Marine Toxins
Marine toxins are natural poisons possessed by fish and shellfish and cause food poisoning. Marine toxins are not only found in fish and shellfish, but also in microalgae or marine algae such as marine microorganisms and plankton, which are bio-concentrated by the food chain and cause poisoning in humans who eat them. In Japan, food poisoning, mainly caused by pufferfish poison (tetrodotoxin) or bivalve shellfish (oysters, scallops, etc.), occurs every year and those toxins are regulated and controlled by the Food Sanitation Act. Furthermore, global climatic changes have been accompanied by changes in the distribution of marine poisons, and the areas where food poisoning occurs are also changing. Therefore research on various marine toxins is in progress.
We provide a variety of reagents and kits related to marine toxins, including okadaic acid, paritoxin, and ciguatoxin.
* Toxins may not be available depending on the country. Please check with your distributor before purchasing.
Classifications and Toxic Components
| Classification | Component | Mechanism of action | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fish | Pufferfish poison | Tetrodotoxin |
|
| Ciguatera poison | Ciguatoxin(CTX1B・CTX3C) |
|
|
| Maitotoxin |
|
||
| Other fish poison | Palytoxin |
|
|
| Blue-green algae | Cyanotoxin | Microcystin(LR・RR) |
|
| Sponge | Sponge poison | Calyculin A |
|
| Mycalolide B |
|
||
| Bivalve shellfish | Diarrhetic shellfish poison | Okadaic Acid(OA), Dinophysistoxin-1(DTX1) |
|
Ciguatoxin CTX1B / CTX3C
Ciguatera food poisoning is the world's largest marine poisoning with over 50,000 people poisoning per year. It is a very strong neurotoxin, and the causative agent is ciguatoxins, which are produced by toxic dinoflagellates. There are numerous analogues of ciguatoxins (CTX). We provide the totally synthesized CTX 1B, CTX 3C, and CTX-ELISA 1B which is high sensitive ELISA kit to detect CTX 1B.
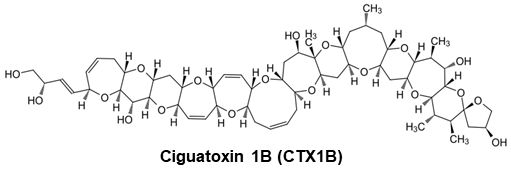
C57H82O16=1023.25
CAS RN®: 148471-85-6
Maitotoxin
Maitotoxin (MTX) is produced by dinoflagellate (Gambierdiscus toxicus). It is named maitotoxin after the Tahitian name of Striated surgeonfish "maito", which is a cause of ciguatera poisoning. MTX is the largest natural organic compound, which known structural formula. Since MTX exhibits a specific intracellular uptake of extracellular Ca2+, it has attracted attention for the mechanism of signal transduction mediated by Ca2+.
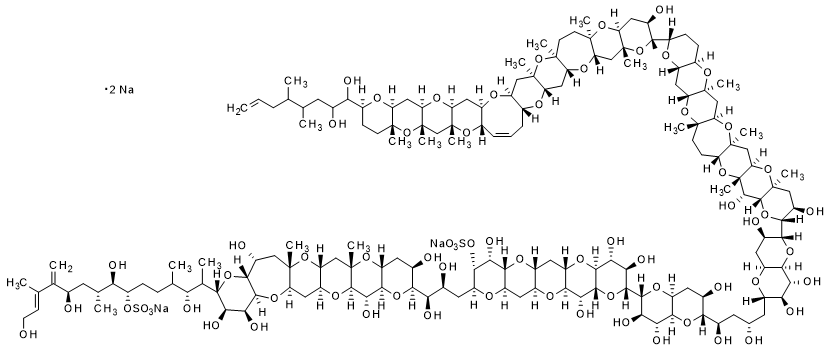
C164H256Na2O68S2=3425.86
CAS RN®: 59392-53-9
Palytoxin
Palytoxin is a toxin isolated from Palythoa tuberculosa. Palytoxin is the most toxic after maitotoxin among non-peptide compounds. Mainly, it causes strong coronary artery contraction. In addition, it has been reported to cause hemolysis, peripheral vasoconstriction, increased Na+ permeability in the nerve membrane, histamine release, and Na+, K+ -ATPase inhibition at high concentrations.
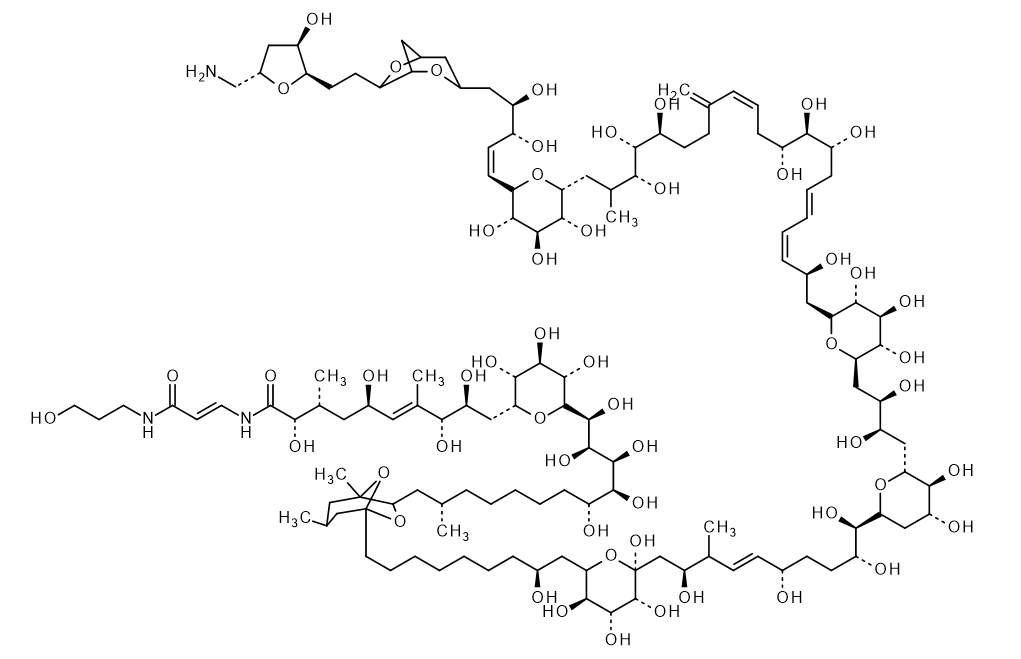
C129H223N3O54=2680.14
CAS RN®:77734-91-9
Okadaic Acid
Okadaic acid is the causative agent of Diarrheic Shellfish Poison isolated from the chlorisokamene. Physiological activities have been reported, including non-TPA type-promoter activity, smooth muscle contraction in a calcium-depleting solution, and phosphorylation of proteins by specific inhibition of protein phosphatases.
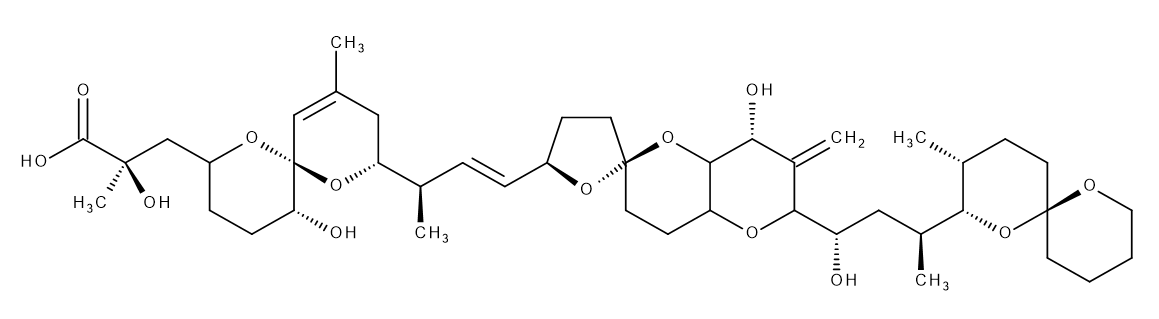
C44H68O13=805.00
CAS RN®:78111-17-8
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
Ciguatera poison
Palytoxin poison and related toxins
Shellfish poison
Other
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.



