Laminin Solution
Laminins are a major basement membrane component of most animal tissues. . In cell culture, laminins have been used for coating the surfaces of cell culture vessels. It is widely known that laminin-coated surfaces enhanced attachment to certain types of cells (primarily epithelial cells, neurons, hepatocytes, and muscle cells).
Overview
- Concentration: 0.5 mg/ml (the value obtained with the first lot)
- Formulation: 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl.
- Sterility: Filtered through a 0.2 μm pore size membrane.
- Storage Conditions: Store at –80°C. (Stable at –20ºC for one year.)
Product Validation
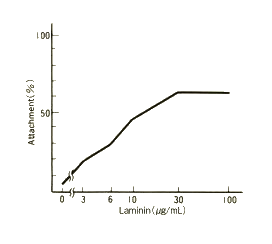
The laminin stock solution was diluted with D-PBS (calcium- and magnesium-free) to the concentrations indicated in the figure. Diluted laminin solutions were placed in 24-well plates (0.3 ml/well) and incubated overnight at 37℃. Following incubation, the laminin solutions were removed by aspiration and the wells were blocked with BSA. TIG-3 cells were then plated at a density of 5×104 cells/ml and were allowed to attach to the wells for 90 min at 37°C. Subsequently, unattached cells were removed by washing. The remaining adherent cells were harvested by treatment with trypsin-EDTA and used for cell number quantification.
Frequently Used Cell Types
- Epithelial cells
- Nerve cells
- Liver cells
- Muscle cells
Instructions for Use
- Slowly thaw the laminin stock solution at 4°C or on ice (Do not voltex).
- Dilute to an appropriate concentration using D-PBS (calcium- and magnesium-free) or medium.
- Coat cell culture vessel with the appropriate volume of diluted laminin solution.
- Incubate for 1 hour at 37℃ or overnight at 4℃.
- Carefully remove the laminin solution by aspiration.
- Wash the culture vessel 2-3 times with D-PBS (calcium- and magnesium-free) or a similar buffer.
- Plate cells.
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.



