APDS Method
APDS (3-Aminopyridyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl Carbamate) is a pre-column derivatization reagent used for primary and secondary amine and amino acid analyses in LC/MS and LC/MS/MS.
Derivatization with APDS followed by separation and detection by LC/MS allow distinction of respective amino acids by m/z even if the retention times are the same and, thus, the analysis time can be shortened significantly.
In addition, APDS is designed to increase the ionization efficiency, allowing highly sensitive amino acid analysis in LC/MS/MS, especially by triple quadrupole.
Line-up
- Derivatization reagents
- UHPLC column
- Buffer / eluent solution
- Amino acid analytical standards
APDS Features
- APDS have an active carbamate, and any of the compounds reacts under a certain condition (under weak alkaline condition, 55°C, 10 minutes).
- The introduction of an aminopyridyl group increases the hydrophobicity of the derivatives, making it easier to retain and separate by reverse-phase HPLC.
- Due to the high ionization efficiency of the aminopyridyl group, it is detected with the mass spectrometer with high sensitivity.
- A regular product ion is generated which allows highly selective detection of common fragment ions (m/z = 121) derived from APDS.
Protocol
A derivative compound of the amino group bound by 3-Aminopyridyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl Carbamate (APDS) is produced by the addition of the reaction reagent to the sample under alkaline conditions and heating. This solution is separated by liquid chromatography, and the area values of the amino acid derivatives are detected for each mass-to-charge ratio. From the obtained area value and the ratio of the area value of the standard solution, the concentration of each amino acid in the sample is calculated.
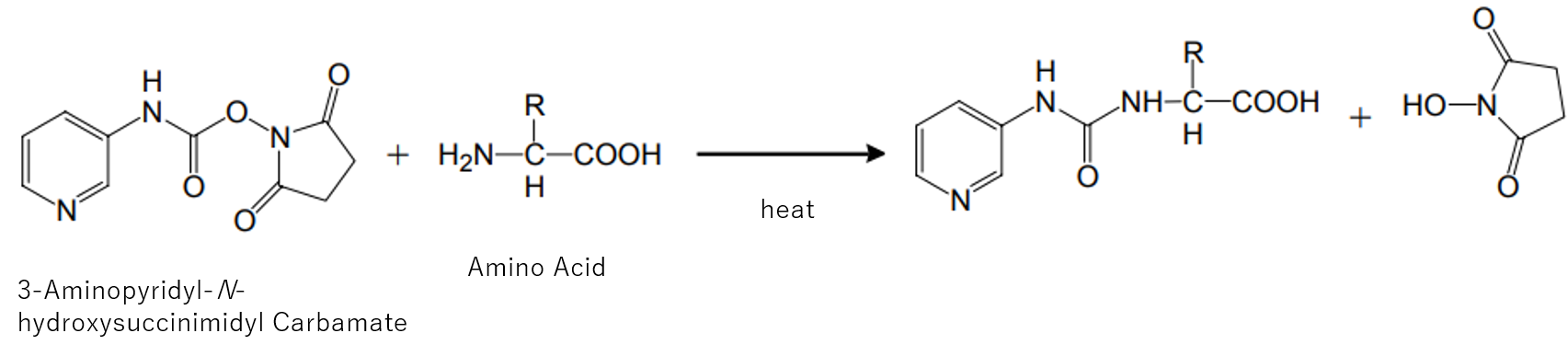
Example of Use [1]
APDS can be used as a derivatization reagent dedicated to the LC/MS high-speed amino acid analysis system of Shimadzu Corporation. This system enables simultaneous analysis of 38 or more amino acid-related substances* in just 9 minutes. In addition, since the derivatization reaction is automated, no complicated pretreatment operation is required.
For details, please see the website of Shimadzu Corporation.
*At least 38 amino acid-related substances including anserine, ctrulline, taurine, GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid), etc. in addition to 20 major amino acids
Example of Use [2]
Amino acid analysis by APDS is possible even by a common LC/MS and LC/MS/MS system.
Reagents
| Reagents | Code No. | Product Name |
|---|---|---|
| APDSTAG | 014-23841 | Amino Acid Analysis Reagent (for LC/MS) (APDSTAG®) |
| Analytical Column | 235-63973 | Wakopak® Ultra APDS TAG® |
| Amino Acid Standards | 016-28161 | Amino Acids Mixture Standard Solution, Type AN (High Range) |
| 012-28141 | Amino Acids Mixture Standard Solution, Type B (High Range) | |
| 019-28151 | Amino Acids Mixture Standard Solution, Type H (High Range) | |
| 015-27891 | Amino Acids Mixture Standard Solution, Type AN [CRM] | |
| 011-27871 | Amino Acids Mixture Standard Solution, Type B [CRM] | |
| 018-27881 | Amino Acids Mixture Standard Solution, Type H [CRM] | |
| Eluent Solution | 010-23061 | APDSTAG Wako Eluent |
| 019-23151 | APDSTAG Wako Borate Buffer | |
| 012-19851 | Acetonitrile |
Derivatization
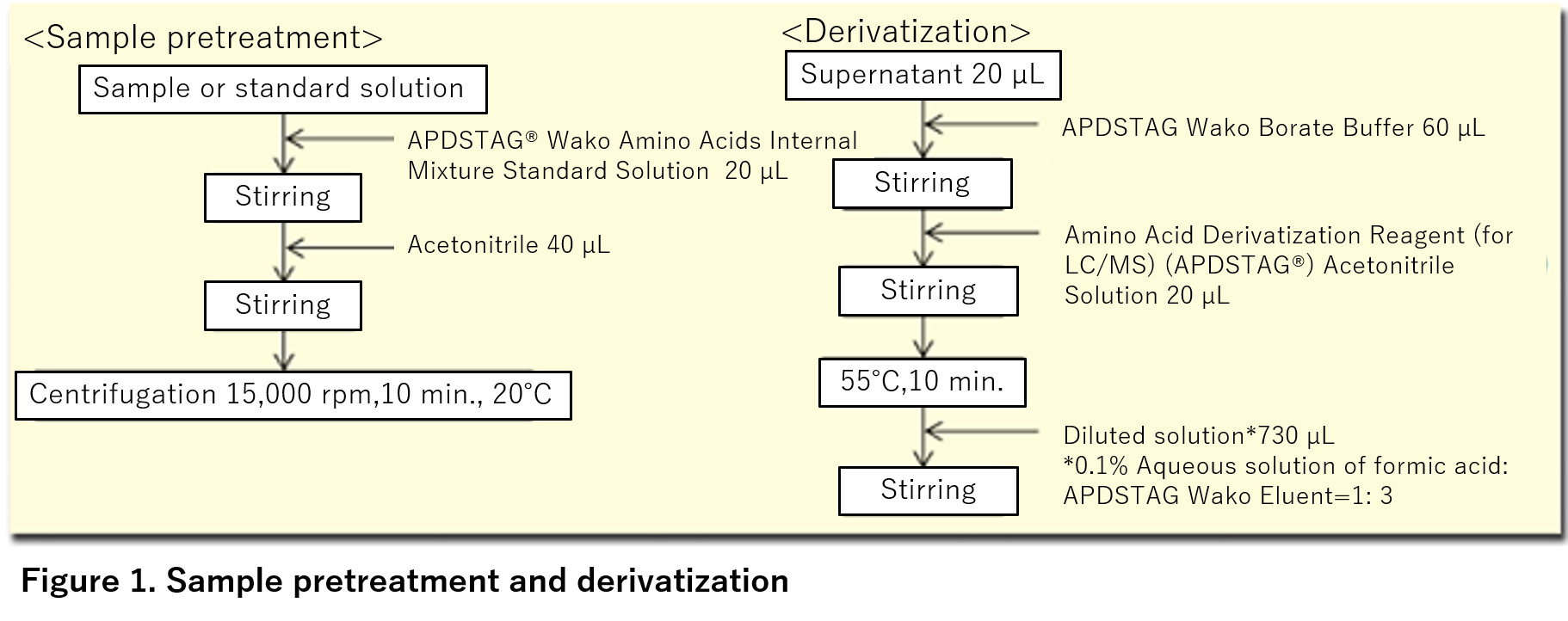
Analytical conditions (Typical conditions can also be measured by LC/MS.)
| Equipment | Prominence LC-20A XR (Shimadzu Corporation) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Column | Wakopak® Ultra APDS TAG® | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Mobile Phase | A) APDSTAG Wako Eluent B) 60% Acetonitrile Solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Gradient Conditions |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Flow Rate | 0.3 mL/min. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Column Temperature | 40℃ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Injection Volume | 1 µL | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Equipment | LCMS-8030 Plus (Shimadzu Corporation) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization | ESI positive | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Measurement Mode | MRM | ||||||||||||||||||||
| DL Temperature | 250℃ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Nebulizer Gas Flow Rate | 1.5 L/min. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat Block Temperature | 250℃ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Drying Gas Flow Rate | 10 L/min. |
LC/MS/MS Chromatogram
-
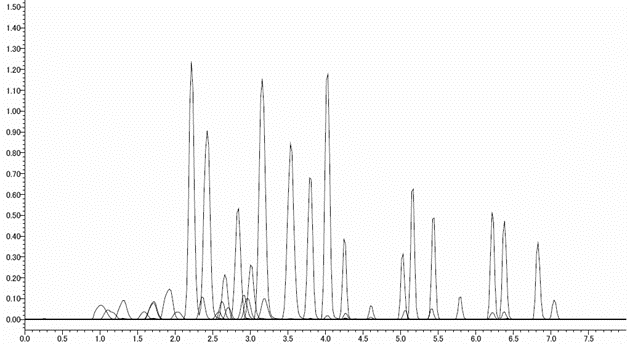
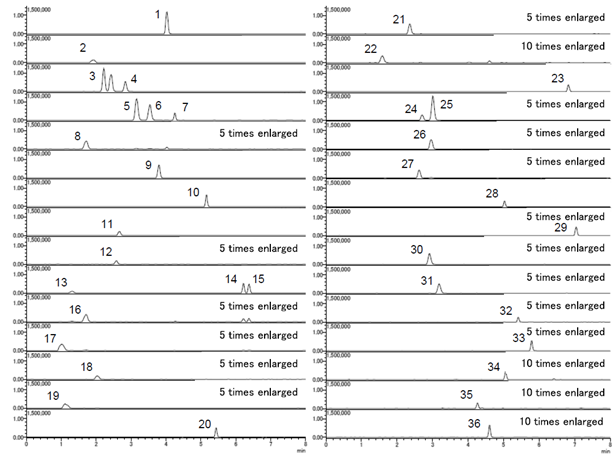
-
No. Target amino acids Abbreviations Q1 Q3 1 2-Aminoethanol EtOHNH2 182.1 121.0 2 Glycine Gly 196.1 121.0 3 Sarcosine Sar 210.0 121.0 4 Alanine Ala 210.1 121.0 5 4-Aminobutyric acid GABA 224.1 121.0 6 3-Aminoisobutyric acid β-AiBA 224.0 121.0 7 2-Aminobutyric acid α-ABA 224.0 121.0 8 Serine Ser 226.1 121.0 9 Proline Pro 236.1 121.0 10 Valine Val 238.1 121.0 11 Threonine Thr 240.1 121.0 12 Taurine Tau 246.1 121.0 13 Hydroxyproline Hypro 252.1 121.0 14 Isoleucine Ile 252.1 121.0 15 Leucine Leu 252.1 121.0 16 Asparagine Asn 253.1 121.0 17 Aspartic acid Asp 254.1 121.0 18 Glutamine Gln 267.1 121.0 19 Glutamic acid Glu 268.1 121.0 20 Methionine Met 270.1 121.0 21 Histidine His 276.2 156.0 22 α-Aminoadipic acid α-AAA 282.1 121.0 23 Phenylalanine Phe 286.2 121.0 24 1-Methyl-L-histidine 1MeHis 290.2 170.0 25 3-Methyl-L-histidine 3MeHis 290.2 170.0 26 Arginine Arg 295.2 175.1 27 Citrulline Cit 296.3 121.0 28 Tyrosine Tyr 302.2 121.0 29 Tryptophan Trp 325.2 121.0 30 Carnosine Car 347.2 227.1 31 Anserine Ans 361.3 241.1 32 Ornithine Orn 373.5 121.0 33 Lysine Lys 387.5 147.0 34 5-Hydroxylysine HyLys 403.5 163.0 35 Cystathionine Cysthi 463.2 223.1 36 Cystine Cys2 481.2 121.0
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
Derivatization reagent
UHPLC column
Buffer solution & Eluent
Amino Acids Mixture Standard Solution (High Range)
Amino Acids Mixture Standard Solution (CRM)
Mixture Internal Standard Solution
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.



