Silica Gel TLC Plate (NH2 Modified)
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) is a method that uses a thin layer made of a stationary phase such as silica gel, polyamide, alumina, etc. on a glass or aluminum plate, separates the mixture sample into each component with a mobile phase. TLC is widely used for substance identification, purity testing, and for examining separation conditions when using column chromatography. Fujifilm Wako provides Silica Gel TLC Plates (Unmodified), NH2 modified Silica Gel Plates, and TLC plates, which thin layer is made from polyamide.
"NH2 Silica Gel 60F254 Plate-Wako" is a thin-layer chromatography plate coated with aminopropyl-modified silica gel on a glass plate. By irradiating the UV (λ=254 nm), the separated spots can be observed as black on a green background. Fujifilm Wako provides the NH2 Silica Gel 60F254 Plate-Wako with three kind of layer thickness, 0.25 mm type, which is suitable for examining separation conditions, 0.5 mm and 0.75 mm type, which are suitable for preparative separation.
How to Choose a TLC Plate
(1) Type of carrier
| Unmodified silica gel | Used in adsorption chromatography mode, mainly suitable for separation of acidic or neutral compound. |
|---|---|
| Chemically modified silica gel | Various functional groups are bonded to the silanol groups on the surface of unmodified silica gel to change the function. C18 modified silica gel, which is octadecyl group (ODS) bonded silica gel, suitable for reversed-phase chromatography mode. NH2 modified silica gel, which is aminopropyl group bonded silica gel, suitable for separation of sugars, catecholamines, etc. |
| Polyamides | Used in adsorption chromatography mode, suitable for separation of phenols and carboxylic acids. |
(2) Pore size/specific surface area
The smaller the pore size, the greater the specific surface area of the silica gel and the higher the resolution of small molecules. Conversely for macromolecules such as proteins, the larger the pore size, the higher the resolution. It is necessary to select an appropriate pore size so that sample molecules can easily enter and exit the pores.
(3) Type of support
Glass has excellent chemical resistance and is the most widely used. Aluminum and paper can be cut easily with scissors, but the carrier peels off from support or the TLC bends depending on the developing solvent. In addition, strong acids/bases cannot be used as developing solvents or coloring reagents.
(4) Type of fluorescent substance
| Not contain | It is suitable for detection of fluorescing samples and spot detection using coloring TLC stains (sulfuric acid, ninhydrin, iodine, etc.) because it does not contain fluorescent substances. |
|---|---|
| Mono fluorescent substance | 254 nm UV irradiation causes the entire plate to fluoresce green, and samples with UV absorption turn black colored spots. |
| Mixture fluorescent substance | Red, green, and blue fluorophores substance are added. Under broadband UV (250-400 nm) irradiation causes the entire plate to white, and samples with UV absorption turn the characteristic colored spot such as, red, blue, etc. |
| Product name | Pore size | Specific surface area | Pore volume | Layer thickness | Support | Sticking agent | Fluorescent substance | Detection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH2 Silica Gel 60 F254 plate-Wako (layer thickness 0.25 mm) |
6 nm | 450 m2/g | 0.7 mL/g | 190-250 μm | Glass plate | Polymer | Mono fluorescent substance | UV (254 nm) |
| NH2 Silica Gel 60 F254 plate-Wako (layer thickness 0.5 mm) |
400-550 μm | |||||||
| NH2 Silica Gel 60 F254 plate-Wako (layer thickness 0.75 mm) |
650-850 μm |
Application
Separation of nucleosides
| Sample | Thymidine Adenosine Cytidine |
10 mg/mL 10 mg/mL 10 mg/mL |
| Development mobile phase | Acetonitrile/Methanol/Water= 80/10/10 (v/v/v) | |
| Spot volume | 2 μL | |
| Layer thickness 0.25 mm | Layer thickness 0.5 mm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample name | Deployment distance | Rf value | Deployment distance | Rf value |
| Thymidine | 40 mm | 0.36 | 40 mm | 0.38 |
| Adenosine | 31 mm | 0.28 | 31 mm | 0.27 |
| Cytidine | 15 mm | 0.13 | 14 mm | 0.12 |
| (front) | 112 mm | - | 113 mm | - |
Separation of pigments
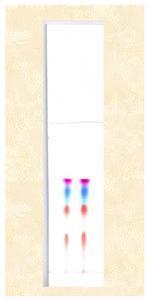
| Sample | Acid red Brilliant blue FCF Eosin Y New coccine in methanol |
52.4 mg 2 mg 4 mg 2 mg 1 mL |
| Development mobile phase | LiCl/Methanol= 1/100 (w/v) | |
| Layer thickness | 0.25 mm | |
| Spot volume 1 μL | Spot volume 2 μL | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample name | Deployment distance | Rf value | Deployment distance | Rf value |
| Acid red 52 | 68 mm | 0.61 | 68 mm | 0.61 |
| Brilliant blue FCF | 60 mm | 0.54 | 60 mm | 0.54 |
| Eosin Y | 46 mm | 0.41 | 47 mm | 0.42 |
| New coccine | 24 mm | 0.22 | 24 mm | 0.23 |
| (front) | 111 mm | - | 111 mm | - |
Separation of strong basic compounds
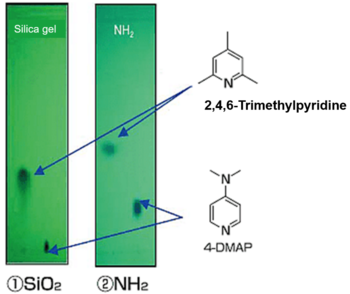
| TLC | ①Silica Gel 70F254 Plate-Wako |
| ②NH2 Silica Gel 60F254 Plate-Wako | |
| Sample | 1) 2,4,6-Trimethylpyridine (left spot) |
| 2) 4-Dimethylaminopyridine (right spot) | |
| Development mobile phase | n-Hexane/IPA = 90/10 (v/v) |
The separated spots can be observed as black spots on a green background by irradiation with UV light (λ=254 nm).
NH2 Silica Gel 60F254 Plate-Wako can make the spots of strong basic compounds less tailing.
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.




