SCALEVIEW
The SCALEVIEW series are reagents designed for use in the Scale method. Developed by Dr. Atsushi Miyawaki and his colleagues at RIKEN, the Scale method is an optical clearing technique that employs urea-based reagents. This method is not only useful for clearing biological samples containing fluorescent proteins but also significantly enhances the efficiency of labeling thick samples with antibodies and fluorescent dyes. It is particularly useful as an analytical tool for studying brain tissues, spheroids, and organoids.
What is Scale?
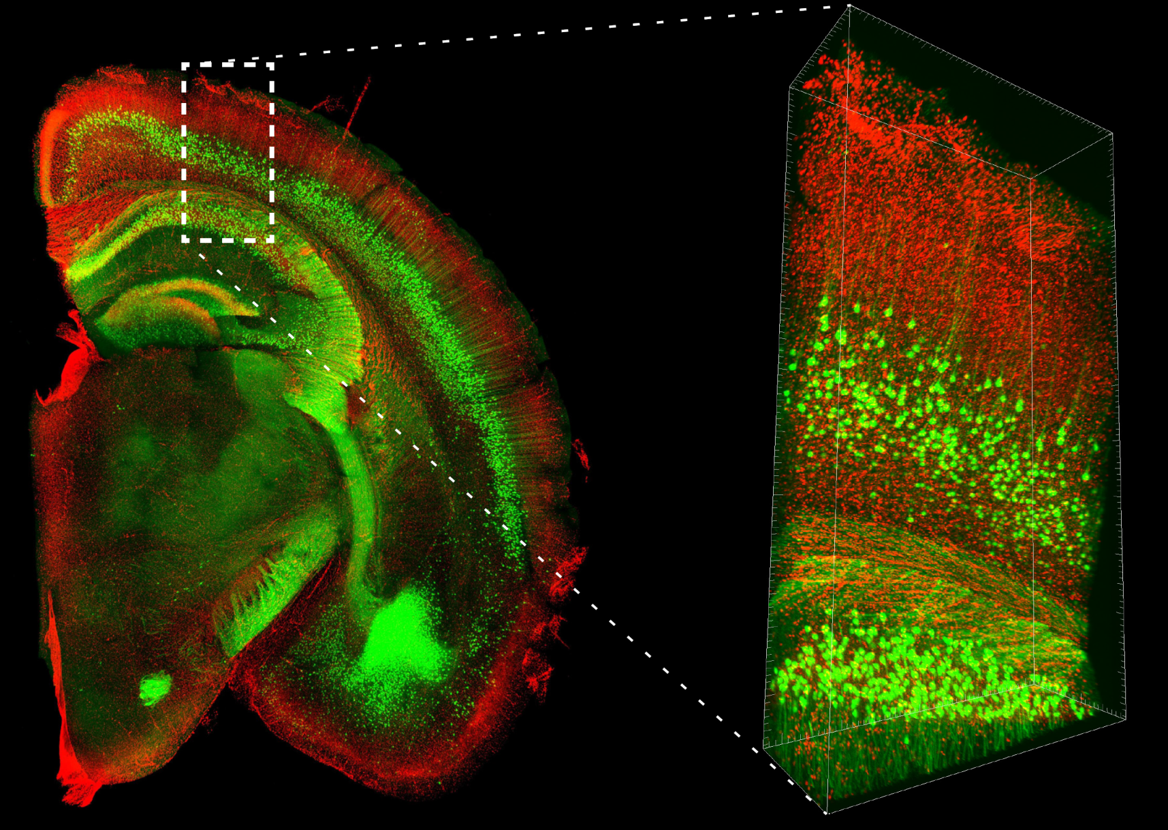
PI-stained brain hemisphere slice from a YFP-H mouse
Data by courtesy of
Drs. Hama, Hoshida, and Miyawaki of Laboratory for Cell Function Dynamics, RIKEN Center for Brain Science, and Biotechnological Optics Research Team, RIKEN Center for Advanced Photonics (With support from Evident)
Overview
Organic solvents have been widely used in conventional clearing techniques; however, fluorescent proteins that depend on water molecules for fluorescence emission tend to fade significantly. To address this issue, the Scale method (a collective term for the ScaleS and ScaleA2 methods) was developed1-2). This technique uses water-based reagents composed of urea, surfactants, and either sorbitol (in the ScaleS method) or glycerol (in the ScaleA2 method) to suppress light scattering, enabling tissue clearing without fading of fluorescent proteins. Moreover, the low surfactant content required for lipid removal helps maintain ultrafine structures after clearing. With its exceptional balance of transparency and structural preservation, the Scale method is highly recommended for those new to tissue clearing.
Features
- Simple operation (just immerse samples sequentially in the solutions)
- Clears 2 mm brain tissue blocks in about one day
- Compatible with fluorescent dye staining (ChemScale) and Immunostaining (AbScale)
Samples suitable for clearing
Mouse brain, Postmortem human brain, Bone (requires decalcification), Organoids/Spheroids, and more.
Selection of SCALEVIEW Series
| Applications | Fluorescent proteins | Fluorescent dyes | Antibody (Immunostaining) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methods | ScaleS | ChemScale | AbScale | |
| Required Reagents | SCALEVIEW-S Trial Kit | ✔ | ||
| SCALEVIEW-A2 | ✔ | ✔ | ||
| SCALEVIEW-S0 | ✔ | ✔ | ||
| SCALEVIEW-S4 | ✔ | ✔ | ||
| deScale solution | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Time required for clearing | Approx. 1 day | 4 to 7 days | 4 to 7 days | |
| Note | •Compatible with co-staining of fluorescent proteins | •Compatible with co-staining of fluorescent proteins | ||
Description of Each Reagent
SCALEVIEW-S Trial Kit
A kit containing six solutions: SCALEVIEW-S0, SCALEVIEW-S1, SCALEVIEW-S2, SCALEVIEW-S3, SCALEVIEW-S4, and SCALEVIEW-SMt. Sequential immersion of tissue samples in these solutions allows for simple and rapid tissue clearing and refractive index adjustment.
SCALEVIEW-A2
A clearing solution based on the Scale method reported in 2011. With a relatively low refractive index (RI = 1.377- 1.381 at 20°C), it allows easy refractive index matching even without expensive microscopy equipment, making it ideal for those new to tissue clearing.
deScale solution
A reagent used in the washing process of the ScaleS method.
Simplified Spheroid Clearing (Optional)
A simplified clearing protocol for spheroids using only SCALEVIEW-S4 has been reported3).
Details of the protocol and experimental data for simplified clearing are available on the SCALEVIEW-S4 product details page.
Other Required Equipment, Instruments, and Reagents
Equipment and Instruments
- Fluorescence microscope
Ensure that the objective lenses are compatible with the refractive indices (SCALEVIEW-A2: RI=1.38, SCALEVIEW-S4: RI=1.47, SCALEVIEW-SMt: RI=1.49). Consulting the microscope manufacturer before data acquisition is recommended.
- Conical tubes (choose from among 5 mL, 15 mL, 30 mL, or 50 mL tubes based on the sample)
- Plastic petri dishes (choose from among 35 mm, 60 mm, or 100 mm diameter dishes based on the sample)
- See-Saw Rocking Shakers
Reagents
Data
Brain Tissue
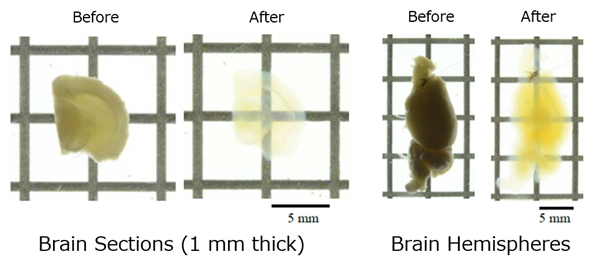
Protocol
| Perfusion fixation + Post-fixation | Clearing | Washing | Clearing | Observation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4% PFA/PBS(-) | PBS(-) | SCALEVIEW-S0 | SCALEVIEW-S1 | SCALEVIEW-S2 | SCALEVIEW-S3 | deScale Solution | SCALEVIEW-S4 | SCALEVIEW-SMt | SCALEVIEW-SMt |
| 4°C 3 days |
RT Several times |
37°C 30 minutes |
37°C 30 minutes |
37°C 30 minutes |
37°C 30 minutes |
4°C 3 hour x 2 times |
37°C 12-24 hours |
37°C 1 hour |
RT |
Volume of Each Solution Used (Approximate volumes for 1-2 mm thick mouse brain hemisphere sections*)
[Tissue Clearing] SCALEVIEW-S0/S1/S2/S3: 5 mL each / deScale Solution 5 mL
[Observation] SCALEVIEW-SMt: 5 mL
* The volume of reagents and processing time vary with sample size.
Species: Mouse (Thy1-YFP-H line, 20W, Male)
Tissue: Whole brain
Microscope: Multiphoton microscope (Evident, FVMPE-RS)
Objective lens: XLPLN10XSVMP (NA 0.6)
Laser: 960 nm (YFP)
Image size: 512 x 512, 170 tiles, Z=8,000 μm, Z Step 16 μm
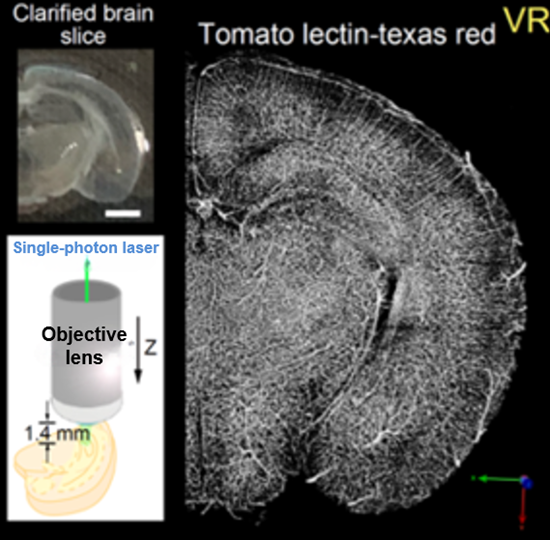
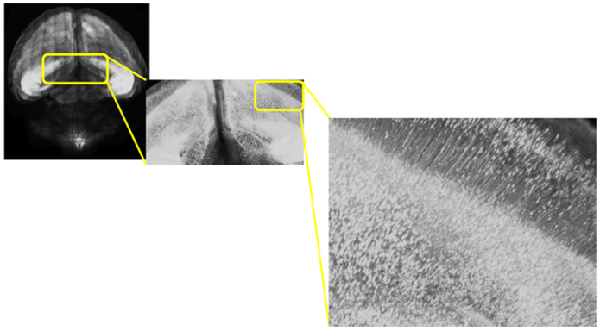
Species: Mouse (C57BL6/J, 10.5 days old)
Tissue: Coronal section of cerebral cortex (1.2 mm thick)
Microscope: Confocal microscope (Upright)
Lectin: Texas Red labeled tomato-lectin
Species: Mouse
Tissue: Whole brain
Objective lens: XLSLPLN25XSVMP (NA 0.90, WD 8 mm)
Species: Mouse
Tissue: Hippocampus
Objective lens: XLPLN25XSVMP (NA1.0, WD 4 mm)
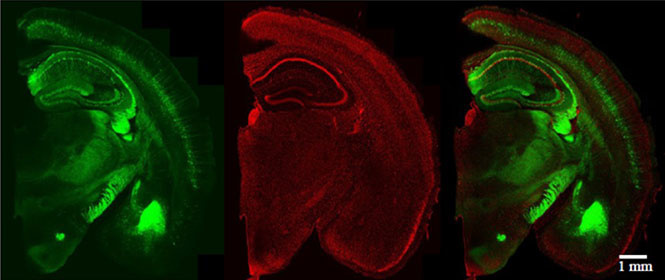
Species: Mouse (Thy1-YFP-H line, 42W, Male)
Tissue: Coronal section of the Brain (2 mm thick)
Microscope: Confocal microscope (Evident, FV3000, Inverted)
Objective lens: UPLSAPO10x2 (NA 0.40)
Laser: 488 nm (YFP) / 561 nm (PI)
Protocol (For detailed protocol, see here)
| Perfusion fixation + Post-fixation | Pretreatment | Staining with Fluorescent Dye | Clearing | Observation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4% PFA/PBS(-) | PBS(-) | SCALEVIEW-S0 | SCALEVIEW-A2 | 8M Urea | SCALEVIEW-A2 | deScale Solution | Fluorescent Dye*/ SCALEVIEW-A2 |
SCALEVIEW-A2 | deScale Solution | SCALEVIEW-S4 | SCALEVIEW-S4 |
| 4°C 3 days |
RT Several times |
37°C 4 hours |
37°C 4 hours |
37°C 12 hours |
37°C 4 hours |
4°C 6 hours |
RT 2 hours |
RT 2 hours x 1, 1 hour x 1 |
4°C 3 hours |
37°C 6-8 hours |
RT |
Volume of Each Solution Used (Approximate volumes for 1-2 mm thick mouse brain hemisphere sections)
- [Pretreatment]
- SCALEVIEW-S0: 10 mL / SCALEVIEW-A2: 10 mL x 2 / deScale Solution: 10 mL
- [Staining]
- Staining solution : 8 mL /deScale Solution: 10 mL
- [Clearing]
- SCALEVIEW-S4: 10 mL
- [Observation]
- SCALEVIEW-S4: 10 mL
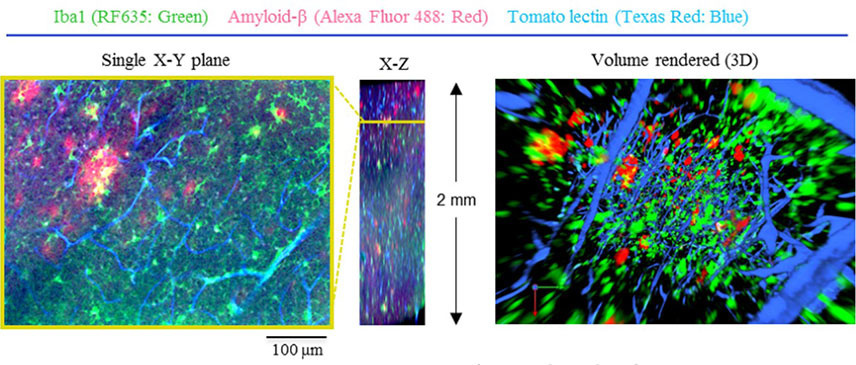
Species: Mouse (Alzheimer’s disease model, 17 months old)
Tissue: Brain section (2 mm thick)
Microscope: Confocal microscope (Evident, FV1200, Inverted)
Objective lens: XLPLN10XSVMP (NA 0.60)
Protocol (For detailed protocol, see here)
| Perfusion fixation + Post-fixation | Pretreatment | Immunostaining | Clearing | Observation | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4% PFA/PBS(-) | PBS(-) | SCALEVIEW-S0 | SCALEVIEW-A2 | 8M Urea | SCALEVIEW-A2 | deScale Solution | 1% Blocking agents* /PBS(-) | Antibody /AbScale Solution** | AbScale Solution** | 4% PFA /PBS(-) | deScale Solution | SCALEVIEW-S4 | SCALEVIEW-S4 |
| 4°C 3 days |
RT Several times |
37°C 4 hours |
37°C 4 hours |
37°C 12 hours |
37°C 4 hours |
4°C 6 hours |
RT 2 hours |
37°C > 1 day |
RT 2 hours x 1, 1 hour x 1 |
4°C 6 hours |
4°C 6 hours |
37°C 6-8 hours |
RT |
** AbScale Solution: 0.33 M Urea, 0.1% (wt/vol) Triton X-100 in PBS
Volume of Each Solution Used (Approximate volumes for 1-2 mm thick mouse brain hemisphere sections)
- [Pretreatment]
- SCALEVIEW-S0: 10 mL / SCALEVIEW-A2: 10 mLx2 / deScale Solution: 10 mL
- [Immunostaining]
- AbScale Solution: 1.5 mL /deScale Solution: 10 mL
- [Clearing]
- SCALEVIEW-S4: 10 mL
- [Observation]
- SCALEVIEW-S4: 10 mL
Organoids/Spheroids
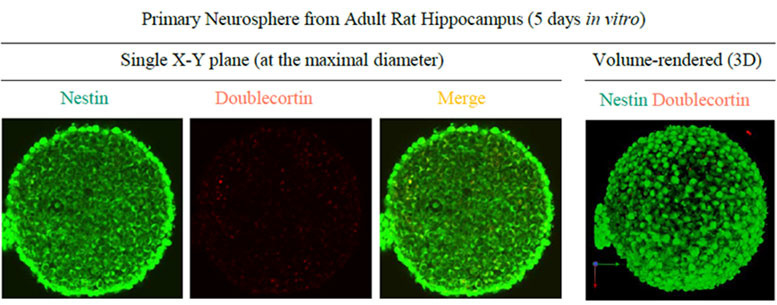
Sample: Neurospheres derived from rat hippocampal neural stem cells
Microscope: Confocal Microscope (Evident, FV1000)
Objective lens: UMPLFLN10XW (NA 0.3)
Protocol
| Perfusion fixation + Post-fixation | Pretreatment | Immunostaining | Clearing | Observation | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4% PFA/ PBS(-) |
PBS(-) | SCALEVIEW-S0 | SCALEVIEW-A2 | 8M Urea | SCALEVIEW-A2 | deScale Solution | 1% Blocking agents* /PBS(-) | Antibody /AbScale Solution** | AbScale Solution** | 4% PFA /PBS(-) | deScale Solution | SCALEVIEW-S4 | SCALEVIEW-S4 |
| 4°C 3 days |
RT Several times |
37°C 4 hours |
37°C 4 hours |
37°C 12 hours |
37°C 4 hours |
4°C 6 hours |
RT 2 hours |
37°C > 1 day |
RT 2 hours x 1, 1 hour x 1 |
4°C 1 hour |
4°C 3 hours |
37°C 4 hours |
RT |
** AbScale Solution: 0.33 M Urea、0.1% (wt/vol) Triton X-100 in PBS
Volume of Each Solution Used
- [Pretreatment]
- SCALEVIEW-S0: 1.2 mL / SCALEVIEW-A2: 1.2 mL / deScale Solution: 1.2 mL
- [Immunostaining]
- Follows the AbScale protocol
- [Clearing]
- SCALEVIEW-S4: 1.2 mL
- [Observation]
- SCALEVIEW-S4: 1.2 mL
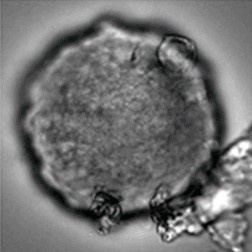
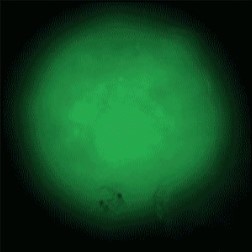
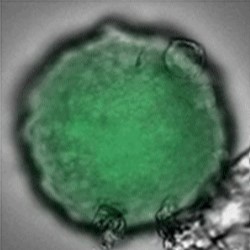
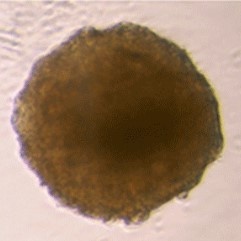
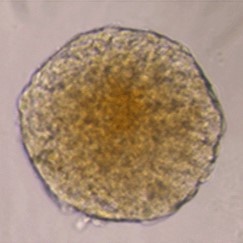
Sample: iCell® Hepatocytes2.0
Plate for spheroid formation: Prime Surface® 96 Slit-well Plate
Primary Antibody: Anti-ABCB11 antibody
Secondary Antibody: Anti-rabbit IgG(H+L), Goat, FITC-conjugated
Protocol
SCALEVIEW Q&A
About protocol
- Do samples expand during clearing?
- There is minimal change; however, samples may expand slightly during the clearing process. They return to nearly their original size in the final clearing step.
- Are there any steps in the clearing process where the procedure can be put on hold?
- [Pre-treatment steps for AbScale and ChemScale]
During SCALEVIEW-S0 or A2 processing, samples can be kept at 4°C for 12 hours to 3 days.
- How should samples be stored after clearing?
- Store the samples in SCALEVIEW-S4 solution, sealed by Parafilm to prevent drying, at room temperature and in the dark.
About observation
- How long is the fluorescent protein signal retained?
- The signal remains stable for approximately six months.
- What type of observation container should be used?
- Use a dish with a diameter slightly larger than the tissue sample or a See Through Chamber appropriate for the sample’s thickness.
- What type of microscope should be used?
-
Use a confocal or two-photon microscope. Ensure that the objective lens is compatible with the refractive index of SCALEVIEW-S4 (RI=1.47) or SCALEVIEW-SMt (RI=1.49).
Tips: If a compatible microscope is unavailable or observation under high refractive index conditions is difficult, consider using SCALEVIEW-A2 (RI=1.38) as a substitute. For more details, refer to the information provided.
References
- Hama, H. et al.: Nat Neurosci., 14, 1481 (2011).
Scale: a chemical approach for fluorescence imaging and reconstruction of transparent mouse brain - Hama, H. et al.: Nat Neurosci., 18, 1518 (2015).
ScaleS: an optical clearing palette for biological imaging - Boutin, M. E. et al.: Sci. Rep., 8(1), 11135 (2018).
A high-throughput imaging and nuclear segmentation analysis protocol for cleared 3D culture models
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.