DNA Extractor® Kit Series
A widely used method to extract DNA from tissues derived from living body is to precipitate and collect DNA using phenol and chloroform. However, this method requires the use of phenol and chloroform, hazardous substances.
This DNA extraction method uses sodium iodide known as a chaotropic agent instead of these organic solvents. Sodium iodide has protein denaturation action and solubilization action. Sodium iodide releases chaotropic ions (I-) into the solution; the ions increase water solubility of hydrophobic molecules in the sample, and its action to weaken hydrophobic bond contributes particularly to denaturation and solubilization of membrane proteins such as nuclear membrane.
In addition, no solid phase extraction using silica carrier inhibits DNA loss by adsorption; moreover, the entire operation is performed in a single tube, realizing a high yield rate.
Features
- Organic solvents such as hazardous phenol and chloroform are not required.
- The entire process is performed in a single tube, causing no loss, contamination, or mechanical DNA damage in operation.
- No solid phase extraction using silica carrier causes no loss by adsorption.
- Little oxidation damage to DNA and mechanical DNA damage
- A high yield rate is realized.
- The product series used in the accumulated total of 963 publications※1
※1: Source: Google scholar
Kit Selection by Sample Property
| Sample | Whole Blood | Serum | Plasma | Tissues | Biopharmaceuticals | Cultured Cells | Hair, Nail, Bloodstain & Saliva |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| genomic DNA | DNA ExtractorTM WB Kit | DNA ExtractorTM Kit DNA ExtractorTM SP Kit |
DNA ExtractorTM SP Kit | DNA ExtractorTM WB Kit | DNA ExtractorTM Kit | DNA ExtractorTM WB Kit | DNA ExtractorTM FM Kit |
| mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) | - | - | - | mtDNA ExtractorTM CT Kit | - | mtDNA ExtractorTM CT Kit | - |
| free DNA | - | DNA ExtractorTM SP Kit | DNA ExtractorTM SP Kit | - | - | - | - |
| low-oxidized DNA | DNA ExtractorTM WB Kit | DNA ExtractorTM TIS Kit | - | DNA ExtractorTM TIS Kit | - | ||
| bacterial genomic DNA from biologicals | - | DNA ExtractorTM Kit | - | - | DNA ExtractorTM Kit | - | - |
| virus DNA | - | DNA ExtractorTM Kit | - | - | - | - | - |
DNA Extractor® Kit
Extraction of viral DNA in serum and an infinitesimal amount of fungus-derived DNA in biological products
-
Extraction from serum
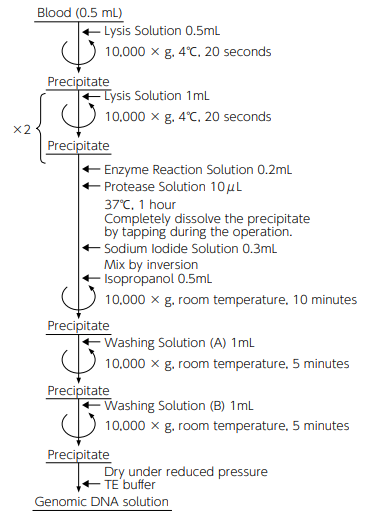
Operation time: 1 to 1.5 hours
Sample amount: 100 μL/test -
This kit is intended for use in extracting host cell-derived residual DNA remaining in biological components using the Sodium Iodide method. Extracted DNA can be quantified by qPCR. Use the DNA Extractor® kit for testing and management of the amount of DNA derived from host cells such as CHO cells, Escherichia coli, and yeast. DNA from any species extracted using this kit is suitable for using the Threshold Immunoassay System® provided by Molecular Devices, LLC. The kit can also be used for DNA extraction from serum.
Features
- Efficient recovery of trace DNA (100-1,000 fg)
- Perform in a single tube for complete the process
- Extraction completed in 60-90 minutes
- Pretreatment protocol for samples containing high protein concentration
- Adopts Sodium Iodide method*
*Sodium Iodide method is a residual DNA extraction technique that is described in The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) 42-NF37, <509> Residual DNA Testing.
Kit Contents [50 tests (sample 500 μL)]
1. Sodium Iodide Solution.......................................................2 x 26 mL
2. Sodium N-Lauryl Sarcosinate Solution................................1 x 1.2 mL
3. Washing Solution (A)..........................................................1 x 42 mL
4. Washing Solution (B) .........................................................2 x 40 mL
5. Glycogen Solution ............................................................1 x 0.1 mL
Principle of DNA extraction
i. Cell membrane and cytoplasm are destroyed by surfactant, isolating cell nuclei.
ii. The nuclear membrane and nuclear protein are decomposed by protease to expose DNA.
iii. Protein and lipids are made soluble by the action of sodium iodide, and DNA is precipitated with isopropanol.
DNA Extractor® Kit Data
Recovery test of CHO cell-derived DNA
Purpose:
To examine the yields of CHO cell-derived DNA from culture supernatant.
Methods:
Using the kit, DNA was extracted from culture supernatants of PANC-1 cells to which 10 fg to 1 ng of CHO cell-derived DNA was added. A qPCR assay was then performed using the extracted DNA to obtain Cq values.
A qPCR was also performed using purified water to which CHO cell-derived DNA was added, without DNA extraction (standard conditions), to obtain Cq values. The DNA yield under each set of conditions was calculated based on a calibration curve generated from the results of the standard conditions.
Samples:
1. Purified water containing CHO cell-derived DNA (no DNA extraction): Standard conditions
2. DNA extracted from the culture supernatants of PANC-1 cells containing CHO cell-derived DNA, using the kit.
qPCR reagents:
・GeneAce SYBR® qPCR Mix α No ROX (Nippon Gene#319-07703)
・Optical Flat 8–Cap Strips for 0.2 mL tube strips/Plates (BIO-RAD#TCS0803)
・Hard-Shell® Thin-wall 96-well PCR plates (BIO-RAD#HSP9601)
Results:
| 1. Standard conditions | 2. Culture supernatants | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Added DNA (fg) | Cq 1 | Cq 2 | Mean | Cq 1 | Cq 2 | Mean |
| 0 | ND | |||||
| 10 | ||||||
| 100 | 36.89 | ND | 36.89 | 37.44 | 36.73 | 37.09 |
| 1,000 | 33.44 | 33.91 | 33.68 | 34.09 | 34.01 | |
| 10,000 | 30.23 | 30.17 | 30.20 | 30.72 | 30.96 | 30.84 |
| 100,000 | 26.74 | 26.68 | 26.71 | 26.90 | 27.03 | 26.96 |
| 1,000,000 | 23.39 | 23.28 | 23.33 | 23.61 | 23.48 | 23.54 |
ND: Not detected
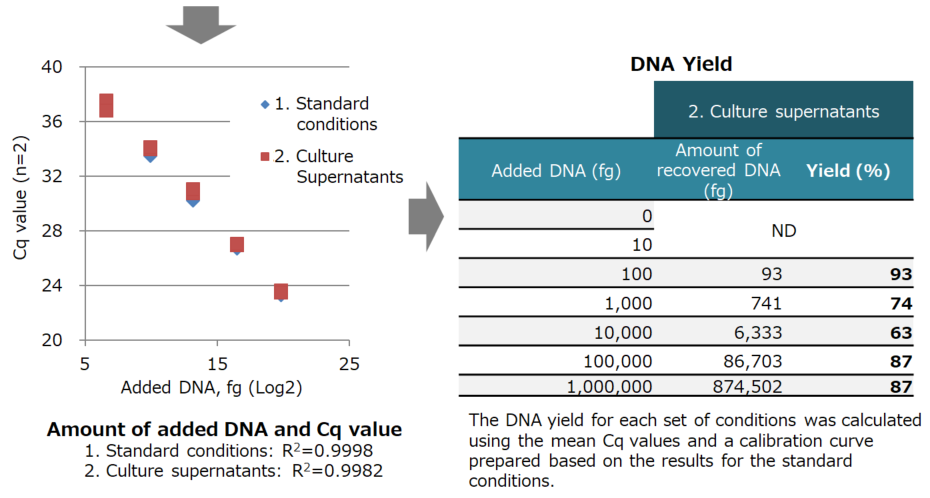
| DNA added to culture supernatants (100 fg to 1 ng) was extracted with high yield. |
This test was performed in accordance with Protocol #2 described in the manual.
Recovery test of E. coli-derived DNA
Purpose:
To examine the yields of E. coli-derived DNA.
Methods:
E. coli-derived DNA (10 fg to 1 ng) was added to purified water, and Cq values were measured before and after DNA extraction using the kit. Calibration curve was generated from mean Cq values of samples before the DNA extraction to calculate the yields after the extraction.
Samples:
Purified water containing E. coli-derived DNA
qPCR reagents:
・GeneAce SYBR® qPCR Mix α No ROX (Nippon Gene#319-07703)
・Optical Flat 8–Cap Strips for 0.2 mL tube strips/Plates (BIO-RAD#TCS0803)
・Hard-Shell® thin-wall 96-well PCR plates (BIO-RAD#HSP9601)
Results:
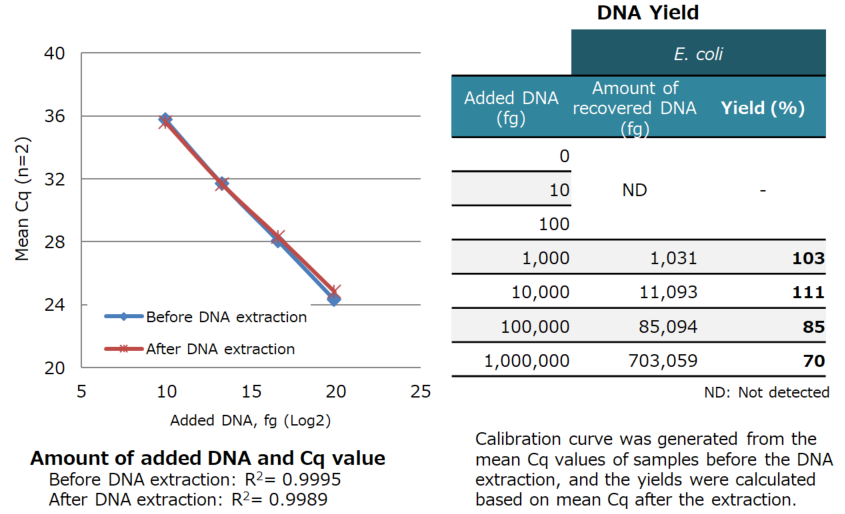
| E. coli-derived DNA added to the samples (1 pg to 1 ng) was extracted with high yield. |
This test was performed in accordance with Protocol #1 described in the manual.
Examples of using DNA Extractor® Kit

Reference
Ishizawa, M. et al., Nucleic Acids Res., 19, 5792 (1991).
DNA Extractor® WB Kit
Genomic DNA extraction from human whole blood sample
Extraction from cow/horse blood, cultured cells, and tissues is also possible
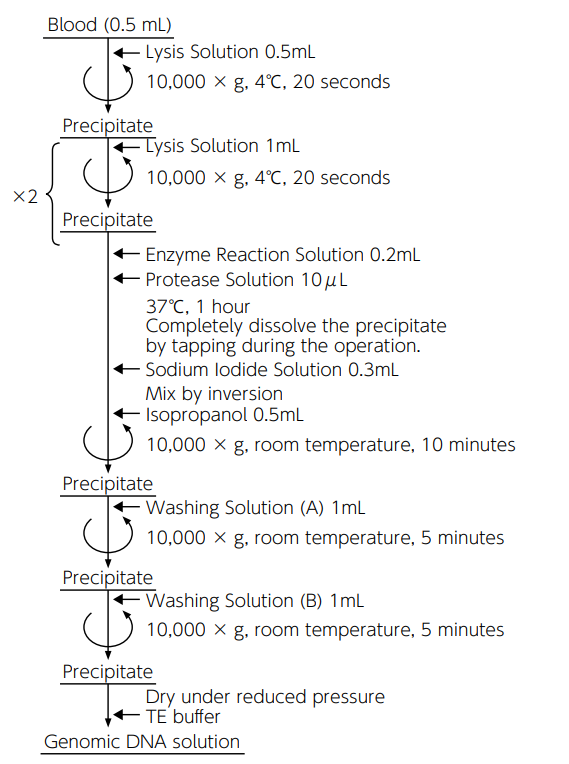
Operation time: 1.5 hours
Sample amount: 500 μL/test-
Human genomic gene analysis requires the preparation of high-molecular genomic DNA. Although many types of genomic DNA extraction methods are practiced at present, most of them use organic solvents such as phenol. Its toxicity and extraction procedures requiring time and effort are the disadvantages.
This kit is primarily for the extraction of genomic DNA from human whole blood. A high yield of DNA with high purity can be obtained in a single tube in a short time without using hazardous phenol and chloroform.Features
- A high yield rate of high-molecular DNA of over 90%
- The entire process is completed in a single tube in about 1.5 hours.
- Organic solvents such as phenol and chloroform are not required.
- Extraction from human whole blood as well as cow/horse blood, cultured cells, and tissues is also possible.
- The operation is easier than the phenol/chloroform extraction method and suitable for processing multiple samples.
- The entire procedure is performed in a single tube, reducing genomic DNA damage by mechanical cutting in operation.
Kit Contents [50 tests (sample 500 μL)]
. Lysis solution................................................................65 mL × 2
2. Enzyme reaction solution................................................10 mL × 1
3. Sodium iodide solution.....................................................15 mL × 1
4. Washing solution (A) ........................................................50 mL × 1
5. Washing solution (B) ........................................................50 mL × 1
6. Protease..............................................................................10 mg × 1
Principle of DNA extraction
i. Cell membrane and cytoplasm are destroyed by surfactant, isolating cell nuclei.
ii. The nuclear membrane and nuclear protein are decomposed by protease to expose DNA.
iii. Protein and lipids are made soluble by the action of sodium iodide, and DNA is precipitated with isopropanol.
DNA Extractor® WB Kit Data
Examples of using DNA Extractor® WB Kit
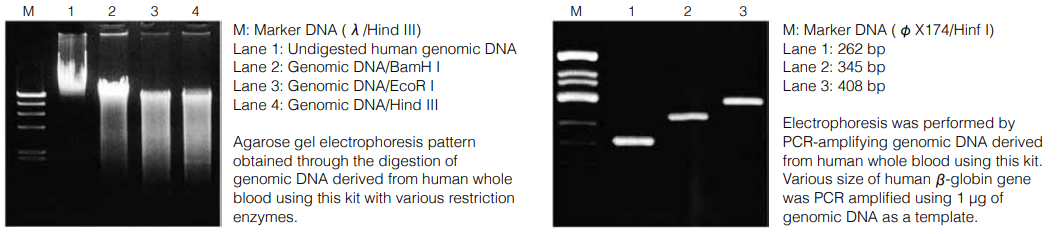
Reference
Wang, L. et al., Nucleic Acids Res., 22, 1774 (1994).
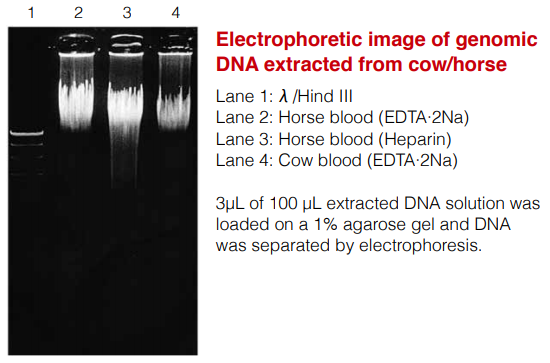
Genomic DNA extraction from cow/horse whole blood
Genomic DNA with high purity can be efficiently extracted from cow/ horse whole blood by partially changing the standard protocol. Protease treatment is performed for 2 hours for horse blood, whereas washing operation with lysis solution is repeated 4 times for cow blood, followed by treatment with protease for 4 hours.
The operation time is about 3 hours for horse blood and 5 hours for cow blood.
Blood samples used were added with EDTA·2Na or heparin as an anticoagulant agent.
-
Operation procedure
Extraction from horse blood
Treatment with protease is performed for 2 hours until there is no nuclear pellet.
Follow the standard protocol except for this operation.Extraction from cow blood
This operation, which isolate cell nuclei and wash it by adding lysis solution, is repeated 4 to 5 times, because it is difficult to remove foreign substances such as hemoglobin only with 2 operations as described in the protocol. The reference is until the red pellets become transparent.
Since pellets after centrifugation are very prone to peeling, sufficient attention is required in decantation.
Also, perform treatment with protease for about 4 hours.Yield and purity of genomic DNA extracted from cow/horse
Sample DNA yield (μg/mL blood) A260/A280 Horse (EDTA·2Na) 56.62 1.91 Horse (Heparin) 48.34 1.88 Cow (EDTA·2Na) 22.04 1.86 Notes) Each horse blood sample was collected from different horses.
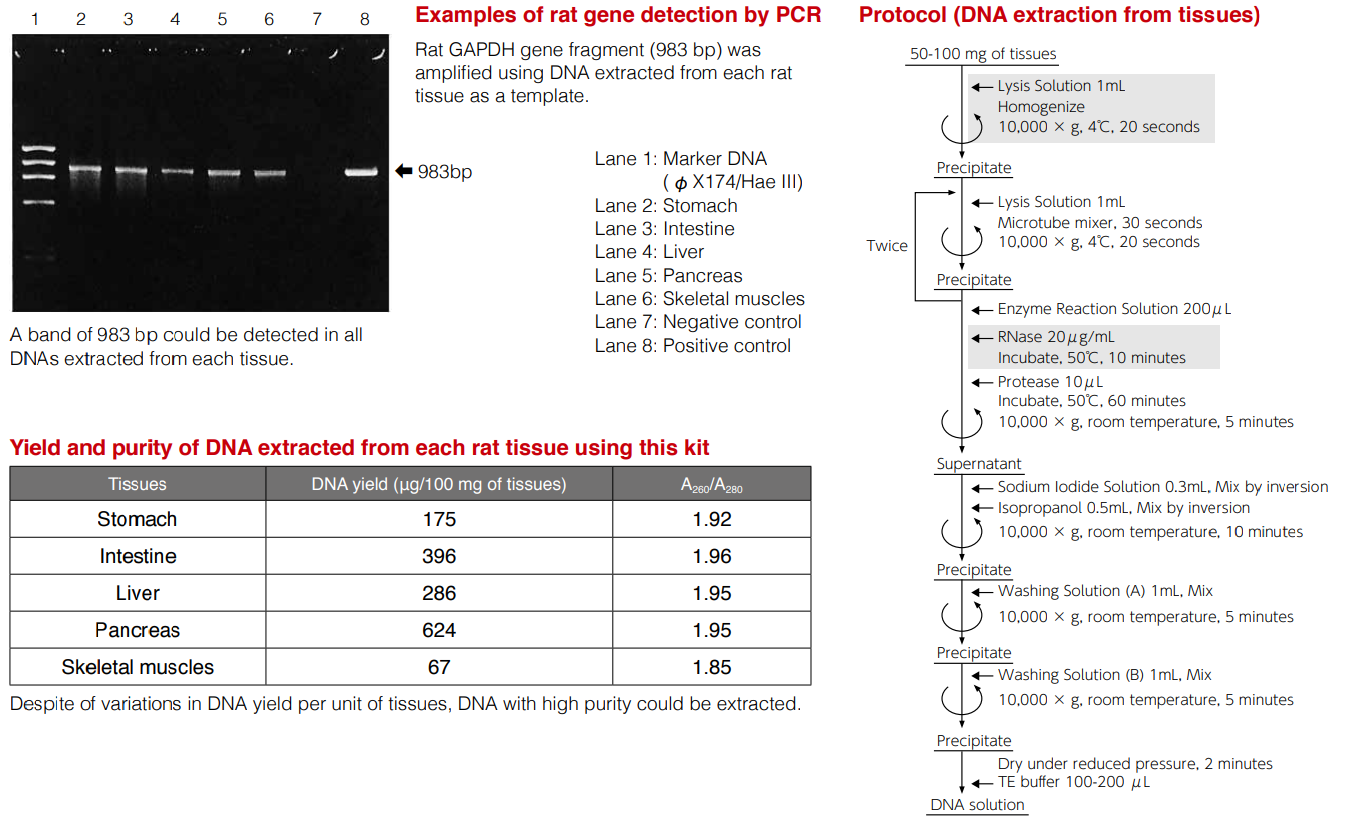
DNA extraction from tissues
Genomic DNA can be extracted from tissues by adding 2 to 3 simple operations to the standard protocol. The operation is completed in about 2 hours.
Resulting DNA has little contamination with RNA or protein and can be used in restriction enzyme treatment, PCR, Southern blotting analysis, fingerprinting, etc.
Q&A for DNA Extractor® WB Kit
Q1. What is the principle of DNA Extractor® WB Kit?
This kit is for the extraction of genomic DNA from whole blood and cultured cells. Only cell nuclei are collected by adding a lysis solution containing surfactant first. Next, the nuclear membrane and foreign substances are decomposed by protease to release DNA. Then, after protein is made soluble with sodium iodide, isopropanol is added to precipitate and collect genomic DNA only. Also, with this method, the whole DNA extraction process can be performed in a single tube.
Q2. Isn’t it contaminated with RNA?
Although contamination with RNA is rare in extraction from whole blood, cultured cells will be contaminated with RNA more or less. In this case, RNA can be almost completely removed by newly adding the treatment with RNase at 37°C for 10 minutes to the basic protocol.
Q3. The yield rate of DNA is low. Why?
The followings are the possible reasons.
1. First centrifugation operation
For the centrifugation operation at 10,000 × g for 20 seconds, perform centrifugation for 20 seconds after the centrifuge completely reached 10,000 × g. Cell nuclei will not completely detach in 20 seconds after the start button of the centrifuge is pressed; therefore, the DNA yield rate may drop by 20 to 30%. Although it varies by centrifuge, 10,000 × g is equivalent to approximately 12,000 rpm in case of a tabletop centrifuge.
2. Supernatant removing operation after centrifugation
Perform all operations by decantation. Removal with a pipette may result in a low yield of DNA.
3. DNA dissolution
As DNA in high concentration is extracted, add TE buffer (100- 200 μL) and slowly dissolve it at room temperature for 3 hours or at 4°C overnight. DNA will not be completely dissolved in a short time, which may result in an apparent low yield.
Q4. Can DNA be extracted from 100 μL of blood?
Yes. In this case, use the standard protocol by scaling it down. Also, when the amount of blood is 100 μL or less, add physiological saline to make up to 100 μL and perform the same procedure. One kit can be used 250 tests for 100 μL of blood.
Q5. Can DNA be extracted by using heparin as an anticoagulant agent instead of EDTA?
DNA can be successfully extracted at a usual concentration of heparin (10 units/mL of blood) or less, but the yield rate markedly decreases from a concentration of around 20 units/mL. Also, DNA extracted from blood added with heparin may affect restriction enzyme treatment or PCR reaction. Therefore, the use of EDTA·2Na or EDTA·2K (1 mg/mL of blood) is recommended.
Q6. Can DNA be extracted from stored blood?
DNA can be extracted successfully if blood is stored at 4°C for 3 weeks or less. However, in case of a long-term storage of 1 month or more, DNA will be gradually decomposed. Blood should be stored frozen in case of long-term storage.
Q7. What should be done without a microtube mixer?
Mix the sample by inversion for about 1 to 2 minutes.
Q8. We want to suspend the experiment.
Store the precipitate separated by centrifugation with the addition of lysis solution at -20°C.
Q9. We do not have a refrigerated centrifuge.
Extraction can be performed with a tabletop centrifuge. In that case, perform the operation quickly.
Q10. How much DNA can be extracted from 1 mL of blood?
Although there are variations by sample, approximately 20 to 70 μg of DNA can be extracted from normal humans.
Q11. Can DNA be extracted from tissues with this kit?
Yes. DNA can be extracted by fragmenting tissues by homogenization.
Q12. What is the initial cell number when extracting DNA from cultured cells?
103 to 106 cells will be enough for extraction. Cultured cells will be contaminated with RNA; therefore, before treatment with protease, add 20 μg/mL of RNase A and treat at 37°C for 10 minutes.
Q13. Can mitochondrial DNA be extracted?
Yes. Please see the following publication. Kubota, N., Hayashi, J., Inada, T. and Iwamura, Y.: Radiation Research, 148, 395 (1997).
For the extraction of mitochondrial DNA alone, the use of mtDNA Extractor® WB Kit (Wako Cat. No. 293-54401) and mtDNA Extractor® CT Kit (Wako Cat. No. 291-55301) is recommended.
Q14. What are the differences from DNA Extractor® Kit (Wako Cat. No. 295-50201)?
The purpose of use is different. DNA Extractor® Kit is for the extraction of a slight amount of viral DNA (DNA virus such as hepatitis B virus) in serum and a slight amount of fungus-derived DNA in biological products, while DNA Extractor® WB Kit specifically extracts genomic DNA from whole blood and cultured cells.
Q15. How should protease be stored after prepared?
It is stable at -20°C for 6 months.
Q16. What are the differences from DNA Extractor® WB-Rapid Kit?
DNA Extractor® WB-Rapid Kit is an improved product to enable DNA extraction in about 20 minutes. It is suitable for treating many samples in a small volume.
Q17. Some insoluble matters still remain after treatment with protease at 37°C for 1 hour. What should be done?
Failure to digest in an hour is considered attributable to insufficient washing with lysis solution in the first step. When cell nuclei are precipitated in the beginning, repeat washing until red pigment derived from hemoglobin is eliminated.
Q18. When DNA extraction from cultured cells was performed, white insoluble matters emerged at the time of adding sodium iodide. Should we move on to the next step after removing these matters?
Insoluble matters may be observed depending on types of cultured cells. In this case, there is no problem to move to the next step, washing operation with washing solution (A), without removing the matters. Insoluble matters will be dissolved by adding washing solution (A). If the purity of resulting DNA is low, it is recommended to repeat the operation of cell nuclei precipitation by lysis solution.
Q19. The A260/A280 ratio of DNA is 1.8 or below. What should be done?
Sodium iodide may be remained in DNA. In this case, repeat washing with washing solution (B).
Q20. Is there any reference literature?
See the following reference: Wang, L., Hirayasu, K., Ishizawa, M. and Kobayashi, Y.: Nucl. Acids Res., 22, 1774 (1994).
DNA Extractor® SP Kit
Genomic DNA extraction from serum and plasma
-
Method
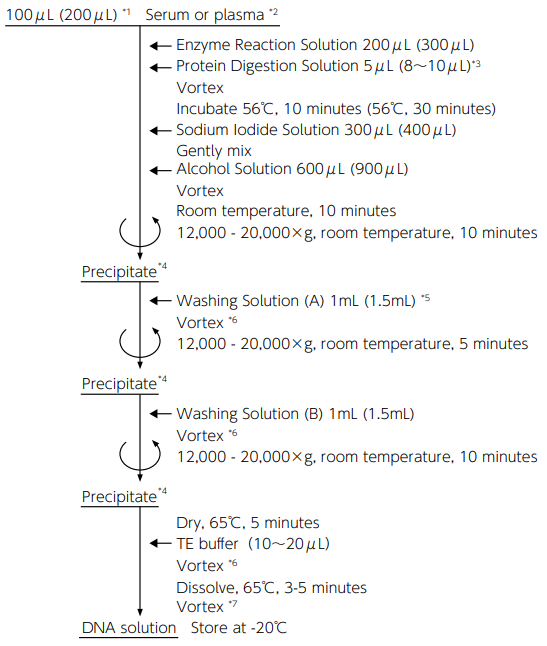
Operation time: 1 hour or more
Sample amount: 100 μL/test*1 The protocol starting with 200 μL of sample is shown in the parentheses.
*2 Handle serum (plasma) samples on the ice. Add enzyme reaction solution as early as possible so that DNase in serum (plasma) will not be activated.
*3 Take it out of the kit and transfer it on the ice before use.
*4 Discard the supernatant, place the tube upside down on a paper towel, and remove remaining supernatant by pressing the mouth of the tube to the paper towel.
*5 After washing solution (A) is added, the sample can be stored for a long term at -20°C.
*6 Mix well until the precipitate peels off from the wall of the tube.
*7 Dissolve completely until there is no precipitate. -
This kit, an improved version of DNA Extractor® Kit, is a DNA extraction kit optimized for the extraction of DNA fragments in serum or plasma. It can obtain a very high DNA yield, so is useful as a pretreatment reagent to detect and analyze the target gene with a high sensitivity. Also, this product uses the sodium iodide method without using organic solvents such as phenol and chloroform.
Features
- DNA can be obtained at a high yield rate from a small amount (100 μL) of serum and plasma sample.
- “Sodium iodide method” achieving nearly 100% yield rate is adopted.
- Organic solvents such as phenol and chloroform are not required.
- No use of solid phase extraction method using silica carrier realizes a high yield of DNA.
- High-quality DNA suitable for PCR can be obtained.
- Lipids, etc., derived from blood sample can be completely removed with specially prepared alcohol solution included in the kit.
- The entire operation is completed in a single tube.
Kit Contents [50 tests (sample 100 μL)]
1. Enzyme reaction solution..................................................10 mL × 1
2. Protein digestion solution.............................................. 250 μL × 1
3. Sodium iodide solution.....................................................15 mL × 1
4. Alcohol solution..................................................................30 mL × 1
5. Washing solution (A) ........................................................50 mL × 1
6. Washing solution (B) ........................................................50 mL × 1Principle of DNA extraction
i. Protein derived from serum/plasma is decomposed by protease.
ii. Protein and lipids derived from serum/plasma are made soluble by the action of sodium iodide and removed with alcohol solution included in the kit to precipitate DNA.Reference
1) Ishizawa, M. et al., Nucleic Acids Res., 22, 1774 (1994).
2) Sozzi, G. et al., Clin. Cancer Res., 5, 2689 (1999).
3) Silva, J. M. et al., Cancer Res., 59, 3251 (1999).
4) Shao, Z. M. et al., Clin. Cancer Res., 7, 2222 (2001).
DNA Extractor® SP Kit Data
Examples of using DNA Extractor® SP Kit
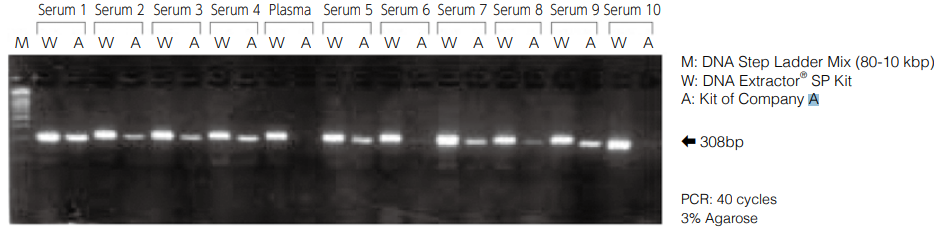
Amplification of p53-Exon 5 region of DNA extracted from human serum and plasma
Using this kit, DNA was extracted from human serum (10 samples) and human plasma (1 sample) and dissolved in 20 μL of TE buffer (pH 8.0) to prepare DNA samples. The p53-Exon 5 region (308 bp) was amplified from 5 μL of each sample. The kit was compared with DNA extraction kit (Company A) which is based on the extraction principle with silica carrier (centrifugal filtration method) as control.
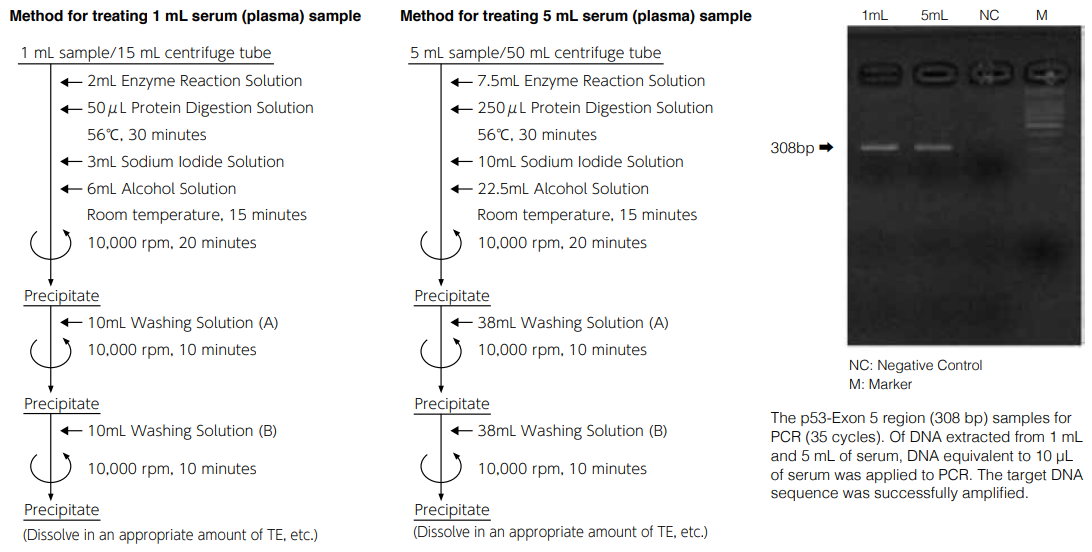
Method of extracting DNA from 1 to 5 mL sample using DNA Extractor® SP Kit
After dissolving in TE buffer, insoluble matters were precipitated and absorption was detected in the background (absorbance 320 nm), indicating lower purity than the standard method (extraction from 100- 200 μL). However, amplification by PCR can be performed successfully.
DNA Extractor® TIS Kit
DNA extraction for 8-OHdG measurement
DNA extraction from human and animal parenchyma tissues
-
Methods
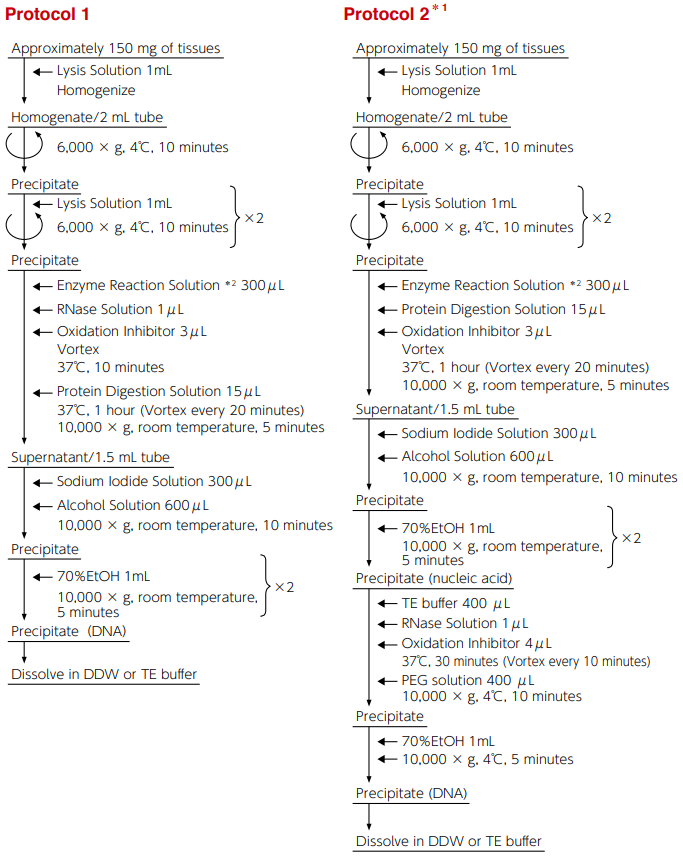
-
The sodium iodide method, the basic principle of DNA Extractor® Kit series, is known as a DNA extraction method causing relatively little oxidation during operations. This kit further inhibits oxidation of DNA with the use of an oxidation inhibitor and is useful for the measurement of 8-OHdG (8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine), an oxidative stress marker.
Features
- Useful for the detection and measurement of oxidative stress markers.
Sodium iodide method causes little oxidation of DNA during operation. The use of oxidation inhibitor further inhibits oxidation of DNA. - Organic solvents such as phenol and chloroform are not required.
- Suitable for DNA extraction from human and animal parenchyma tissues.
Kit Contents [50 tests (sample 100μL)]
1. Lysis solution..................................75 mL × 2
2. Enzyme reaction solution.................15 mL × 1
3. RNase solution .................................50 μL × 1
4. Protein digestion solution.................750 μL× 1
5. Oxidation inhibitor ...........................350 μL × 1
6. Sodium iodide solution......................15 mL × 1
7. Alcohol solution.................................30 mL × 1
8. PEG solution ....................................20 mL × 1 - Useful for the detection and measurement of oxidative stress markers.
Protocol 1 is a simplified method where treatment with RNase is performed before treatment with protease.
Protocol 2 is a method to collect DNA by polyethylene glycol (PEG) precipitation method where protease treatment and RNase treatment are performed in different processes to enhance the purity of DNA.
There is no difference in the amount of 8-OHdG between the two methods, and the levels of DNA oxidation inhibition are comparable.
*1 DNA purity can be enhanced with this protocol.
*2 If there is any deposit in enzyme reaction solution, completely dissolve the deposit by heating it to 37°C or returning it to room temperature and mix before use.
DNA Extractor® TIS Kit Data
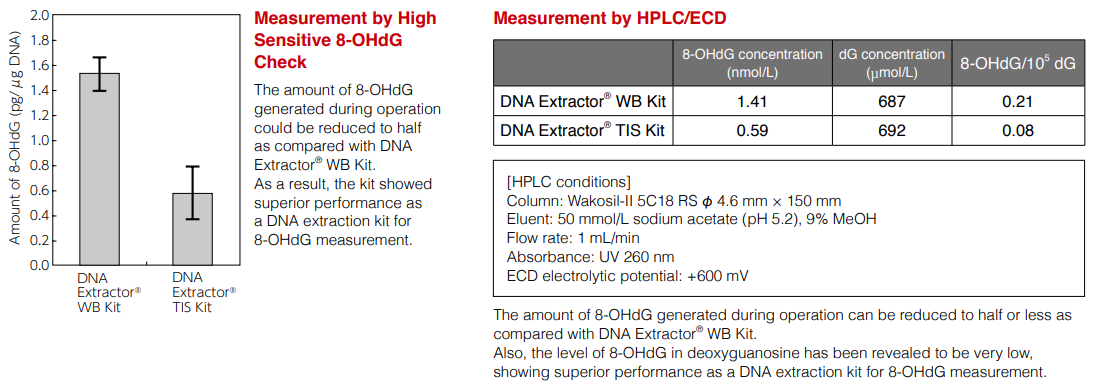
DNA extraction from mouse liver and 8-OHdG measurement
DNA was extracted from mouse liver (the same mouse) using DNA Extractor® WB Kit [Wako Cat. No. 291-50502] and DNA Extractor® TIS Kit [Protocol 1]. Resulting DNA was treated with nuclease P1, the amount of 8-OHdG was measured by High Sensitive 8-OHdG Check [Wako Cat. No. 307-07921] and HPLC/ ECD, and two methods were compared.
DNA Extractor® FM Kit
DNA extraction from forensic samples
(DNA extraction from trace amount of samples such as body hairs, blood stains, saliva stains, and nails)
This kit is to extract trace amount of DNA from forensic samples such as body hairs (hairs), blood stains, saliva stains, and nails used for personal identification. Although a low yield of DNA becomes an obstacle in determination in some cases, this kit rapidly dissolves samples and efficiently collects DNA suitable for the amplification of STR (short tandem repeat) and hypervariable region of mitochondrial DNA. Also, this product uses the sodium iodide method without using organic solvents such as phenol and chloroform.
-
Protocol for DNA recovery from human hairs
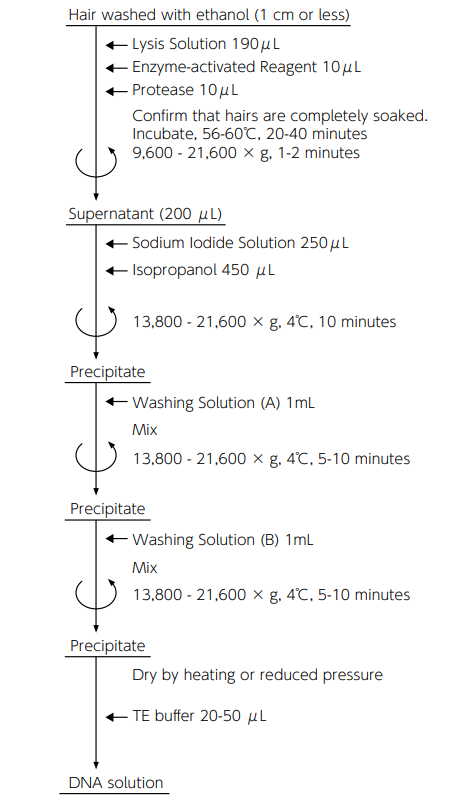
Reference
Wang, L. et al., Nucleic Acids Res., 22, 1774 (1994).
-
Features
- DNA can be extracted from low-soluble and trace amount samples such as body hairs (hairs), blood stains, and nails.
- DNA can also be extracted from hair shaft.
- No solid-phase extraction reduces loss of trace amount DNA by adsorption to the carrier.
- Organic solvents such as phenol and chloroform are not required.
- DNA suitable for PCR can be obtained.
Kit Contents [50 tests]
1. Lysis solution..................................................................9.5 mL × 1
2. Enzyme activated reagent (EAR)..................................80 mg × 1
3. Reconstitution solution for EAR.....................................500 μL× 1
4. Protease...........................................................................10 mg × 1
5. Sodium iodide solution.................................................. 12.5 mL× 1
6. Washing solution (A) ........................................................50 mL × 1
7. Washing solution (B) ........................................................50 mL × 1Sample volume
- Body hair: 1 cm or less. Two hairs or less (2 cm or less) should be used if possible due to possible inhibition of PCR reaction by melanin.
- Spots such as blood and saliva stains:
Cut into a size of about 5 mm × 5 mm.
Use up to 2 pieces of a 5 mm × 5 mm spot per test. - Nail: Cut a fingernail of 0.5 mg or less (size of approximately 1 mm × 1 mm) into pieces of about 0.5 mm × 1 mm. DNA extraction will become easier with smaller pieces.
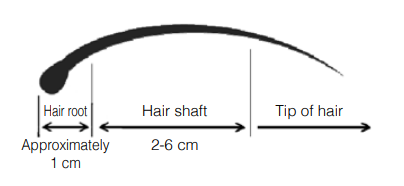
DNA Extractor® FM Kit Data
Nucleic acid amplification reaction in hypervariable region of mitochondrial DNA (nucleotide positions 16159-16401) by using DNA extracted from hair root.
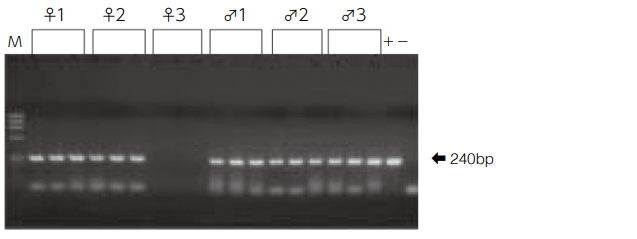
- The lengths of hair shaft are all 0.5 cm, 1.0 cm, and 1.5 cm from the left of the lane for males and females.
The same band (240 bp) was detected in all subjects except for female 3. Female 3 has dyed permed hair.
Amplification of hypervariable region of mitochondrial DNA by using DNA extracted from hair dyed with different types of dyes.
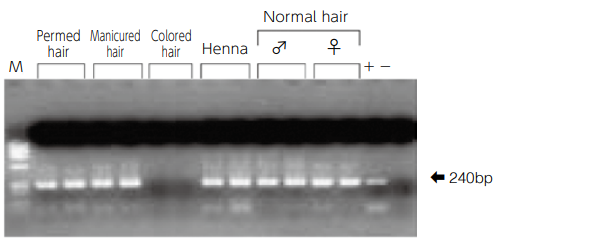
- The hair lengths are all 0.5 cm and 1.0 cm from the left of the lane. The same band (240 bp) was detected in differently dyed hairs except for hairs dyed with hair color.
For hairs dyed with hair color, DNA itself in hairs may be affected by decomposition, etc., or the dye may have PCR inhibitory effect.
mtDNA Extractor™ CT Kit
Mitochondrial DNA extraction from mammalian tissues and cells, quickly and easily
Mitochondrial DNA extraction from compound feeds
-
Procedure
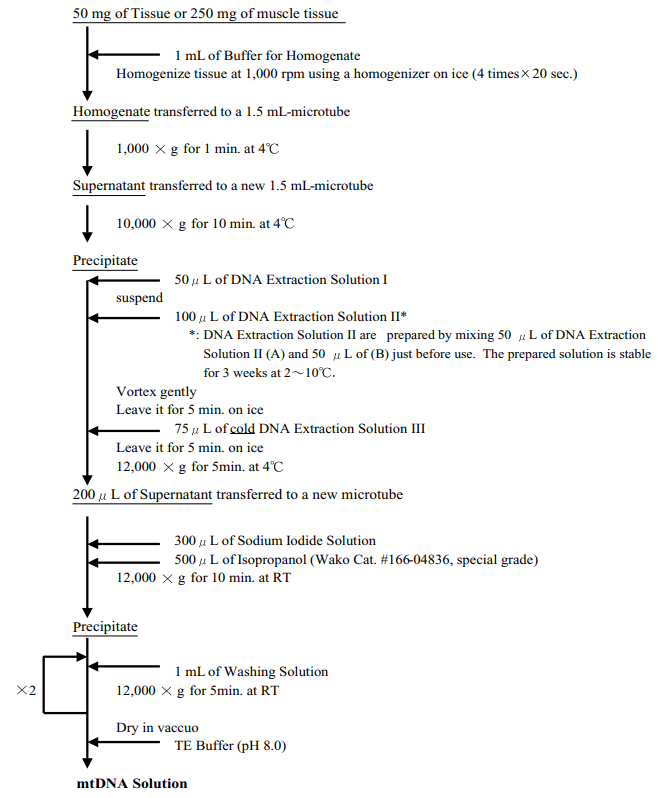
-
Features
- mtDNA detected by agarose gel electrophoresis can be extracted from 50 to 250 mg of tissue.
- The extracted mtDNA can be used in PCR and restriction enzyme digestion.
- mtDNA can also be extracted from frozen tissues.
- Organic solvents such as phenol or chloroform are not required.
Principle
- Cell lysate is centrifuged to obtain the mitochondrial fraction.
- Genomic DNA in the mitochondrial fraction is removed by alkaline denaturation and precipitation using the alkaline-SDS method, which is used for plasmid DNA purification, and mitochondrial DNA, which is circular DNA, is recovered.
- Contaminating proteins are solubilized with sodium iodide, and mitochondrial DNA is purified with Washing Solution.
mtDNA Extractor™ CT Kit Data
Extraction of mitochondrial DNA from fresh and frozen mouse tissues
-
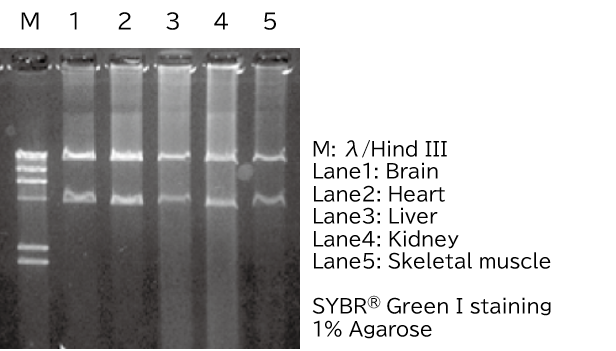
Half of the mtDNA extracted from fresh mouse tissues was digested with Pst I and confirmed by agarose gel electrophoresis. -
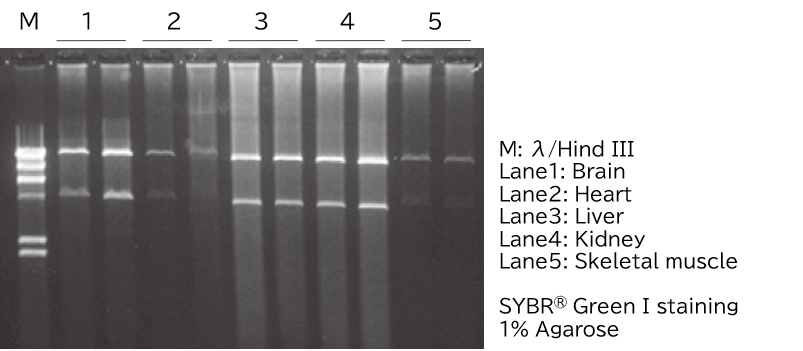
Half of the mtDNA extracted from frozen mouse tissues was digested with Pst I and confirmed by agarose gel electrophoresis.
Precautions
Since this kit is designed to extract small amounts of mitochondrial DNA, we recommend GelRed™ staining to detect mitochondrial DNA.The mitochondrial DNA cannot be detected by ethidium bromide staining.
8-OHdG Assay Preparation Reagent Set
When measuring 8-OHdG in tissues, extracted DNA from tissues need to be hydrolyzed. This product is a reagent kit including enzyme, buffer, etc., used in pretreatment of 8- OHdG measurement.
Add a specified amount of each reagent to DNA samples for measurement to promote reaction, thereby reducing variability in the nuclease treatment status (mononucleotide release) and realizing stable measurement of 8-OHdG.
Method

Kit Contents [50 tests]
1. Acetic acid buffer..................................................... 950 μL × 1
2. Nuclease P1..............................................................500 units × 1
3. Tris buffer ....................................................................... 1 mL × 1
4. Alkaline phosphatase solution..........................................50 μL× 1
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.
The prices are list prices in Japan.Please contact your local distributor for your retail price in your region.



