Guide to Selection of a Capillary Column for GC
Reason for Capillary Column Selection
1. Stationary Phase
|
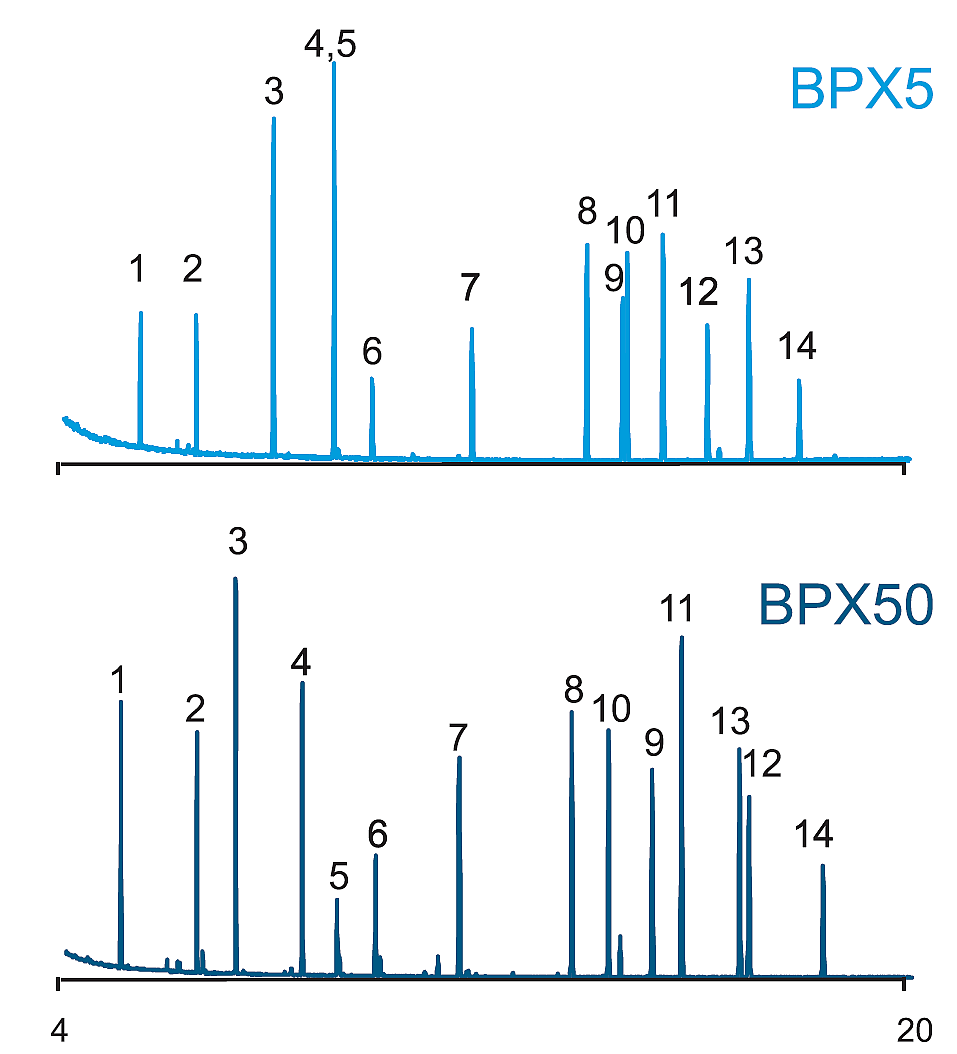 Initial Temp:45 ℃(1 min) 1st Temp Ramp:30 ℃/min to 200 ℃(0.1 min) 2nd Temp Ramp:7 ℃/min Final Temp:315 ℃ (hold 10 min) Injector Temp:280 ℃ Splitless Time :1 min Carrier :He, 1 mL.min |
Organophosphorus Pesticides
|
2. Internal Diameter
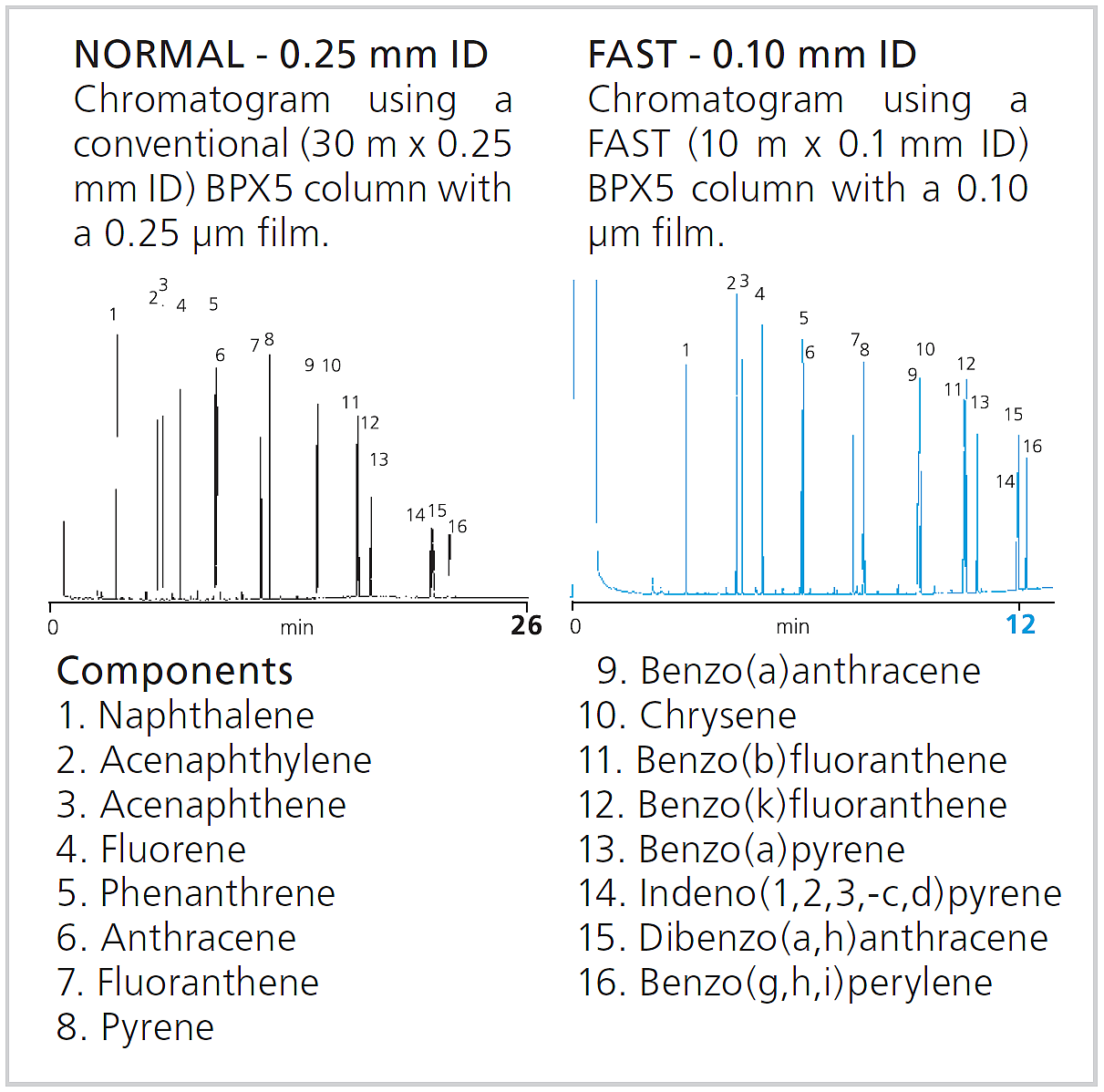
- The narrower the inner diameter of the column, the higher the column efficiency and the higher the resolution. If using a thin inner diameter column, the length of the column can be shortened, compared with the conventional column, and the analysis time can be shortened with equivalent separation. However, it is necessary to pay attention to the upper limit of the sample load.
3. Film Thickness
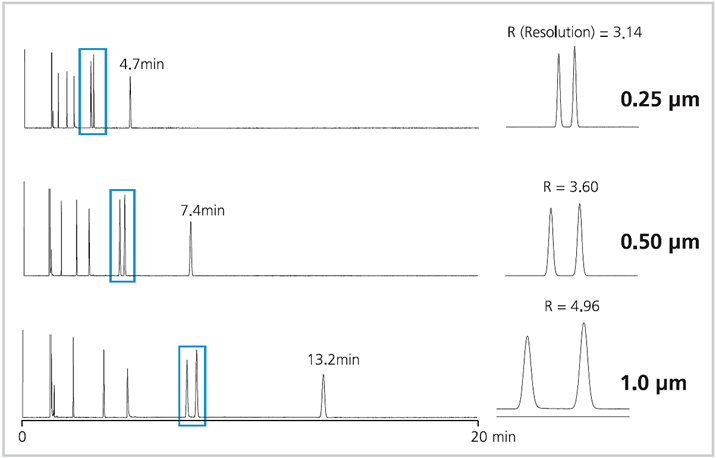
Keeping similar phase ratios when changing column inner diameters for columns of the same type will give similar results without significant changes in chromatography parameters.
| Film Thickness (µm) | Internal diameter of the column (μm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 150 | 220 | 250 | 320 | 530 | |
| 0.10 | 250 | - | 550 | 625 | 800 | 1325 |
| 0.15 | - | 250 | - | - | - | 883 |
| 0.25 | - | 150 | 220 | 250 | 320 | 530 |
| 0.50 | - | 75 | 110 | 125 | 160 | 265 |
| 1.00 | - | - | 55 | 63 | 80 | 132 |
| 3.00 | - | - | - | - | 27 | 44 |
| 5.00 | - | - | - | - | 16 | 26 |
- If the concentration range of each component in a sample is wide, a column with a thick film is recommended. By selecting a column with a thick film, leading of the peak of high concentration component due to the impact of overload or overlapping with other component peaks that should have been separated in a mixture of the same concentration may be prevented. If the separation of each component is sufficient to avoid the influence of a concentration difference, a column with a thinner film shall be selected, considering the peak shape.
- The thicker the film, the longer the elution time, and the higher the elution temperature. In order to elute at the same retention time by doubling the film thickness in a thermostatic analysis, it is necessary to increase the oven temperature from 15°C to 20°C. The temperature program can be used to reduce the elution temperature slightly.
- The phase ratio (β) is one of the parameters that shows suitability for various applications. A column with a low β value means a high ratio of film thickness relative to inner diameter, i.e., a strong retention force, suitable for volatile component analysis. On the other hand, a column with a high β value has a thin film and a relatively weak retention force, which is suitable for analysis of compounds with a large molecular weight and a high boiling point.
β = id/4df
β = phase ratio
id = internal diameter of the column (μm)
df = film thickness (μm)
<Scope of application by phase ratio>
| Phase ratio (β) | Application |
|---|---|
| 16-100 | gas, low M.W. hydrocarbons, solvents, Volatile halogen compounds (M.W.16-250) |
| 100-320 | semi-volatile compounds, common applications (M.W. 100-700) |
| 320-1325 | high M.W. hydrocarbons, wax, petroleum products (M.W. 300-1500) |
When changing the inner diameter etc. of a column of the same type, a column with the same phase ratio can be selected to obtain a similar chromatogram.
4. Column Length
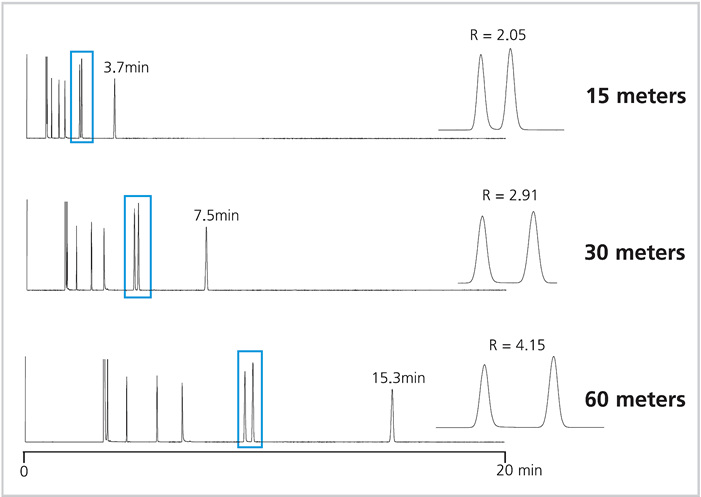
- The shortest column possible to achieve the required separation shall be selected. If a longer column cannot provide sufficient separation, it is necessary to examine the stationary phase and phase ratio again.
- The resolution is proportional to the square root of the column length. When the column length is doubled, the resolution is basically improved by a factor of approximately 1.4.
Stationary Phase and Features of the SGE Capillary Column
| Column | Stationary phase | Structural formula | Features | Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BP1 | 100 % Dimethyl Polysiloxane | 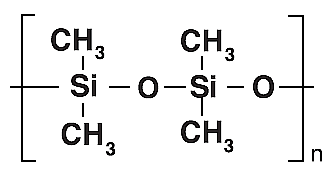 |
|
Hydrocarbons, Aromatic compounds, Insecticides, Herbicides, Banned drugs, Phenols, Amine analysis |
| BP1 PONA | 100 % Dimethyl Polysiloxane |
|
Petroleum hydrocarbon, Gasoline hydrocarbon, MTBE, Paraffin, Olefins, Naphthenes, Aromatic compounds | |
| BPX1 | 100 % Dimethyl Polysiloxane |
|
ASTM method: D2887, D6532 | |
| SolGel-1ms™ | 100 % Dimethyl Polysiloxane in a SolGel matrix |
|
Ideal for analysis of highly active compounds. | |
| BP5 | 5 % Phenyl / 95 % Dimethyl Polysiloxane | 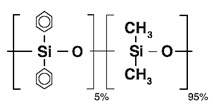 |
|
General analysis, Aromatic compounds, Insecticides, Herbicides, Drug, Hydrocarbon, Polychlorinated biphenyls, Essential oil, Semi-volatile compounds |
| HT5 | 5 % Phenyl Polycarborane-siloxane | 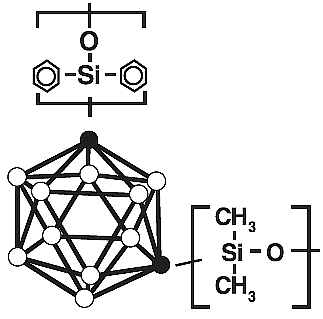 |
|
Distillation simulation, Hydrocarbon, Insecticides, Herbicides |
| HT8 | 8 % Phenyl Polycarborane-siloxane |
|
PCB analysis, Aromatic nitro compounds, Polycyclic aromatic compounds, Insecticides, Herbicides | |
| BPX5 | 5 % Phenyl Polysilphenylene-siloxane | 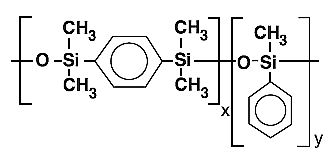 |
|
Ultra-trace component analysis, Insecticides, Herbicides, Hydrocarbon, Solvent, Phenols, Amines, Ideal for GC/MS and other GC analysis |
| BPX35 | 35 % Phenyl Polysilphenylene-siloxane |
|
Environmental analysis, Insecticides, Herbicides, Banned drugs, Pharmaceuticals, Polycyclic aromatic compounds | |
| BPX608 | 35 % Phenyl Polysilphenylene-siloxane |
|
Environmental analysis, U.S. EPA method: 608, Insecticides, Herbicides | |
| BPX50 | 50 % Phenyl Polysilphenylene-siloxane |
|
U.S. EPA method: 604, 608, 8060, 8081, Triazine pesticides, Drug screening, Steroid, Pharmaceuticals, GC2D | |
| BPX70 | 70 % Cyanopropyl Polysilophenylene Siloxane | 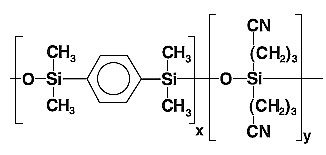 |
|
Fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs), Carbohydrate, Pharmaceuticals, GC/MS application |
| BPX90 | 90 % Cyanopropyl Polysilophenylene Siloxane |
|
Fragrance, Aromatic compounds, Petrochemicals, Insecticides, PCB, Fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs), Trans fatty acids | |
| SolGel-WAX™ | Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) in a SolGel matrix |
|
Ideal for analysis of highly active compounds | |
| BP20(WAX) | Polyethylene Glycol |
|
Alcohols, Free acid, Fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs), Aromatic compounds, Solvent, Essential oils | |
| BP21(FFAP) | Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) TPA treated |
|
Free acid, Fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs), Alcohols, Aldehydes, Acrylates, Ketones | |
| BP10(1701) | 14 % Cyanopropylphenyl 86 % Dimethyl polysiloxane | 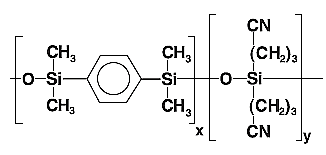 |
|
Environmental analysis, US EPA method: 608, 8081, Insecticides, Herbicides, Abuse drugs, Pharmaceuticals |
| BPX-VOLATILES | Cyanopropylphenyl Polysiloxane |
|
Environmental analysis, Volatile organic compounds, Alcohols, USP G43 | |
| BP624 | Cyanopropylphenyl Polysiloxane |
|
US EPA method: 624, Volatile organic compounds, chlorinated hydrocarbons, solvents in drinking water (EPA method: 501.3, 502.2, 503.1, 524.2, 601, 602, 8010, 8015, 8020, 8240, 8260) | |
| CYDEX-B™ | Permethyl-β-cyclodextrin (chiral) |
|
Separation of enantiomers in natural products |
Correspondence Table for Each Compound and Capillary Column
◎: Stationary phase recommended for application
● : Stationary phase able to respond to application
| Compounds | SOLGEL-1ms BP1 | BPX1 BP1-PONA | BPX5 BP5 | HT5 | HT8 | BPX35 | BPX-Volatiles BP624 | BP10 | BPX50 | SOLGEL- WAX BP20 | BP21 | BPX70 | CYDEX-β | BPX20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acidic/Neulral Drugs | ● | ◎ | ||||||||||||
| Acids | ● | ● | ◎ | |||||||||||
| Alcohols | ● | ● | ◎ | ● | ● | |||||||||
| Amines Aliphatic | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||
| Amines Aromatic | ● | ◎ | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| Antidepressants | ● | ◎ | ||||||||||||
| Aromatics - PAH | ● | ◎ | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| Aroclors | ◎ | ● | ||||||||||||
| Beverages - Alcohols | ◎ | ● | ||||||||||||
| Butter - Fat | ● | ◎ | ||||||||||||
| Chiral Compounds | ◎ | |||||||||||||
| Chlorinated Aromatics | ● | ◎ | ◎ | ● | ||||||||||
| Cigarette Lighter Fuel | ● | ● | ||||||||||||
| Dioxins | ◎ | ● | ||||||||||||
| Essential Oils | ◎ | ◎ | ● | |||||||||||
| Food - FAME | ● | ● | ◎ | ◎ | ||||||||||
| Glucose - Methylated | ● | ◎ | ||||||||||||
| Herbicides | ● | ● | ● | ◎ | ||||||||||
| Industrial Solvents | ● | ● | ◎ | |||||||||||
| Ketones | ● | ● | ● | ◎ | ||||||||||
| Monomers | ● | ● | ◎ | |||||||||||
| Nitroaromatics | ● | ◎ | ● | ◎ | ● | ● | ||||||||
| Organochlorine Pesticides | ● | ◎ | ● | ● | ◎ | ● | ||||||||
| Organophosphorous Pesticides | ● | ◎ | ● | ◎ | ● | |||||||||
| Paraffins | ● | ◎ | ● | ◎ | ||||||||||
| PCB's | ● | ◎ | ● | |||||||||||
| Petroleum | ● | ◎ | ● | ◎ | ||||||||||
| Phenols | ◎ | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| Phthalates | ● | ◎ | ● | |||||||||||
| Plant Sterols | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||
| Polymers | ◎ | ◎ | ||||||||||||
| Polywax | ● | ● | ◎ | |||||||||||
| Pyrethroids | ● | ◎ | ◎ | ● | ● | |||||||||
| Racehorse Doping Mixture | ◎ | ● | ||||||||||||
| Sedatives | ● | ◎ | ||||||||||||
| Semivolatiles | ● | ◎ | ● | |||||||||||
| Silicon Oil | ◎ | |||||||||||||
| Solvents | ◎ | ◎ | ● | |||||||||||
| Sugars-Alditol Acetates | ● | ● | ◎ | |||||||||||
| Triglycerides | ◎ | ◎ | ||||||||||||
| TRPH | ◎ | ● | ◎ | |||||||||||
| Volatiles | ● | ◎ | ◎ | |||||||||||
| Xylenes | ● | ● | ● | ● | ◎ | ◎ |
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.



