DNA ExtractorR Kit
- for Genetic Research
- Manufacturer :
- FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation
- Storage Condition :
- Keep at RT.
- GHS :
-
- Structural Formula
- Label
- Packing
- SDS
|
Comparison
|
Product Number
|
Package Size
|
Price
|
Inventory
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
50Tests
|
|
In stock in Japan |
Please check here for notes on products and prices.
Document
Kit component
50 tests
| Sodium Iodide Solution | 1 x 26 mL |
|---|---|
| Sodium N-Lauryl Sarcosinate Solution | 1 x 1.2 mL |
| Washing Solution (A) | 1 x 42 mL |
| Washing Solution (B) | 2 x 40 mL |
| Glycogen Solution | 1 x 0.1 mL |
Outline
Residual DNA testing for vaccines and biopharmaceuticals
This is sodium iodide method based DNA extraction kit to isolate residual host cell DNA from biological samples. This kit follows the residual DNA extraction protocols described in the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) 43-NF38, <509> Residual DNA Testing.
The isolated DNA can be used for qPCR. This is suitable for the residual DNA testing derived from host cells including CHO cells, E.coli and yeast.
This kit can also be used for DNA isolation for Threshold® System provided by Molecular Devices, LLC, which can quantify total DNA regardless of the origin.
Virus DNA quantification in human serum
This can be used for virus DNA isolation from human serum.
Features
- Efficient extraction of trace DNA (100-1,000 fg)
- Perform in a single tube for whole process
- Extraction complete in 60-90 minutes
- Suitable for quantification by qPCR and Threshold® System (Molecular Devices, LLC)
- Pretreatment protocol for samples containing high concentration protein
Basic operation of DNA extraction by sodium iodide method
- Add sodium iodide, a chaotropic ion and detergents to solubilize protein and lipids.
- Add 2-propanol and DNA is coprecipitated with glycogen.
- Collect DNA pellets.
Application
Spike and recovery test of CHO cell-derived DNA
Examined the recovery rate of CHO cell-derived DNA from spiked culture supernatant to evaluate the extraction efficiency.
Methods
- Added 10 fg to 1 ng of CHO cell-derived DNA to culture supernatant of PANC-1 cells.
- Extracted DNA from the supernatant with this kit following the manual.
-Protocol: Protocol #2
-Pretreatment: None - Conducted qPCR and measured the Cq value of the extracted DNA. The same measurement was conducted for purified water spiked with CHO cell-derived DNA without DNA extraction, this was used as standard condition.
- Create a standard curve using the mean Cq values of the standard condition, and calculated the recovery rate.
Samples
- Purified water containing CHO cell-derived DNA (no DNA extraction): Standard conditions
- DNA extracted from the culture supernatants of PANC-1 cells containing CHO cell-derived DNA by this kit: Culture supernatants
qPCR reagents
- GeneAce SYBR® qPCR Mix α No ROX (Nippon Gene#319-07703)
- Optical Flat 8–Cap Strips for 0.2 mL tube strips/Plates (BIO-RAD#TCS0803)
- Hard-Shell® Thin-wall 96-well PCR plates (BIO-RAD#HSP9601)
Results
| 1. Standard conditions | 2. Culture supernatants | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spike DNA (fg) | Cq 1 | Cq 2 | Mean | Cq 1 | Cq 2 | Mean |
| 0 | ND | |||||
| 10 | ||||||
| 100 | 36.89 | ND | 36.89 | 37.44 | 36.73 | 37.09 |
| 1,000 | 33.44 | 33.91 | 33.68 | 33.94 | 34.09 | 34.01 |
| 10,000 | 30.23 | 30.17 | 30.20 | 30.72 | 30.96 | 30.84 |
| 100,000 | 26.74 | 26.68 | 26.71 | 26.90 | 27.03 | 26.96 |
| 1,000,000 | 23.39 | 23.28 | 23.33 | 23.61 | 23.48 | 23.54 |
ND: Not detected
| Good extraction efficiency of CHO-derived DNA from culture supernatant within the range of 100 fg to 1 ng. |
Spike and recovery test of E. coli-derived DNA
Examined the recovery rate of E. coli-derived DNA from spiked sample to evaluate the extraction efficiency.
Methods
- Added 10 fg to 1 ng of E.coli-derived DNA to purified water.
- Extracted DNA from the spiked sample with this kit following the manual.
-Protocol: Protocol #1 - Conducted qPCR and measured the Cq value of the extracted DNA. The same measurement was conducted for the spiked sample before DNA extraction.
- Create a standard curve using the mean Cq values of the spiked samples before extraction, and calculated the recovery rate after the extraction.
Samples
Purified water spiked with E. coli-derived DNA
qPCR reagents
- GeneAce SYBR® qPCR Mix α No ROX (Nippon Gene#319-07703)
- COptical Flat 8–Cap Strips for 0.2 mL tube strips/Plates (BIO-RAD#TCS0803)
- CHard-Shell® thin-wall 96-well PCR plates (BIO-RAD#HSP9601)
Results
| Good extraction efficiency of E.Coli-derived DNA within the range of 1 pg to 1 ng. |
Spike and recovery test from Human serum sample
λ/HindⅢ 10 to 1,000 pg was labeled with 32P and added to 100 μL of human serum. DNA was extracted using this kit and the recovery rate was calculated.
Reference
Ishizawa, M. et al., Nucleic Acids Res., 19, 5792 (1991).
| Good extraction efficiency from serum sample. |
Detection of virus DNA from human serum by PCR
Serum containing hepatitis B virus (HBV) was diluted in stages. DNA was extracted using this kit and the phenol method. HBV-DNA was amplified with PCR, and DNA was detected using agarose gel electrophoresis.
Lane 1: Marker DNA(φⅩ174 DNA/HaeⅢ)
| HBV-DNA was detected with higher specificity and sensitivity using this kit than phenol method. |
Evaluation For Antibody Drug
DNA extraction from high concentration protein-containing solution
Conducted DNA spike and recovery test from various concentration of IgG solution.
Methods
- Added CHO cell-derived DNA (final DNA concentration: 2 pg/mL) to 10 – 100 mg/mL of IgG solution.
- Extracted DNA from the spiked IgG solution with this kit following the manual.
-Protocol: Protocol #2
-Pretreatment: Protocol for the sample containing more than 2 mg/mL of protein (Proteinase K treatment) - Measured the recovery rate by qPCR
Results
Recovery rate of CHO cell-derived DNA from IgG solution
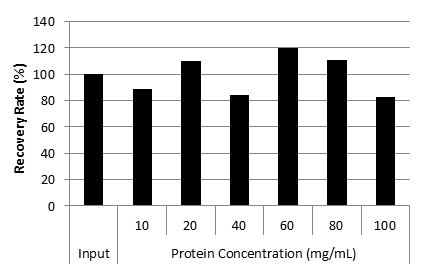
Cq value of IgG solution at various concentration
| Sample | Input | Protein Concentration (mg/mL) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 | ||
| Cq | 31.596 | 31.566 | 31.351 | 31.726 | 31.502 | 31.282 | 31.658 |
| 31.599 | 31.608 | 31.774 | 31.787 | - | 31.485 | 31.660 | |
| 31.338 | 31.861 | 31.500 | 31.850 | 31.560 | 31.369 | - | |
| Average Cq | 31.511 | 31.678 | 31.542 | 31.788 | 31.531 | 31.379 | 31.659 |
| Difference of Cq | 0 | -0.167 | 0.136 | -0.246 | 0.257 | 0.152 | -0.280 |
| Power | 1 | 0.891 | 1.099 | 0.843 | 1.195 | 1.111 | 0.824 |
| Recovery Rate (%) | 100 | 89.1 | 109.9 | 84.3 | 119.5 | 111.1 | 82.4 |
| Good DNA extraction efficiency from solution containing high concentration protein (100 mg/mL). |
DNA extraction from antibody drug-mimic solution
Conducted DNA spike and recovery test from IgG solutions made of various types of buffers generally used in antibody drug and from IgG solutions containing various additives used in antibody drug.
Methods
- Made antibody drug-mimic solutions by adding 20 mg/mL of IgG to various buffers generally used in antibody drug (Table 1. ①-⑥) and to phosphate buffer containing various additives (Table 2. ①-⑩). Then add CHO cell-derived DNA (final DNA concentration: 20 pg/mL) to those antibody drug-mimic solutions.
- Extracted DNA from the spiked samples with this kit following the manual.
-Protocol: Protocol #2
-Pretreatment: Protocol for the sample containing more than 2 mg/mL of protein (Proteinase K treatment) - Measured the recovery rate by qPCR.
-
Table 1. Buffer Composition
No. Buffer Composition ① 10mM PB pH6.0, 0.15M NaCl, 2mM EDTA ② 10mM PB pH7.4, 0.15M NaCl, 2mM EDTA ③ 50mM NaOAc pH5.2, 0.15M NaCl, 2mM EDTA ④ 10mM PB pH6.0, 2mM EDTA ⑤ 10mM PB pH7.4, 2mM EDTA ⑥ 50mM NaOAc pH5.2, 2mM EDTA -
Table 2. Additive-containing Buffer
Buffer: 10mM PB pH6.0, 0.15M NaCl, 2mM EDTA
No. Additive & Concentration ① Sucrose (10w/v%) ② Trehalose Dihydrate (10w/v%) ③ D(-)-Mannitol (10w/v%) ④ D(-)-Sorbitol (10w/v%) ⑤ D(+)-Maltose Monohydrate (10w/v%) ⑥ L(+)-Arginine Hydrochloride (1w/v%) ⑦ L‐Histidine (1w/v%) ⑧ Glycine (1w/v%) ⑨ Polyoxyethylene(20) Sorbitan Monooleate (Tween80) (0.5v/v%) ⑩ Polyoxyethylene(20) Sorbitan Monolaurate (Tween20) (0.5v/v%)
Results
DNA Recovery Rate from each buffer
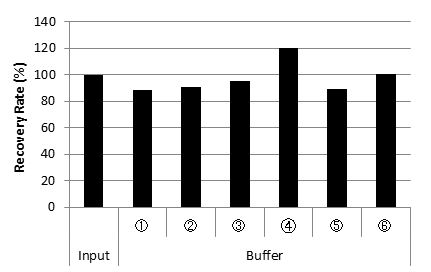
Cq values of each buffer
| Sample | Input | Buffer | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| Cq | 31.473 | 31.693 | 31.544 | 31.218 | 31.058 | 31.595 | 31.181 |
| 31.364 | 31.196 | 30.973 | 31.568 | 31.085 | 31.343 | 31.112 | |
| 31.045 | 31.530 | 31.787 | 31.315 | 30.942 | 31.452 | 31.558 | |
| Average Cq | 31.294 | 31.473 | 31.435 | 31.367 | 31.028 | 31.463 | 31.284 |
| Difference of Cq | 0 | -0.179 | -0.141 | -0.073 | 0.266 | -0.169 | 0.010 |
| Power | 1 | 0.883 | 0.907 | 0.951 | 1.203 | 0.890 | 1.007 |
| Recovery Rate (%) | 100 | 88.3 | 90.7 | 95.1 | 120.3 | 89.0 | 100.7 |
Cq values of each additive-containing buffer
| Sample | Input | Additive-containing buffer | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ① | ② | ③ | ④ | ⑤ | ⑥ | ⑦ | ⑧ | ⑨ | ⑩ | ||
| Cq | 31.473 | 31.826 | 31.327 | 30.907 | 31.143 | 31.071 | 31.525 | - | 31.525 | 31.013 | 31.086 |
| 31.364 | 31.194 | 30.991 | 31.759 | 31.103 | 31.279 | 31.068 | 31.442 | 31.203 | 31.340 | 30.870 | |
| 31.045 | 30.703 | - | 31.009 | - | 30.978 | 31.225 | 31.479 | 30.757 | 31.020 | 31.020 | |
| Average Cq | 31.294 | 31.241 | 31.159 | 31.225 | 31.123 | 31.109 | 31.273 | 31.461 | 31.162 | 31.124 | 30.992 |
| Difference of Cq | 0 | 0.053 | 0.135 | 0.069 | 0.171 | 0.185 | 0.021 | -0.167 | 0.132 | 0.170 | 0.302 |
| Power | 1 | 1.037 | 1.098 | 1.049 | 1.126 | 1.137 | 1.015 | 0.891 | 1.096 | 1.125 | 1.233 |
| Recovery Rate (%) | 100 | 103.7 | 109.8 | 104.9 | 112.6 | 113.7 | 101.5 | 89.1 | 109.6 | 112.5 | 123.3 |
DNA Recovery Rate from each additive-containing buffer
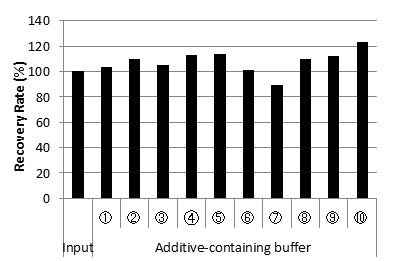
| Good DNA extraction efficiency from various buffer and additive. |
Overview / Applications
| Outline | This is for research use only. Do not administer it to human. Molecular Biology-DNA Extraction Kits. Detects and quantitates contaminant DNA in serum and residual DNA in biopharmaceuticals. Employs a new extraction procedure for DNA purification from a single tube. This procedure, using Sodium Iodide (NaI) as a chaotropic agent, realizes DNA isolation of both high quality and high recovery from biological fluids without the use of phenol or chloroform. Complex and laborious manipulations are avoided when using this kit. In addition, this kit has a modified application for use with Molecular Devices' Threshold(TM) System. PRINCIPLE of DNA EXTRACTION: A high concentration of chaotropic reagent, NaI, and an anionic detergent participate in solubilization of the proteins and lipids contained in biological samples. After addition of isopropanol to the mixture, nucleic acids are co-precipitated with polysaccharide glycogen as a carrier, while other components remain soluble in the solution phase. Ref.: Ishizawa, M., Kobayashi, T. and Matsuura, S., ''Simple procedure of DNA Isolation from Human Serum'', Nucleic Acids Res., 19, 5792 (1991). Hui Cai, Xuelin Gu, Mary S. Scanlan, and ChrisR. Lively,: Development of a quantitative PCR assay for residual mouse DNA and comparison of four sample purification methods for DNA isolation., Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 55, 71-77 (2011). This method was listed on USP39-NF34, page 1413/Pharmacopeial Forum. Vol.41(4). |
|---|---|
| Purpose | DNA extraction. |
Property
Manufacturer Information
Alias
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.
The prices are list prices in Japan.Please contact your local distributor for your retail price in your region.









