AI Driven Drug Discovery Service

drug2drugs® is an AI and chemical simulation-based drug discovery support service which generates many candidate compounds with different scaffolds from the structural information of one active compound.
drug2drugs® applies our proprietary AI-AAM (amino acid mapping) method, which is an innovative in silico method that combines amino acid interaction mapping with scaffold-hopping to identify structurally diverse compounds with improved drug properties and pharmacological activity.
Harness the potential of drug2drugs® to discover compounds with superior bioactivity, efficacy, thermal stability, and synthesizability while minimizing drug toxicity. drug2drugs® opens new possibilities, enabling you to overcome IP limitations and even potentially transform peptides into small-molecule therapeutics.
Key features
- Streamlined Lead Optimization: Our proprietary AI-AAM method, developed by FUJIFILM Analysis Technology Center, simplifies the lead optimization process, requiring only the structural information of the bioactive region of the compound.
- Efficient drug discovery & development: Accelerate your drug development pipeline with our ability to quickly generate backup compounds and refine many aspects of existing drug molecules.
- Confidential and secure: We do not need the target information of the protein, and we require little to no experimental data from the client to acquire results. We also prioritize the confidentiality and security of your data throughout the process.
We have an on-demand webinar for drug2drugs AI-AAM available on Drug Discovery World. If you are interested in viewing this webinar, you may access it here.
How to increase active compounds with AI-AAM®
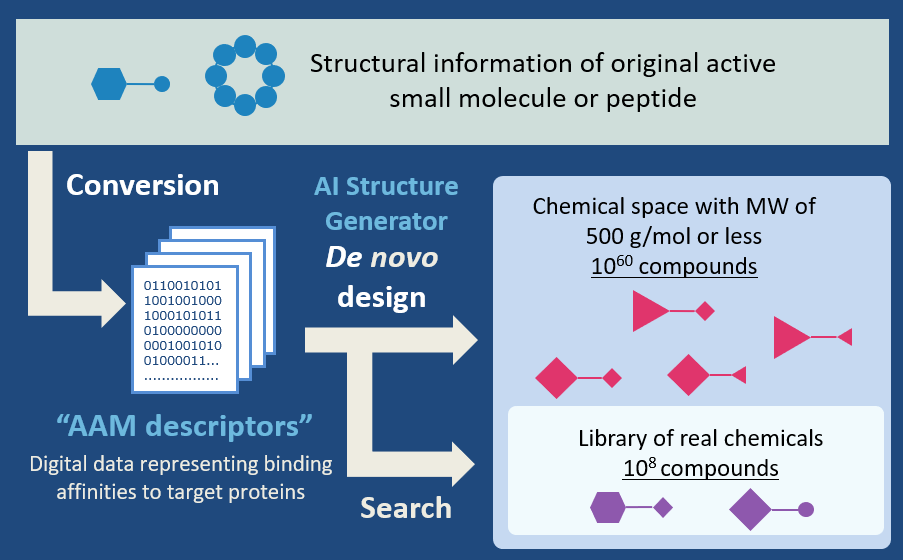
AI-AAM® that consisting of AAM descriptors and AI structure generator
1. AAM (Amino-Acid Mapping) descriptors[1]
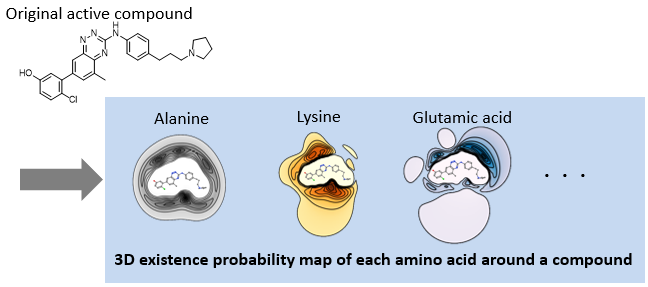
AAM descriptors are the set of the 3D existence probability map of 20 amino acids around each compound computed by chemical simulations. Two compounds with the same AAM descriptors but different scaffolds interact with the same amino acids and bind to proteins with the same binding pattern.
2. De novo design by our AI[2]
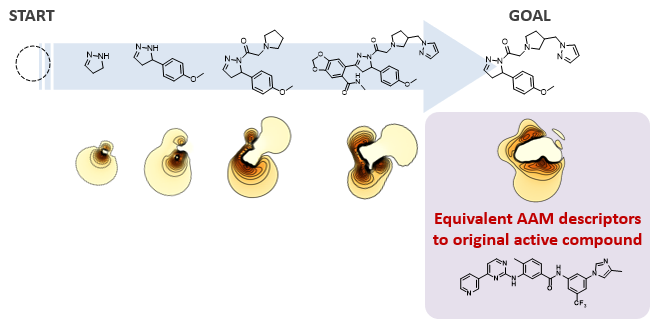
Our developed AI automatically designs chemical structures with completely different scaffolds but equivalent AAM descriptor. Since the initial structure is not required and the design is performed at the atomic level, about 1060 compounds can be designed. The compounds designed by our AI exhibit high thermal stability.
Experimental results of scaffold hopping of active compounds of a small molecule or a peptide using AI-AAM®
1. Scaffold hopping between small molecules[3]
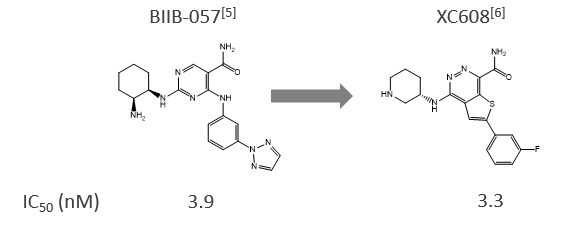
From the structural information of BIIB-057, XC608 was selected as the compound with the most similar AAM from approximately 12 million compounds in our chemical library within a month.
2. Scaffold hopping from a peptide to a small molecule[4]
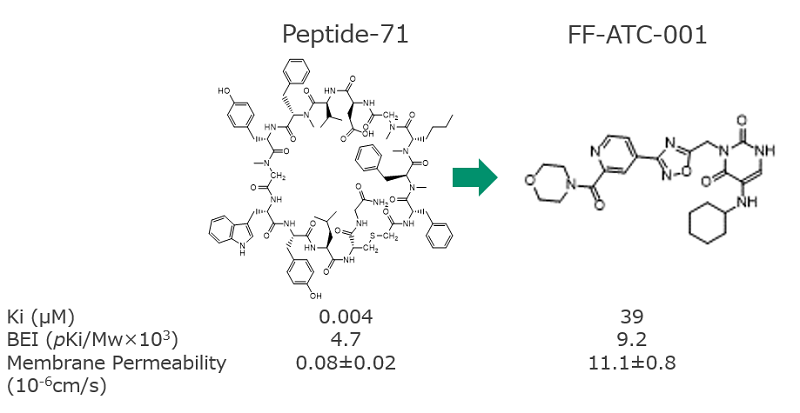
From the binding conformation and site of the Peptide-71, the partial structure of Peptide-71 in contact with PD-L1 when binding to the protein, the small molecule compound FF-ATC-001 was also designed within a month.
| [1]JP6826672B2, [2]JP7191969B2, JP7190498B2, JP7116186B2, [3] CBI Annual Meeting 2022, P08-14; bioRxiv (2023), doi:https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.03.547598, [4] CBI Annual Meeting 2022, P08-07, Excellent Poster Awards, [5]WO 2009/136995, [6]WO 2011/035077, [7]US20140294898 A1 |
Correlations between binding affinity and AAM similarity
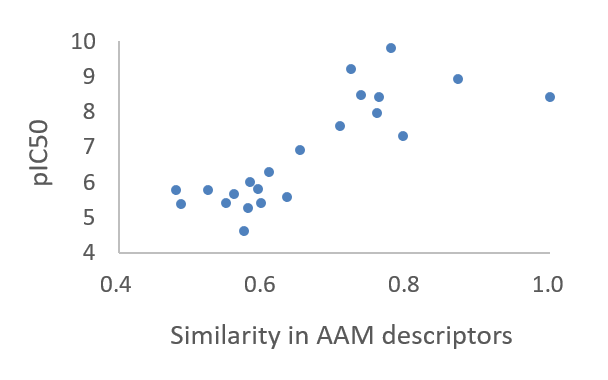
The AAM similarities of 22 compounds computed from the reference SYK inhibitor BIIB-057 exhibited the high correlation with the target affinity.
References
A novel in silico scaffold-hopping method for drug repositioning in rare and intractable diseases
Tanabe, M et al. : bioRxiv (2023)
A service that increases the number of active compounds using AI-AAM®
Here is the basic procedure of our drug2drugs® service. You should provide us the structural formula of the compound of the interest in the case of scaffold hopping between small molecules, and the binding conformation and site of your peptide for the scaffold hopping from a peptide to small molecules. Using the information, we first search from our library of the real chemicals and propose promising compounds. You then purchase the compound, evaluate its activity, and inform us of the result without letting us know the target information. Next, we use the results to design new compounds and propose more promising structures.
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.




