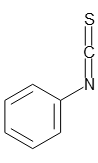
5% Phenyl Isothiocyanate, n-Heptane Solution
- for SHIMADZU Protein Peptide Sequencer
- Manufacturer :
- FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation
- Storage Condition :
- Keep at 2-10 degrees C.
- CAS RN® :
- 103-72-0
- Molecular Formula :
- C6H5N:CS
- Molecular Weight :
- 135.19
- GHS :
-
- Structural Formula
- Label
- Packing
- SDS
|
Comparison
|
Product Number
|
Package Size
|
Price
|
Availability
|
Certificate of Analysis
|
Purchase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
40mL
|
|
In stock in Japan |
※Check availability in the US with the distributor.
Document
Edman Degradation Method
Edman degradation method is a method to determine the primary structure of proteins by sequentially cleaving peptide bonds from the N-terminus of proteins or peptides.
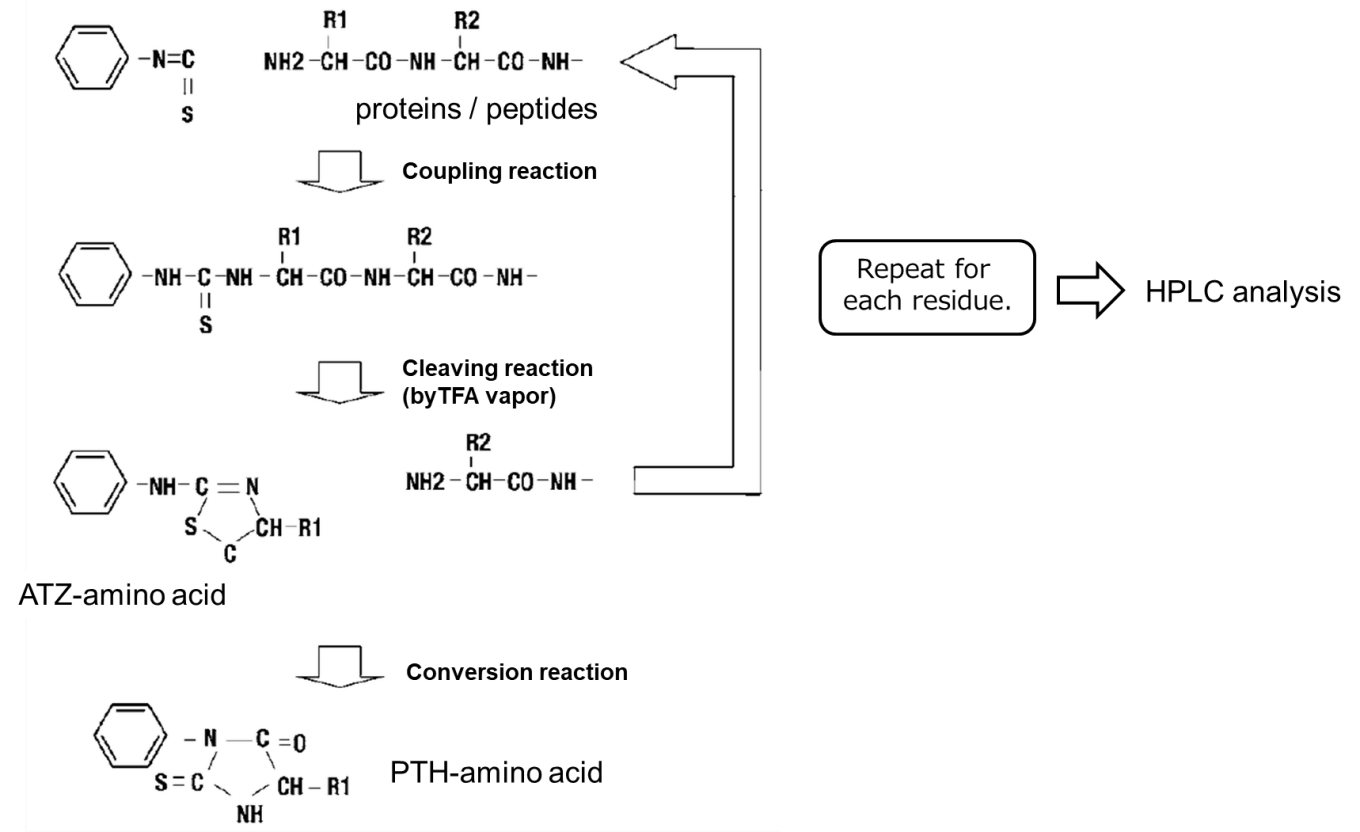
Edman degradation scheme1)
Principle
- Phenyl isothiocyanate (PITC) should be reacted with free amino groups at the N-terminus of proteins or peptides to form an phenylthiocarbamyl amino acid (PTC-amino acid).
- Isolate an anilinothiazolinone amino acid (ATZ-amino acid) using trifluoroacetic acid (TFA).
- Convert to a stable 3-phenyl-2-thiohydantoic acid (PTH-amino acid) under acidic conditions for analysis.
Analytical Procedures
In 1967, Edman developed an automated processing device for Edman degradation in a liquid phase2). In the 1980s, the first domestic gas-phase protein sequencer PSQ-1 was developed to automatically perform Edman degradation in the gas phase and analyze amino acids via isocratic elution with high-speed liquid chromatography (HPLC)3). Subsequently, the PPSQ (protein sequencer) series have evolved through the development of analyzing unit and data processing software.
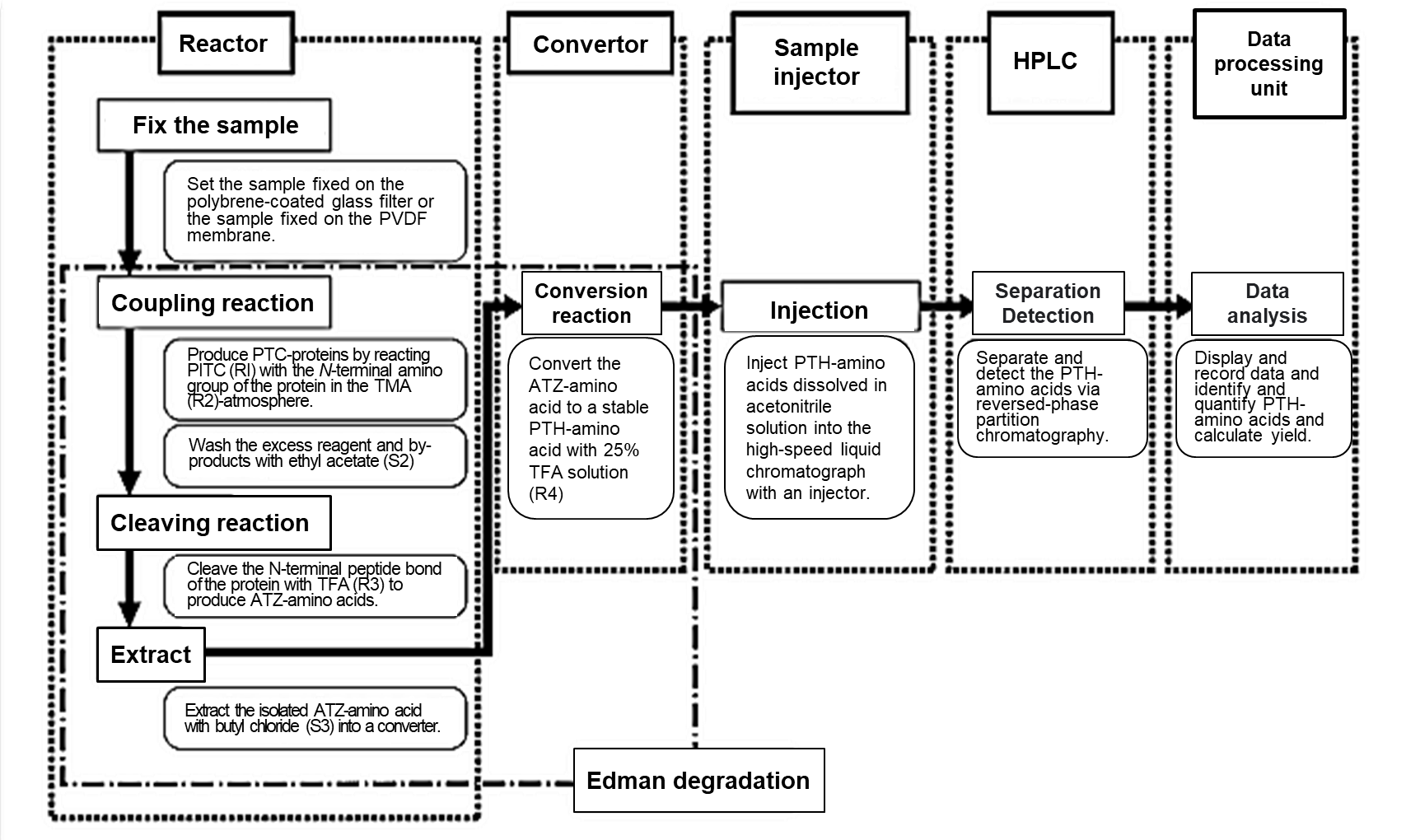
Fig 1. Flow chart for automated amino acid sequencing analysis1)
PITC; Phenyl isothiocyanate, TMA; Trimethylamine, TFA; Trifluoroacetic acid
PTC; Phenylthiocarbamyl, PVDF; Polyvinylidene fluoride
The flow chart of automated amino acid sequencing analysis is shown in Fig 1.
Automated amino acid sequencing analysis begins with the development of Edman degradation in the reactor and converter. The stable PTH-amino acid is injected into HPLC for identification, and the data are analyzed in the data processing unit.
For PPSQ, the isocratic elution with a constant mobile-phase composition and the gradient elution in which the mobile phase composition is continuously changing are available.
The chromatogram for the gradient elution of a PTH-amino acid mixture standard (2 pmol) is shown in Fig 2 (a), and the chromatogram for the isocratic elution is shown in Fig 2 (b).
Overall, gradient elution enables the detection of peaks that are about 3 to 5 times higher than those of isocratic elution, allowing the separation of highly hydrophobic amino acids.
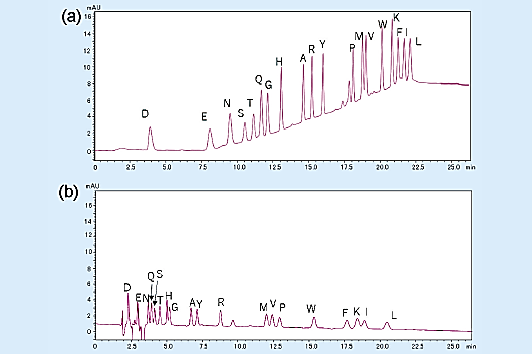
Fig 2. Analysis of amino acid mixture standard (2 pmol).1)
(a) gradient elution, (b) isocratic elution
In addition, the gradient elution enables PTH-amino acid separation and detection even when trace 500 fmol samples are analyzed and enables easy detection of increasing PTH-amino acids (Fig 3).
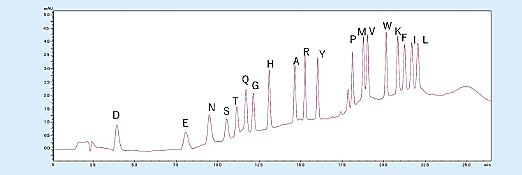
Fig 3. Analysis of amino acid mixture standard (500 fmol).1)
For PPSQ, various reaction reagents and eluents are required, and the processing is complicated. “Reagents for SHIMADZU Protein Peptide Sequencer” sold in FUJIFILM Wako are dedicated for PPSQ, of which container can be directly set on the equipment.
Background Reduction
The background that appears on the chromatogram includes dimethyl phenylthiourea (DMPTU), diphenylthiourea (DPTU), and diphenylurea (DPU), which are mainly by-products of Edman degradation, and substances contained in Edman’s reagent. These are produced from phenyl isothiocyanate (PITC); a coupling reagent; and trimethylamine (TMA), which creates a basic atmosphere. When the quantity of sample is small, the peaks of DMTPU; this by-product; and dithiothreitol (DTT), an antioxidant contained in 25% trifluoroacetic acid used for conversion reaction, interfere with the detection of amino acid peaks (PTH-Asp, PTH-His).
These problems can be solved by changing the reagent that creates a basic atmosphere from TMA to N-methylpiperidine and using 25% trifluoroacetic acid, which does not contain DTT (Fig 4).
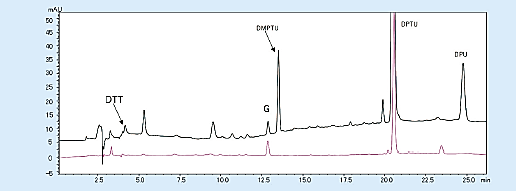
Fig 4. Chromatogram from the first cycle with the modified reagent (horse myoglobin 10 pmol)1)
Black; Existing Edman reagent, Red; modified Edman reagent
References
- Kuriki, T. et al. : Wako Jun-yaku Jiho, 86 (4), 6 (2018).
- Edman, P. and Begg, G. : Eur. J. Bouchem., 1,80 (1967).
- Ueda, A. et al.: SHIMADU Hyouron, 46 (4), 207 (1989).
Overview / Applications
| Outline | This product is for research use only. Do not administer it to human. For export only. The Edman method developed by Edman is widely used as an extremely useful method for amino acid sequencing of proteins and peptides. Since Edman and Begg developed the automated Edman method, the need for micro and rapid analysis has increased, so pmol-order analysis has been performed using, for example, a sequencer. This reagent for amino acid sequencing analysis is most suited for use with the fully automated protein sequencers of Shimadzu Seisakusho, Co., Ltd. (PSQ-1, PSQ-2, PPSQ-10). |
|---|---|
| Precautions for Use | Packed on Argon gas |
Property
| Appearance | Colorless clear liquid |
|---|---|
| Concentration | 5.0 - 5.5% |
| Purity | 99.9+% (HPLC)(Phenyl isothiocyanate) |
Manufacturer Information
Alias
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.