[PEPTIDE INSTITUTE] Hemoglobin A1c-related Amadori Compounds

While sugars are an essential factor in maintaining life activities, it is known that amino groups of proteins are non-enzymatically modified by glycosylation. This series of reactions is known as the Maillard reaction starting with the Amadori rearrangement, and modified compounds are called Amadori or Maillard compounds. Subsequently, these compounds are converted into advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which have been reported to contribute to age-related diseases.
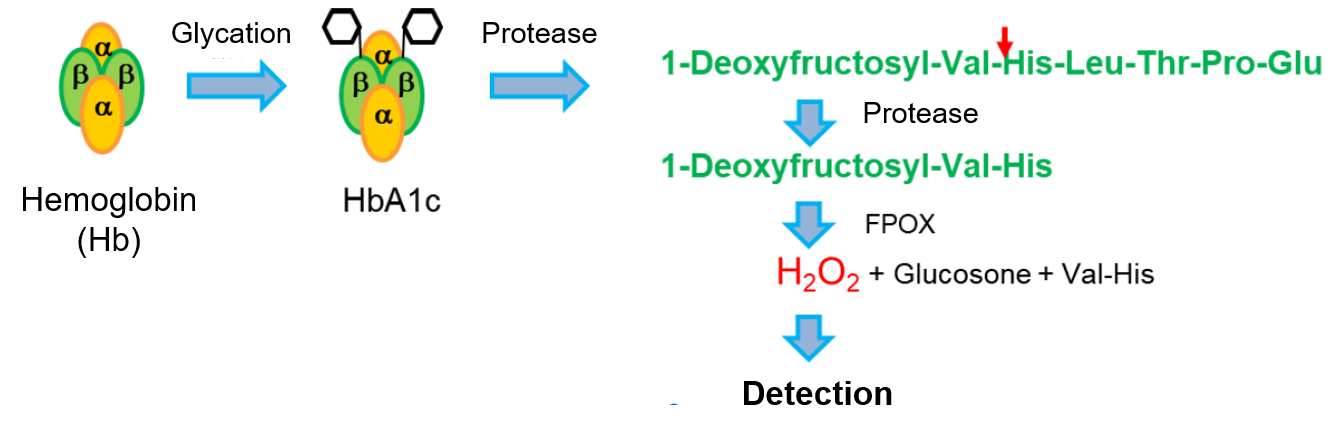
Glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) is an Amadori compound in which blood glucose is bound to the N-terminal Val residue of the hemoglobin β-chain, and is a well-known diagnostic marker for diabetes. In the enzymatic assay of HbA1c, a protease acts on HbA1c to release 1-Deoxyfructosyl-Val-His-Leu-Thr-Pro-Glu or 1-Deoxyfructosyl-Val-His, which are fructosyl compounds. Fructosyl peptide oxidase (FPOX) then acts on released 1-Deoxyfructosyl-Val-His to form hydrogen peroxide, which is subsequently detected by chromogenic substrates to obtain the HbA1c concentration.
Deoxyfructosyl compounds, for which a long-standing need has existed, are available in small quantities at affordable prices.
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
Hemoglobin A1c-related Amadori Compounds
Amadori Compounds / AGEs-related Compounds
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.



