Wetting Tension Test Mixture
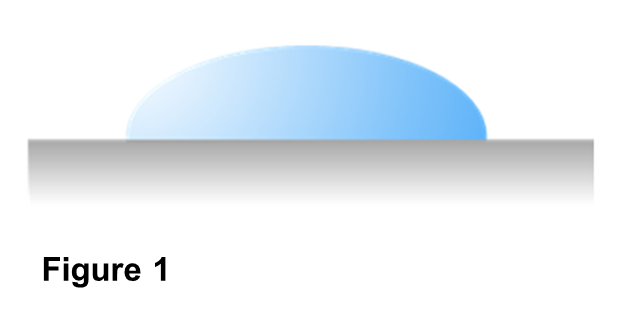
When painting, coating, or adhesion is applied to a plastic film, the plastic film surface must be wet (applied evenly) with ink, coating agents, or adhesives. A scale that shows this wet state is called wetting tension.
As shown in Figure 1, the presence of water droplets on the film surface does not mean that it is wet. To wet the surface with a liquid having a high surface tension like water, the film surface must be highly polarized for hydrophilicity. On the other hand, in case of solvents with weak surface tension such as organic solvents, the film surface gets wet even in a state where water is repelled.
Therefore, it is important to know the wetting tension of the plastic film when painting, coating, or adhesion is applied to a plastic film. The test method for wetting tension is specified in JIS K6768 "Plastics -- Film and sheeting -- Determination of wetting tension". In this test method, a series of wetting tension test mixtures having surface tensions increasing in a stepwise manner is prepared. The wetting tension is determined in observation of them dripped on the film surface. However, it is very hard to prepare a series of 36 wetting tension test mixtures. In FUJIFILM Wako, 36 wetting tension test mixtures for the wetting tension test, which were prepared in advance, are available for use.
Test Method1)
A series of wetting tension test mixtures with different surface tensions in sequence is applied to the plastic film surface, and the surface tension (µN/cm) {dyn/cm*} of a wetting tension test mixture No. that is determined to just wet the film is called the wetting tension of the film. The numerical value of this surface tension in the unit of mN/m corresponds to the item number. For example, the surface tension for No. 31 is 31 mN/ m (310 μN/cm) .
* dyn/cm = 1 mN/m (= 10 µN/cm) (Unification to SI units)
1. Place a few drops of a wetting tension test mixture on a test piece.
2. Immediately spread the wetting tension test mixture using a wire bar, a cotton swab, or a brush.
* Note that the amount of liquid to be applied greatly affects the accuracy of the test.
- In case of excessive application
The liquid film does not break from the inside, and it shrinks from the surroundings and becomes a large liquid drop. (The measured value becomes higher.) - When it is appropriate
The applied liquid film breaks not only from the surroundings but also from the center. - In case of insufficient application
During application, the liquid film breaks in the direction of moving of the cotton swab, resulting in uneven application. (The measured value becomes lower.)
1) Japanese Industrial Standards “JIS K6768:1999 Plastics -- Film and sheeting -- Determination of wetting tension”
Judgment2)
The judgment is made based on the state of the center of the liquid film 2 seconds after application of the reagent. When the applied liquid film remains intact, it is judged to be “wet,” and when it breaks, it is judged to be “not wet.” (Figure 2)*
Figure 2
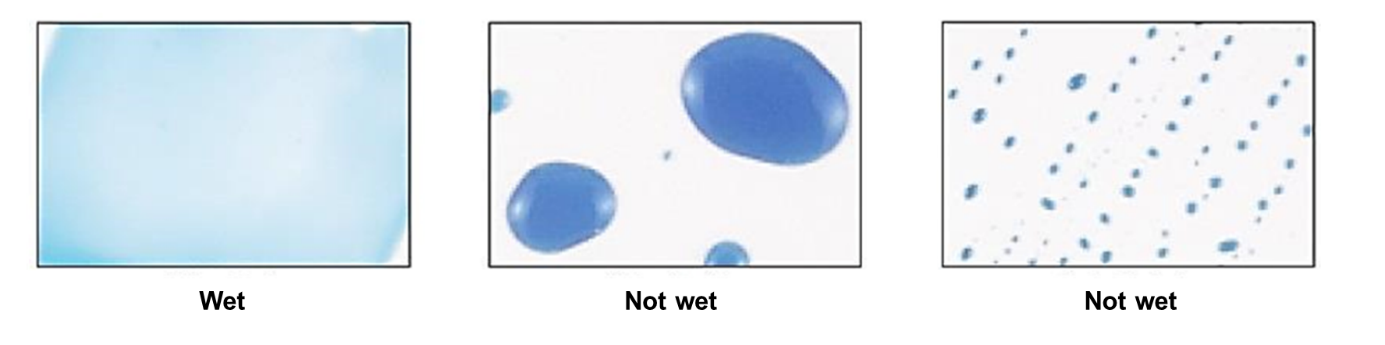
*A blue colorant is added to make it easy to judge whether it is “wet” or not. The quality is not affected.
2) Japanese Industrial Standards “JIS K6768:1999 Plastics -- Film and sheeting -- Determination of wetting tension”
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
ex) The surface tension of No. 31 is 31 mN/m (310 μN/cm).
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.



