LysoPure™ Protein Extraction-PTS Solution
In proteomics, the protein extraction and digestion, the preparatory steps for LC-MS/MS, play a crucial role in determining experimental results. Membrane proteins, in particular, are notoriously difficult to extract due to their high hydrophobicity. Membrane protein extraction in proteomics often necessitates the use of powerful solubilizing agents. However, such agents can inhibit the activity of proteolytic enzymes in subsequent steps and negatively affect peptide separation and ion detection in LC-MS/MS.
LysoPure™ Protein Extraction-PTS Solution is a solubilizing agent designed for protein extraction, an essential pretreatment step in proteomics.
Developed based on the PTS method, this product effectively solubilizes difficult-to-extract proteins while preserving proteolytic enzyme activity and enables easy removal of the agent via liquid-liquid partitioning. This product is an improved version of previously reported PTS solutions, offering improved protein solubilization and greater proteolytic enzyme activity than conventional PTS solutions. Additionally, it reduces cleavage errors by proteolytic enzymes. This product can also be used in proteomic studies of extracellular vesicles, including exosomes.
Challenges in Protein Extraction in Proteomics
Proteomics is a comprehensive analytical method used to identify and characterize all proteins in a sample. The process involves extracting proteins from the sample, digesting them into peptides using proteolytic enzymes, and analyzing the structural information of the resulting peptides using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Over the years, numerous improvements have been made to LC-MS/MS, such as improved columns and packing materials, as well as enhanced sensitivity and speed of mass spectrometers. As a result, multiple samples can now be analyzed simultaneously, and both qualitative and quantitative assessment of low-abundance proteins can now be carried out.
Protein extraction and digestion, the preparatory steps for LC-MS/MS, play a crucial role in determining proteomics outcomes. The main challenge is to maximize protein recovery while ensuring efficient digestion with minimal loss. Membrane proteins, in particular, are notoriously difficult to extract due to their high hydrophobicity. Membrane protein extraction in proteomics often necessitates the use of powerful solubilizing agents. However, such agents can inhibit the activity of proteolytic enzymes in subsequent steps and negatively affect peptide separation and ion detection in LC-MS/MS.
To overcome these challenges, a phase transfer surfactant (PTS) based on sodium deoxycholate was developed as an ideal solubilizing agent1). This surfactant efficiently solubilizes otherwise intractable proteins without inhibiting proteolytic enzyme activity and can be easily removed afterwards. The sample preparation method using this solubilizing agent is known as the PTS method, which has been widely reported as an efficient approach for preparing hydrophobic proteins, including membrane proteins, for proteomics analysis.
-
PTS Proteins -
Extraction of proteins
from the sample -
Enzymatic digestion
-
Acidification of the solution,
followed by stirring and
centrifugation -
Removal of
the upper phase - LC-MS/MS
Figure 1. Protein extraction via the PTS method Adapted from Reference 1).
LysoPure™ Protein Extraction-PTS Solution
LysoPure™ Protein Extraction-PTS Solution is a solubilizing agent designed for protein extraction, an essential pretreatment step in proteomics. Developed based on the PTS method, this product effectively solubilizes difficult-to-extract proteins while preserving proteolytic enzyme activity and enables easy removal of the agent via liquid-liquid partitioning. This product is an improved version of previously reported PTS solutions1-2), offering improved protein solubilization and greater proteolytic enzyme activity than conventional PTS solutions. Additionally, it reduces cleavage errors by proteolytic enzymes. This product can also be used in proteomic studies of extracellular vesicles, including exosomes.
Features
- Enables the extraction of highly hydrophobic proteins, including membrane proteins
- Does not inhibit proteolytic enzyme activity
- The solubilizing agent can be easily removed via liquid-liquid partitioning
Protocol
Protein Extraction from cells
-
Sample
Preparation Harvest cells,
centrifuge, and
discard the supernatant -
Protein
Extraction Add PTS solution
and suspend the cells 
Ultrasonic TreatmentReduce the viscosity of suspended the cells
-
Reduction and
Alkylation Add DTT and IAA -
Protein Digestion Dilute with TEAB
or AmBic,
then add Lys-C/trypsin -
Addition of
Hydrophobic
Solvent Add ethyl acetate
to the solution -
Acidification Acidify with TFA
-
Surfactant
Removal Remove the
upper phase -
Desalting
- LC-MS/MS
Protein Extraction from Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) (when using MagCapture™ Exosome Isolation Kit PS Ver.2)
-
Sample
Preparation Use a magnetic stand
to pellet EV-bound
magnetic beads,
then discard
the supernatant -
Protein
Extraction Add PTS solution
and suspend the beads -
Reduction and
Alkylation Add DTT and IAA -
Protein Digestion Dilute with TEAB
or AmBic,
then add Lys-C/trypsin -
Addition of
Hydrophobic
Solvent Add ethyl acetate
to the solution -
Acidification Acidify with TFA
-
Surfactant
Removal Remove the
upper phase -
Desalting
- LC-MS/MS
For the detailed protocol, please refer to the instruction manual available on the product details page.
Data
Protein Solubilization
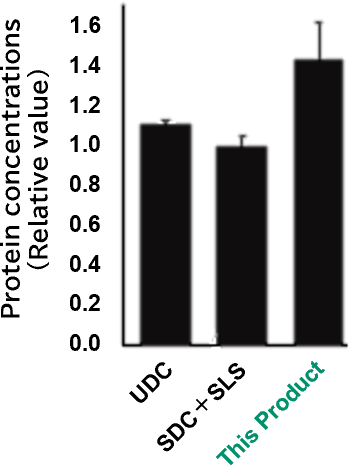
Proteins were extracted from human liver microsomal fractions using various PTS solutions with different surfactant compositions. The resulting protein concentrations were compared across the different solutions.
[Result]
This product demonstrated superior solubilization compared to conventional PTS solutions containing other surfactants.
Proteolytic Enzyme Activity and Cleavage Error Rate
| PTS Solution | Trypsin | Lysyl Endopeptidase (Lys-C) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration of PTS solution |
Activity | Initial velocity | Concentration of PTS solution |
Activity | Initial velocity | |
| SDC+SLS | 4 mM | 12.6 | 4.4 | 4 mM | 2.5 | 1.9 |
| SDC+SC | 8 mM | 5.7 | 2.3 | 8 mM | 2.6 | 2.4 |
| SDC+CDC | 8 mM | 7.5 | 4.4 | 8 mM | 2.4 | 1.8 |
| This Product | 8 mM | 10.3 | 4.6 | 8 mM | 2.6 | 1.8 |
| PTS Solution | Number of Cleavage Error |
|---|---|
| UDC | 586 |
| SDC+SLS | 723 |
| SLS+SC | 273 |
| This Product | 291 |
- CDC
- Kenodeoxycholic acid
- SC
- Sodium cholate
- SDC
- Sodium deoxycholate
- SLS
- Sodium lauroyl sarcosinate
- UDC
- Ursodeoxycholic acid
[Result]
SDC+SLS exhibited the highest trypsin activity but also resulted in the highest number of cleavage errors. In contrast, although this product had lower trypsin activity than SDC+SLS, it exhibited the highest lysyl endopeptidase activity with fewer cleavage errors. These findings show that this product offers well-balanced performance, combining high enzymatic activity while reducing the number of cleavage errors, making it an ideal PTS solution.
References
- Masuda, T., Tomita, M. & Ishihama, Y.: J. Proteome Res., 7(2), 731(2008).
Phase transfer surfactant-aided trypsin digestion for membrane proteome analysis - Masuda, T. et al.: Mol. Cell. Proteomics, 8(12), 2770(2009).
Unbiased Quantitation of Escherichia coli Membrane Proteome Using Phase Transfer Surfactants
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
LysoPure™ Protein Extraction-PTS Solution
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.
The prices are list prices in Japan.Please contact your local distributor for your retail price in your region.