Tissue Decalcifying Solutions
It is difficult to slice hard tissues such as bones and calcified lesions with a microtome knife to prepare thin sections. Therefore, decalcification is performed to remove calcium salts. In this procedure, acids degrade calcium carbonate in the tissue into softer calcium salts to facilitate slicing. Decalcifying agents must satisfy the following conditions:
- Decalcification is completed rapidly.
- Tissue stainability is not affected.
- The process has been made as simple as possible.
- Decalcification causes no damage, for example deformation due to tissue swelling, shrinkage, lysis, etc.
Procedure
| Thickness of tissue section | : | A thickness of ≤5 mm is desirable. |
| Volume of decalcifying solution | : | ≥100 mL per g |
| Decalcification temperature | : | In principle, decalcify at room temperature. Higher temperature increases the rate of decalcification but the significant damage can be seen. Decalcifying Solution B (neutral EDTA) is often operated at 30°C and has been reported to maintain almost unchanged stainability and intact tissue morphology, even at 56°C. |
| Neutralization | : | Decalcification with Kalkitox™, decalcifying Solution A (Plank Rychlo method), hydrochloric acid, or nitric acid requires neutralization with 5% sodium sulfate solution. The duration of neutralization is generally equal to that of decalcification, but may be at least half a day if rapid neutralization is desired. After neutralization, wash the tissue thoroughly with water to remove sodium sulfate. |
| Other tips | : | Adequate stirring increases the rate of decalcification. The rate of decalcification can be improved by stirring two or three times a day. |
Kalkitox™
This product is a decalcifying solution with the properties of both Plank Rychlo decalcifying solution and chelator decalcifying solution.
Usage
The duration of decalcification is approximately one night at room temperature. The duration varies depending on the size of the tissue sample.
Decalcification at low temperature (4°C in the refrigerator for one to two nights) is recommended. After completion of decalcification, neutralize the tissue with sodium sulfate solution for a duration of several hours to overnight and then wash thoroughly with water. Subsequently, proceed with dehydration, clearing, and paraffin embedding.
Features
- Tissues can be simultaneously degreased and decalcified.
- Tissues can be decalcified at low temperature (4°C).
- Tissues can be immunostained.
Composition
The main ingredients are hydrochloric acid and EDTA.
Example of staining
-
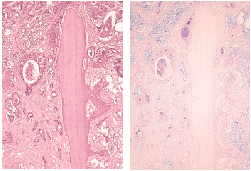
Figure 1. Bone metastasis of colorectal cancer (adenocarcinoma) (× 10)
Left: H&E staining, Right: Alcian blue-PAS staining -
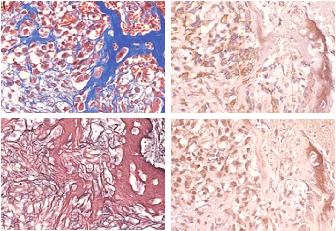
Figure 2. Osteosarcoma of the femur (× 20)
Upper left: Masson's trichrome staining
Lower left: Silver impregnation
Right: Enzyme immunoassay (top: osteocalcin, bottom: osteonectin)
Decalcifying Solutions A and B
| Decalcification method | Decalcifying solution | Composition | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rapid decalcification | Decalcifying Solution A (Plank Rychlo method) |
Aluminum chloride: 7.0 g Hydrochloric acid: 8.5 mL Formic acid: 5.0 mL Use distilled water to make a total volume of 100 mL. |
・Duration of decalcification: Approximately 3 times longer than decalcification with formic or nitric acid ・Antigenicity is not well retained. ・Requires neutralization with 5% sodium sulfate |
| Neutral decalcification | Decalcifying Solution B (EDTA method) |
The main ingredient is 0.5 mol/L EDTA solution (pH 7.0 to 7.5). | ・Causes less damage to tissues ・Structure or stainability is well maintained ・Ideal for immunohistostaining ・Long duration of decalcification |
Example of staining
| Decalcifying Solution A | Decalcifying Solution B | |
|---|---|---|
| H&E Staining | 12-hour complete decalcification, 10 mm thick bone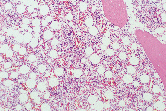 Rapid decalcification |
5-day complete decalcification, 3 mm thick bone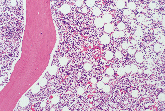 Slow decalcification |
| Immunohistostaining | 12-hour complete decalcification, 3 mm thick bone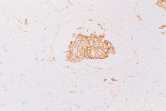 The CEA antigen is lost. |
5-day complete decalcification, 3 mm thick bone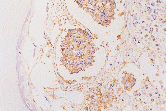 The CEA antigen is well maintained. |
Morse Solution
Morse solution provides approximately 8 times faster decalcification than neutral EDTA solution and has been reported to be comparable to EDTA for immunostaining and in situ hybridization.
Composition
- 22.5% formic acid
- 10% sodium citrate
Example of staining
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.



