosis. While liver biopsy is the most reliable method for assessing fibrosis, it causes significant physical discomfort for patients. Therefore, there is growing interest in less invasive liver fibrosis marker tests, with ATX being considered a promising blood marker for detecting early-stage fibrosis, which is difficult to identify through imaging4). However, caution is needed as ATX levels can decrease in patients receiving adrenal corticosteroids due to reduced production by adipose may increase in pregnant women due to placental ATX.
Methods of ATX Measurement
Lysophosphatidylcholine is hydrolyzed by the lysophospholipase D activity of ATX in the sample to form choline. The resultant choline is oxidized by the action of choline oxidase (COD) to form hydrogen peroxide. The resultant hydrogen peroxide oxidatively condenses N-Ethyl-N-(3-sulfopropyl)-3-methylaniline (TOPS) and 4-aminoantipyrine quantitatively through the action of peroxidase (POD) to produce a blue-violet pigment. The reaction is stopped by addition of the Stop Solution and absorbance is measured to determine ATX activity in the sample.
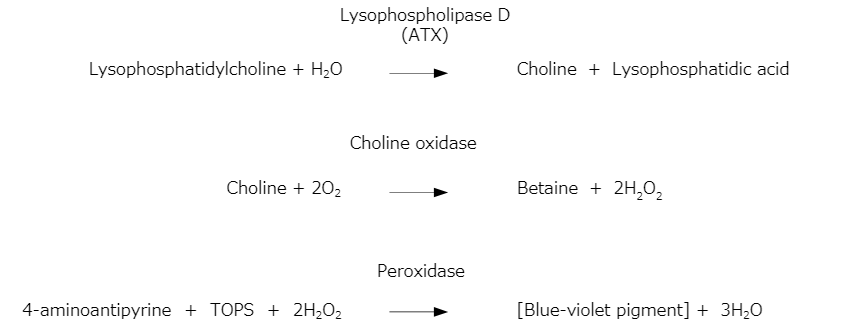
Figure 1. Principle of the ATX assay
LabAssay™ ATX
LabAssay™ ATX is a kit used for the determination of ATX in samples. With the use of a microplate, this kit provides a convenient method for measuring ATX in samples.
Kit performance
| Analysis sample | Human Serum/Plasma (heparin) Mouse Serum/Plasma (heparin) Rat Serum/Plasma (heparin) Culture medium (D-MEM)* |
|---|---|
| Calibration curve range | 1.72-55 U/L |
| Sample volume | 10 μL |
| Measurement duration | Approx. 40 min |
| Wavelength | Primary wavelength 546 nm Reference wavelength 700 nm |
*It is tested by using the samples that standard substances have been added to the culture medium.
Measurement availability depends on the culture medium, cell type and culture conditions. When using cell culture supernatant as a sample, please perform a spiked recovery test or dilution linearity test in advance using the culture medium to be used in your experiment.
References
- Stracke, M. L. et al.: J. Biol. Chem., 267(4), 2524(1992).
Identification, purification, and partial sequence analysis of autotaxin, a novel motility-stimulating protein - Umezu-Goto, M. et al.: J. Cell Biol., 158(2), 227(2002).
Autotaxin has lysophospholipase D activity leading to tumor cell growth and motility by lysophosphatidic acid production - Ikeda, H. et al.: The official journal of Japanese Society of Laboratory Medicine, 57(5), 445(2009). (Japanese)
Significance of serum autotaxin activity in gastrointestinal disease - “Evidence-based Clinical Guidelines for Nanalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/Nanalcoholic Steatohepatitis” ed. by The Japanese Society of Gastroenterology, Nankodo, (2014). (Japanese)
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.



