Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) Assay Kits
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is an enzyme that hydrolyzes phosphomonoester bonds under alkaline conditions (pH 9-11). In biochemical tests, the ALP level in the blood serves primarily as an indicator of diseases of the liver and bile duct. ALP levels can also increase due to bone diseases, pregnancy, and cancer.
Methods using p-nitrophenyl phosphate (p-NPP) as a substrate (the p-nitrophenyl phosphate substrate method or the Bessey-Lowry method) are commonly used for the measurement of ALP. LabAssay™ ALP is a kit used for the determination of ALP in samples using the p-nitrophenyl phosphate substrate method. With the use of a microplate, this kit provides a quick and convenient method for measuring ALP in samples.
What is Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) ?
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is an enzyme that hydrolyzes phosphomonoester bonds under alkaline conditions (pH 9-11). It is found in the following order of abundance: small intestinal mucosa, placenta, mammary glands, kidneys, bones, lungs, liver, and spleen. It is less prevalent in skeletal muscles and connective tissues1). There are different isozymes of ALP depending on the tissue and these are classified into the following four types: (1) tissue nonspecific ALP (liver/bone/kidney ALP), (2) intestinal ALP, (3) placental ALP, and (4) germ cell ALP. While many functions of ALP remain unclear, studies indicate that tissue nonspecific ALP is involved in the calcification of bones and teeth, and tissue-specific ALP is involved in cell differentiation, IgG transport, and lipid metabolism1).
In biochemical tests, ALP levels in the blood serve primarily as an indicator of diseases of the liver and bile duct. In liver inflammation, ALP leaks into the bloodstream, resulting in elevated blood levels. ALP levels also increase with elevated bile duct pressure due to biliary obstruction. Elevated ALP without significant increase in AST and ALT suggests a high likelihood of biliary disease. ALP levels can also increase due to bone diseases, pregnancy, and cancer. As mentioned earlier, there are different isozymes of ALP depending on the tissue. Therefore, if ALP levels are abnormal, the isozymes are examined using techniques such as electrophoresis to identify the organ of origin.
Methods of ALP Measurement
Methods using p-nitrophenyl phosphate (p-NPP) as a substrate (the p-nitrophenyl phosphate substrate method or the Bessey-Lowry method) are commonly used for the measurement of ALP. These methods are superior in terms of sensitivity, reproducibility, ease of operation, and cost. The Kind-King method, which uses phenyl phosphate as a substrate, is another similar technique. While the p-nitrophenyl phosphate substrate method is more advantageous in terms of ease of operation, it is prone to interference from bilirubin2).
Principle of the ALP assay using p-nitrophenyl phosphate substrate method
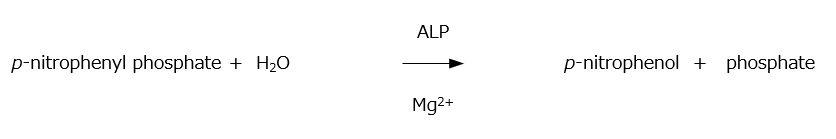
When a sample is incubated in a carbonate buffer (pH 9.8) containing p-nitrophenyl phosphate, the ALP in the sample hydrolyzes p-nitrophenyl phosphate into p-nitrophenol and phosphate. The released p-nitrophenol turns yellow under alkaline conditions. By measuring the absorbance at 405 nm, the ALP activity in the sample can be determined.
LabAssay™ ALP
LabAssay™ ALP is a kit used for the determination of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in samples using the p-nitrophenyl phosphate substrate method. With the use of a microplate, it provides a quick and convenient method for measuring ALP in samples.
[Note] LabAssay™ series are reagents for research purposes. They cannot be used for diagnostic purposes.
Kit Performance
| Analysis sample | Human Serum Mouse Serum Rat Serum Dog Serum Cat Serum Culture medium (D-MEM)* |
|---|---|
| Calibration curve range | 0.0625-0.5 mmol/L *p-nitrophenol |
| Sample volume | 20 μL |
| Measurement duration | Approx. 20 min |
| Wavelength | 405 nm |
*It is tested by using the samples that standard substances have been added to the culture medium.
Measurement availability depends on the culture medium, cell type and culture conditions. When using cell culture supernatant as a sample, please perform a spiked recovery test or dilution linearity test in advance using the culture medium to be used in your experiment.
References
- Ishida, Y., Komaru, K. and Oda, K.: Japanese Journal of Clinical Chemistry, 33(1), 36(2004).
Structure and Function of Alkaline Phosphatases (Japanese) - Tomoda, I.: Journal of the Japan Veterinary Medical Association, 32(2), 93(1979).
臨床血液化学検査の考え方 (IX) V. 血清酵素 3. アルカリフォスファターゼ (Japanese)
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
LabAssay™ ALP
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.



