Presep® 55% Sulfuric Acid-impregnated Silica Gel
SPE Column for Halogenated Dioxins Analysis

Left: Presep® 10% Silver Nitrate-impregnated Silica Gel
Right: Presep® 55% Sulfuric Acid-impregnated Silica Gel
These columns are suitable for separating and evaluating halogenated dioxins.
Chlorinated dioxins are the most toxic and are internationally regulated.
Brominated dioxins are also considered to exhibit the same toxicity and properties as chlorinated dioxins, and are investigated for the effects on human health and for actual emissions from facilities.
Purpose
Presep® 10% Silver Nitrate-impregnated Silica Gel
Separation and evaluation of chlorinated and brominated dioxins
Presep® 55% Sulfuric Acid-impregnated Silica Gel1)
Purification of samples for measuring DXNs*1 / PHB*2 / polyhalogenated PAH*3(PBDE*4)
*1. DXNs: Dioxins
*2. PHB: Polyhydroxybutyrate
*3. PAH: Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
*4. PBDE: Polybrominated diphenyl ether
Column Composition
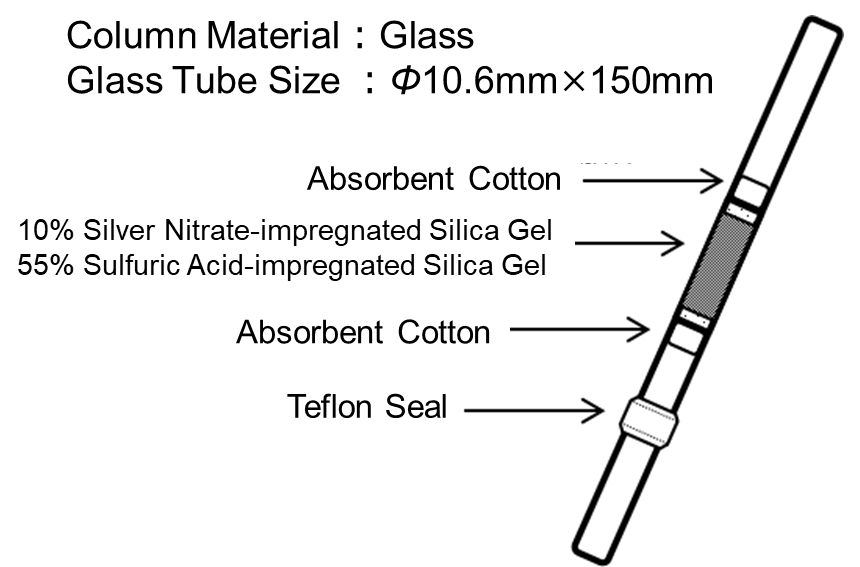
How to Use
Presep® 10% Silver Nitrate-impregnated Silica Gel
Perform the following pretreatment when using this column for the separation of chlorinated and brominated dioxins.
|
|
- 1: N2 is recommended to pass through activated carbon.
- 2: Please use it immediately after conditioning.
- 3: It is recommended that the sample be pretreated with Presep® 55% Sulfate Silica Gel (Code: 293-35581).
Presep® 55% Sulfuric Acid-impregnated Silica Gel
| Conditioning n-Hexane 20 mL |
|
| ▼ | |
| Charge n-Hexane 1 mL |
→ Extracted according to JIS K0311, JIS0312, etc. Add internal standard if necessary. |
| ▼ | |
| Elution n-Hexane 19 mL |
|
| ▼ | |
| Dry | |
| ▼ | |
| Redissolve | → Add internal standard if necessary. |
Application
Recovery rate of brominated and chlorinated dioxins on a 10% Silver Nitrate Silica Gel Column (n = 3)2)
| Recovery rates(%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 mL of n-hexane | 2 mL of n-hexane | 10 mL of 4%acetone/n-hexane | |||||||
| Compounds | IUPAC # | Average | S.D. | Average | S.D. | Average | S.D. | ||
| Native | Brominated dioxins | 2,3,7,8-TeBDD | 96 | 1.8 | |||||
| 1,2,3,7,8-PeBDD | 92 | 3.4 | |||||||
| 1,2,3,6,7,8-HxBDD | 85 | 4.9 | |||||||
| 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-HpBDD | 96 | 1.9 | |||||||
| OBDD | 85 | 6.5 | |||||||
| 2,4,8-TriBDF | 11 | 4.5 | 10 | 4.2 | 68 | 3.2 | |||
| 2,3,7,8-TeBDF* | 96 | 1.9 | |||||||
| 2,3,4,7,8-PeBDF* | 91 | 1.5 | |||||||
| 1,2,3,4,7,8-HxBDF* | 71 | 1.7 | |||||||
| 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-HpBDF* | 94 | 0.97 | |||||||
| OBDF | 85 | 9.5 | |||||||
| 13C-Labeled | Chlorinated dioxins | 2,3,7,8-TeCDD | 90 | 25 | |||||
| 1,2,3,7,8-PeCDD* | 91 | 25 | 0.84 | 1.1 | |||||
| 1,2,3,4,7,8-HxCDD | 90 | 28 | 0.54 | 0.93 | |||||
| 1,2,3,6,7,8-HxCDD* | 80 | 24 | 0.63 | 0.75 | |||||
| 1,2,3,7,8,9-HxCDD | 87 | 24 | 1.1 | 1.3 | |||||
| 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-HpCDD | 85 | 24 | 1.5 | 1.9 | |||||
| OCDD | 86 | 22 | 1.9 | 1.6 | |||||
| 2,3,7,8-TeCDF* | 86 | 25 | 0.65 | 0.15 | |||||
| 1,2,3,7,8-PeCDF* | 87 | 26 | 0.61 | 1.1 | |||||
| 2,3,4,7,8-PeCDF* | 65 | 13 | |||||||
| 1,2,3,4,7,8-HxCDF* | 92 | 25 | 1 | 1.4 | |||||
| 1,2,3,6,7,8-HxCDF | 90 | 26 | 1.1 | 1.3 | |||||
| 1,2,3,7,8,9-HxCDF | 84 | 19 | 0.33 | 0.58 | |||||
| 2,3,4,6,7,8-HxCDF* | 83 | 23 | 0.26 | 0.45 | |||||
| 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-HpCDF | 84 | 22 | 0.92 | 1.6 | |||||
| 1,2,3,4,7,8,9-HpCDF | 93 | 17 | 1.3 | 2.3 | |||||
| OCDF | 98 | 21 | 2.3 | 1.7 | |||||
| Co-PCBs | 3,4,4',5-TeCB | 81 | 88 | 11 | |||||
| 3,3',4,4'-TeCB | 77 | 92 | 16 | ||||||
| 3,3',4,4',5-PeCB* | 126 | 97 | 18 | ||||||
| 3,3',4,4',5,5'-HxCB | 169 | 92 | 18 | ||||||
| 2',3,4,4',5-PeCB | 123 | 86 | 15 | ||||||
| 2,3',4,4',5-PeCB | 118 | 90 | 20 | 0.09 | 0.16 | ||||
| 2,3,3',4,4'-PeCB | 105 | 95 | 22 | 0.06 | 0.1 | ||||
| 2,3,4,4',5-PeCB | 114 | 89 | 17 | ||||||
| 2,3',4,4',5,5'-HxCB | 167 | 92 | 20 | ||||||
| 2,3,3',4,4',5-HxCB | 156 | 88 | 21 | ||||||
| 2,3,3',4,4',5'-HxCB | 157 | 99 | 15 | ||||||
| 2,3,3',4,4',5,5'-HpCB | 189 | 102 | 14 | ||||||
*Major contributors to WHO-TEQ
Recovery rate of brominated and chlorinated dioxins in 55% Sulfuric Acid Silica Gel Column (n = 3)2)
| Recovery rates(%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 mL of n-hexane | |||||||||
| Compounds | IUPAC # | Average | S.D. | ||||||
| Native | Brominated Dioxins | 2,3,7,8-TeBDD | 98 | 2.5 | |||||
| 1,2,3,7,8-PeBDD | 97 | 1.9 | |||||||
| 1,2,3,6,7,8-HxBDD | 90 | 0.86 | |||||||
| 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-HpBDD | 89 | 3.1 | |||||||
| OBDD | 81 | 9.1 | |||||||
| 2,4,8-TriBDF | 90 | 2.3 | |||||||
| 2,3,7,8-TeBDF* | 94 | 2.7 | |||||||
| 2,3,4,7,8-PeBDF* | 90 | 2.6 | |||||||
| 1,2,3,4,7,8-HxBDF* | 89 | 2.3 | |||||||
| 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-HpBDF* | 88 | 2.0 | |||||||
| OBDF | 95 | 2.0 | |||||||
| 13C-Labeled | Chlorinated Dioxins | 2,3,7,8-TeCDD | 80 | 4.5 | |||||
| 1,2,3,7,8-PeCDD* | 95 | 4.8 | |||||||
| 1,2,3,4,7,8-HxCDD | 93 | 6.3 | |||||||
| 1,2,3,6,7,8-HxCDD* | 100 | 7.4 | |||||||
| 1,2,3,7,8,9-HxCDD | 96 | 8.1 | |||||||
| 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-HpCDD | 86 | 6.8 | |||||||
| OCDD | 88 | 8.8 | |||||||
| 2,3,7,8-TeCDF* | 86 | 2.0 | |||||||
| 1,2,3,7,8-PeCDF* | 95 | 6.0 | |||||||
| 2,3,4,7,8-PeCDF | 66 | 3.8 | |||||||
| 1,2,3,4,7,8-HxCDF* | 93 | 5.7 | |||||||
| 1,2,3,6,7,8-HxCDF | 102 | 8.7 | |||||||
| 1,2,3,7,8,9-HxCDF | 79 | 7.8 | |||||||
| 2,3,4,6,7,8-HxCDF* | 75 | 8.3 | |||||||
| 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-HpCDF | 82 | 5.2 | |||||||
| 1,2,3,4,7,8,9-HpCDF | 101 | 5.8 | |||||||
| OCDF | 91 | 4.2 | |||||||
| Co-PCBs | 3,4,4',5-TeCB | 81 | 69 | 2.9 | |||||
| 3,3',4,4'-TeCB | 77 | 74 | 2.1 | ||||||
| 3,3',4,4',5-PeCB* | 126 | 79 | 2.9 | ||||||
| 3,3',4,4',5,5'-HxCB | 169 | 91 | 6.4 | ||||||
| 2',3,4,4',5-PeCB | 123 | 71 | 1.6 | ||||||
| 2,3',4,4',5-PeCB | 118 | 70 | 2.4 | ||||||
| 2,3,3',4,4'-PeCB | 105 | 77 | 4.4 | ||||||
| 2,3,4,4',5-PeCB | 114 | 72 | 1.8 | ||||||
| 2,3',4,4',5,5'-HxCB | 167 | 78 | 4.4 | ||||||
| 2,3,3',4,4',5-HxCB | 156 | 79 | 3 | ||||||
| 2,3,3',4,4',5'-HxCB | 157 | 84 | 6.7 | ||||||
| 2,3,3',4,4',5,5'-HpCB | 189 | 87 | 5.9 | ||||||
*Major contributors to WHO-TEQ
- CDD:Chlorinated Dibenzo-p-dioxin
- CB:Chlorinated Biphenyl
- CDF:Chlorinated Dibenzofuran
- Di:Di-
- Tr:Tri-
- Te:Tetra-
- Pe:Penta-
- Hx:Hexa-
- Hp:Hepta-
- O:Octa-
References
- Patent No. 5691120(2015)
- Suzuki, G., et al.: Separate screening of brominated and chlorinated dioxins in field samples using in vitro reporter gene assays with rat and mouse hepatoma cell lines, Analytica Chimica Acta, 975, 86 (2017).
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.



