Azo Radical Initiators
An azo polymerization initiator is a compound having an azo group (R-N=N-R') which is decomposed by heat and/or light, and forms carbon radical. The formed carbon radical is excellent in reactivity, and progresses polymerization and halogenation reaction of different types of vinyl monomers.
Introduction
We develop a large variety of products taking advantage of our original organic synthesis technology, production technology, and refining technology accumulated in our long experience in the manufacturing of reagents. Azo polymerization initiators are used as reaction initiators in the synthesis of polymers. They are used mainly as radical polymerization initiators in a wide range of industries, such as acryl resins for paints, water absorbent resins, polymer coagulants, adhesives, and paper finishing agents. We have approximately 20 types of azo polymerization initiators of organic-solvent soluble type and water-soluble type.
For product details, please visit our homepage of specialty chemical products.
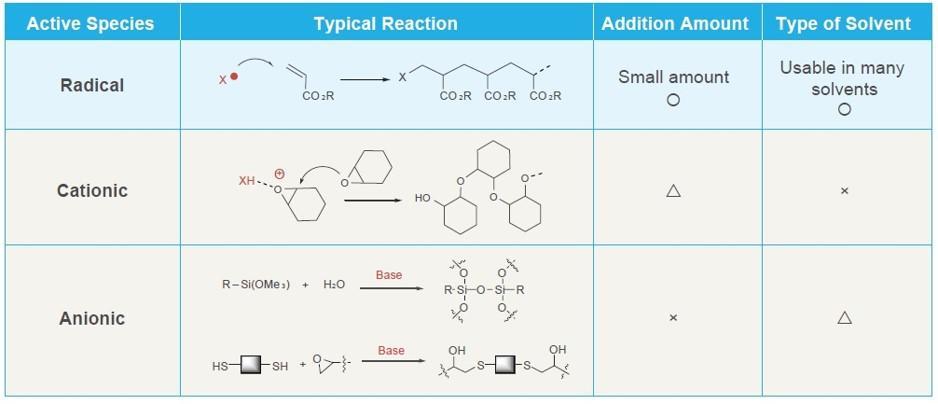
What is Radical Polymerization?
Radical polymerization is initiated by the formation of free radicals. Free radicals are formed by thermic energy, light, or radioactivity. Radical polymerization is mainly used for the polymerization of vinyl monomers. In addition to radical polymerization, cationic polymerization and anionic polymerization are common polymerization methods. In the case of radical polymerization, initiators are generally used. The typical initiators are azo polymerization initiators and peroxides.
Characteristics of Radical Polymerization Initiators
- Radical polymerization initiator shows an effect even in a small amount.
- It is not polar-sensitive, and a large number of solvent is available, a wide range of monomers can be polymerized.
- Polymerization at a low to high temperature ranges is possible.
- Reaction with simple facility and equipment is possible.
Characteristics
Characteristics of Azo Polymerization Initiators
- Azo polymerization initiators can be used safely as they do not decompose by induction and there is no risk of explosion.
- They decompose at a constant rate regardless of the solvent used, so they can be used with different solvents..
- Unlike the case of peroxides, the resulting carbon radical does not cause a hydrogen abstraction reaction, but forms linear polymers..
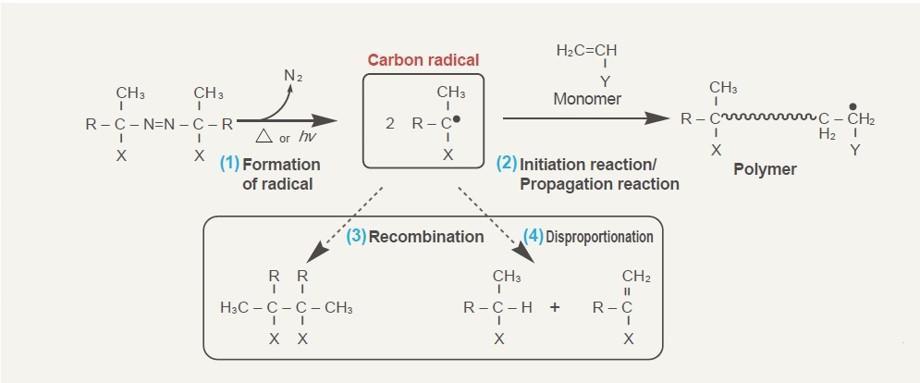
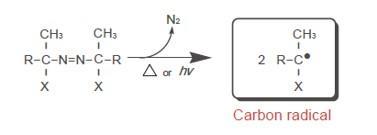
Radical Formation Mechanism
Radical Formation Mechanism of Azo Polymerization Initiators (Thermal Decomposition)
- Formation of radical: Azo polymerization initiators decompose with heat or light, and form nitrogen gas and carbon radicals.
*The decomposition rate (in solution) follows first-order reaction rate kinetics due to structure differences. - Initiation reaction/Propagation reaction: Azo polymerization initiator addition-polymerizes with vinyl monomers and forms a polymer.
*Since a section of the azo polymerization initiator is introduced at the end of polymer, the effect of end group is expected.
The efficiency of common azo polymerization initiators is approximately 0.5-0.7, and the remaining results in (3) recombination or (4) disproportionation - Recombination: The carbon radicals which did not engage in polymerization recombine.
- Disproportionation: The carbon radicals which did not engage in polymerization abstracts hydrogen of other carbon radicals.
Characteristics2
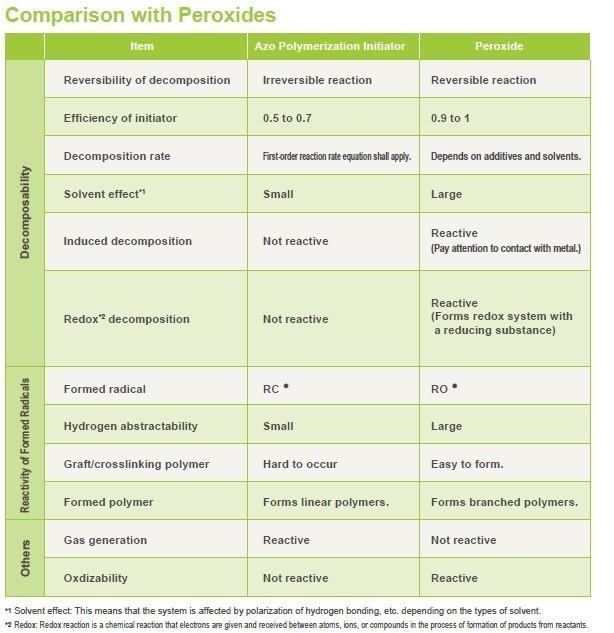
Characteristics of Azo Polymerization Initiators and Comparison with Peroxides
Peroxides are used as an initiator for radical polymerization, in addition to azo polymerization initiators.
Characteristics of Azo Polymerization Initiators
- Azo polymerization initiators can be used safely as they do not decompose by induction and there is no risk of explosion.
- They decompose at a constant rate regardless of the solvent used, so they can be used with different solvents.
- Unlike the case of peroxides, the resulting carbon radical does not cause a hydrogen abstraction reaction, but forms linear polymers.
Reaction examples
Examples of radical reactions using Azo Polymerization Initiators
Azo polymerization initiators are used as catalyst and foaming agent in organic synthesis, in addition to in polymer synthesis.
Polymer Synthesis
Radical polymerization of styrene
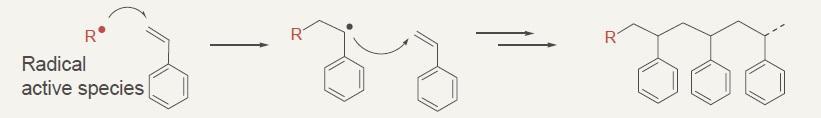
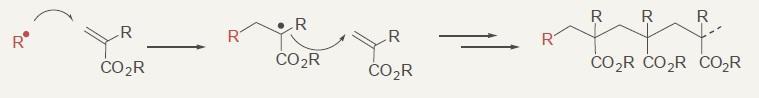
Radical polymerization of acrylic ester
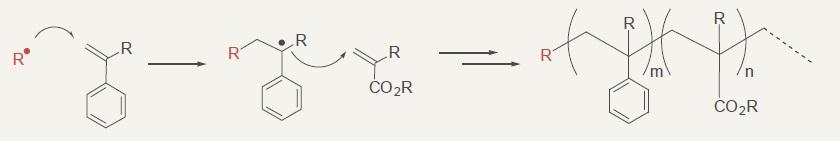
Copolymerization of styrene and acrylic ester
Catalyst for Organic Synthesis
Addition reaction to olefins
Azo polymerization initiator can be used for additional reactions of HBr, H2S, etc. to olefins. Especially, when using styrenes, bromine or mercapto groups may be selectively introduced to the β position.

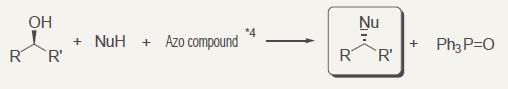
Mitsunobu reaction*3
Azo compounds*4 can be used as reagents for Mitsunobu reaction.
Foaming Agent
Azo polymerization initiators are used as foaming agents for vinyl chloride or other plastics, taking advantage of the property of generating nitrogen gas.
*3 Mitsunobu reaction: Sn2 (reaction) that activates hydroxyl group of alcohol with azo carboxylic acid ester and triphenylphosphine.
*4 Azo compounds: Bis(2-methoxyethyl)azodicarboxylate, etc.
Industrial-scale azo initiator
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
Polymerization Inhibitors
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.






