Capping
In the process for phosphoramidite method, capping reaction after coupling reaction is important in order to avoid generating by-products. Before next step (oxidation) is carried out, unreacted nucleotide/oligonucleotide that is starting material at coupling reaction should be removed by the reaction. Because, by-products after oxidation step make a complicated for purification step when unreacted material remained.
Features
- Suitable for use in the phosphoramidite capping method
- Moisture content has been strictly controlled in both the solution and powder forms
- Available in two types: acetyl-based and phosphoramidite-based capping reagents
Mechanism of capping step
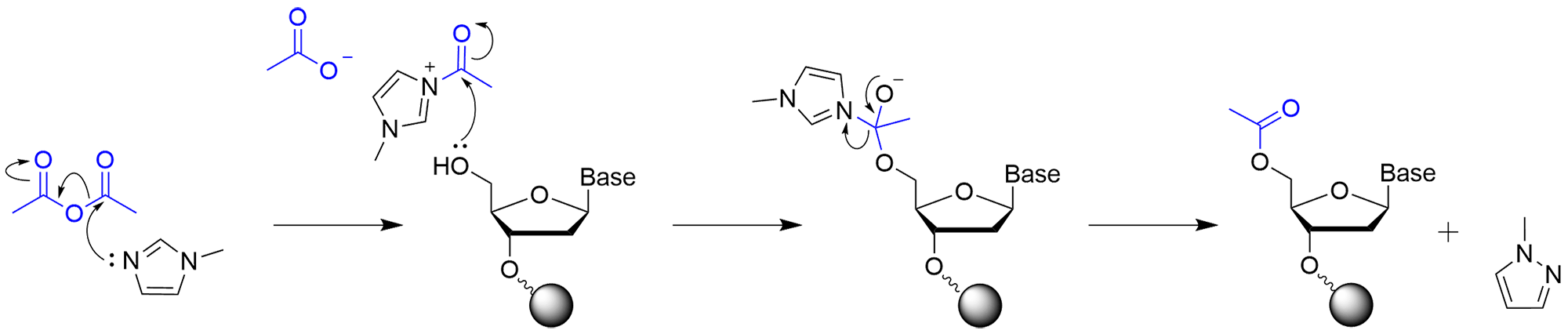
Capping reaction using acetic anhydride
Capping Reaction Using EDCP

Challenges in the Capping Reaction
Issues with Acetyl Capping
In the conventional acetyl capping method using acetic anhydride, impurities originating from adenine and guanine nucleotides are generated. These impurities arise from amide exchange, addition, and substitution reactions mediated by the acylating reagent, and are difficult to remove during purification. In addition, because UnyLinker™ exhibits low reactivity toward the secondary hydroxyl groups, impurities derived from unreacted species are also generated. These by-products are categorized and managed as product-related impurities in nucleic acid therapeutics. Therefore, establishing analytical methods and controlling these impurities remain ongoing challenges.
Generation of Impurities Derived from Adenosine1)

Generation of Impurities Derived from Guanosine2)

Generation of Impurities Derived from Unreacted Secondary Hydroxyl Group Associated with UnyLinker™2)

Phosphoramidite-Type Capping Reagent
To address the issues associated with acetyl capping, various phosphoramidite-type capping reagents have been developed since around 1994 as alternatives to acetic anhydride. Examples of these reagents are shown below. They effectively prevent reductions in purity and reaction yield caused by side reactions commonly observed with acetyl-based capping.

DDP3)
(Diethyl N,N-diisopropyl
phosphoramidite)

Lipocap4) (X=CH2)
high lipophilicity
UniCap5) (X=O)

Cholesterol phosphoramidite6)
high lipophilicity

EDCP
(Cyclic phosphoramidite)
high reactivity
References
- Rodriguez, A. A. et al. : Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 26, 3268 (2016).
- Rodriguez, A. A. et al. : Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 24, 3243 (2014).
- Yu, D. et al. : Tetrahedron Lett., 35, 8565 (1994).
- Natt, F. and Häner, R. : Tetrahedron, 53, 9629 (1997).
- Glen Report 17.13. UniCap Phosphoramidite, AN alternative to acetic anhydride capping
- Ren, Q., Osawa, T. and Obika, S : Tetrahedron., 150, 133774 (2024).
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
Phosphoramidite-Type Capping Reagent
Acetyl-Type Capping Reagent (Acetonitrile solution)
Acetyl-Type Capping Reagent (THF solution)
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.



