Catechins
Catechins are type of polyphenolic compounds contained in tea leaves. Catechins have antibacterial, bactericidal, antiviral, active oxygen scavenging, anti-allergic, fat-burning and bad cholesterol-lowering effects.
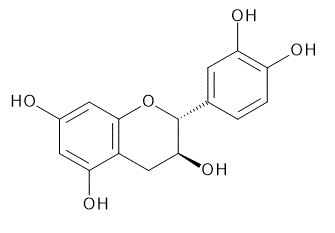
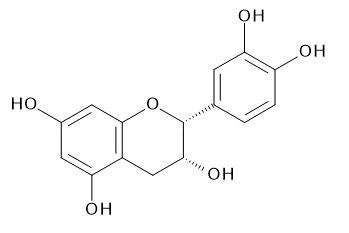
The main catechins are (-)-epicatechin, (-)-epicatechin gallate, (-)-epigallocatechin, and (-)-epigallocatechin gallate. The 4 major catechins in raw tea leaves are (-)-epigallocatechin gallate, (-)-epigallocatechin, (-)-epicatechin gallate, and (-)-epicatechin.
In addition, canned beverages made from heated tea leaves contain (-)-gallocatechin gallate, (-)-gallocatechin, (-)-catechin gallate, and (-)-catechins which have been epimerized each of the above 4 types catechins.
Procyanidins (proanthocyanidins) are compounds in which multiple catechins or epicatechins are bonded. And procyanidins produce anthocyanidins by hydrolyzing. Apple-derived procyanidins have the function of reducing visceral fat, and mainly contain procyanidin B2. Pine-bark-derived procyanidins have the function to lower bad (LDL) cholesterol, and mainly contain procyanidins B1 and B3.
Theaflavins are type of polyphenolic compounds contained in black tea leaves and are produced by bonding 2 molecules of catechin during the fermentation process of black tea. Although its functions are similar to catechins, there are several differences such as anti-influenza activity etc.
Methods for quantifying catechins are HPLC using a reversed-phase column, colorimetric quantification of tannin (a polyphenol in green tea), and capillary column electrophoresis method.
Fujifilm Wako has a lineup of catechin-related reagents that can be used for these tests.
Chemical Structure for Catechins
| (+)-Catechin | (-)-Epicatechin | (+)-Gallocatechin | |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
|
| CAS RN®:154-23-4 | CAS RN®:490-46-0 | CAS RN®:970-73-0 | |
| C15H14O6=290.27 | C15H14O6=290.27 | C15H14O7=306.27 | |
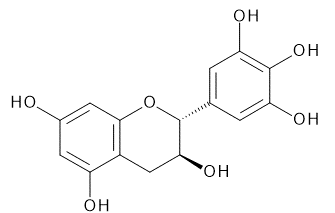
| (-)-Epigallocatechin | (-)-Epicatechin Gallate | (-)-Epigallocatechin Gallate | |
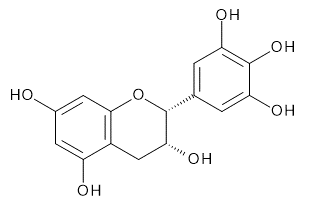 |
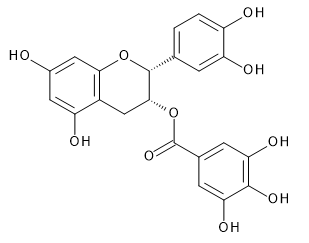 |
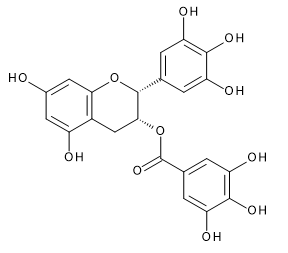 |
|
| CAS RN®:970-74-1 | CAS RN®:1257-08-5 | CAS RN®:989-51-5 | |
| C15H14O7=306.27 | C22H18O10=442.37 | C22H18O11=458.37 | |
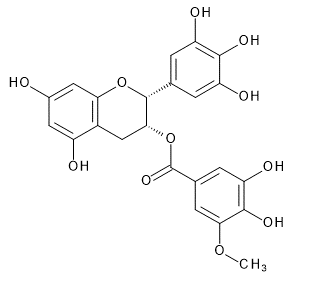
| (-)-Epigallocatechin 3-(3''-O-Methyl)gallate (Methylated Catechin) |
|||
 |
|||
| CAS RN®:83104-87-4 | |||
| C23H20O11=472.40 | |||
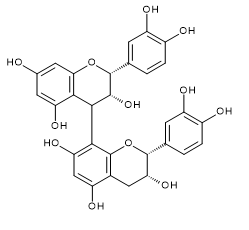
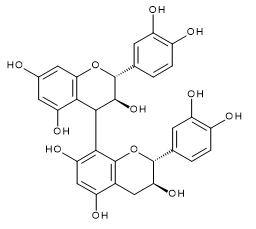
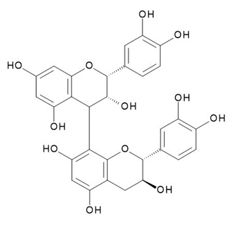
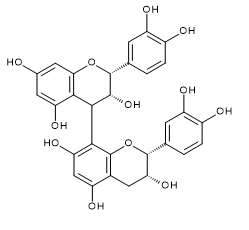
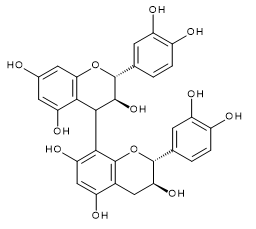
| Procyanidin B1 | Procyanidin B2 | Procyanidin B3 | |
 |
 |
 |
|
| CAS RN®:20315-25-7 | CAS RN®:29106-49-8 | CAS RN®:23567-23-9 | |
| C30H26O12=578.52 | C30H26O12=578.52 | C30H26O12=578.52 | |
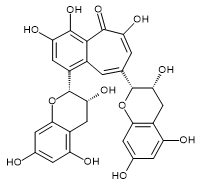
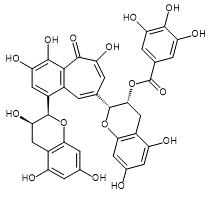
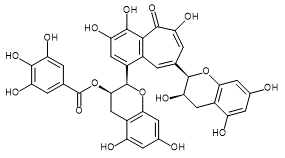
| Theaflavin | Theaflavin 3-Gallate | Theaflavin 3'-Gallate | Theaflavin 3,3'-Digallate |
 |
 |
 |
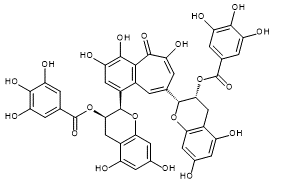 |
| CAS RN®:4670-05-7 | CAS RN®:30462-34-1 | CAS RN®:28543-07-9 | CAS RN®:30462-35-2 |
| C29H24O12=564.49 | C36H28O16=716.60 | C36H28O16=716.60 | C43H32O20=868.70 |
Procyanidins
Procyanidins (procproanthocyanidins) are compounds in which multiple catechins or epicatechins are bonded. And Procyanidins produce anthocyanidins by hydrolyzing. Apple-derived procyanidins have the function of reducing visceral fat, and mainly contain procyanidin B2.
In Japanese Agricultural Standards (JAS) 0024, method for quantifying procyanidins in apple juice (HPLC), which quantifying a series of peaks that match the retention time of procyanidin B2 as procyanidins, is defined.
Pine-bark-derived procyanidins have the function to lower bad (LDL) cholesterol, and mainly contain procyanidins B1 and B3.
Fujifilm Wako has analytical standard that can be used for various procyanidin analysis.
-
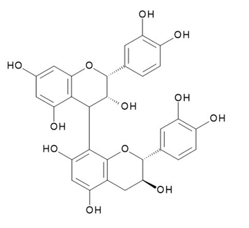
Procyanidin B1
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
Catechins
Procyanidins
Theaflavins
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.