GC Derivatization Reagents
Gas chromatography uses derivatizing reagents to improve detection sensitivity when analytes are poorly volatile or less stable against heat.
FUJIFILM Wako provides Various GC derivatizing reagents.
Properties and Example
Gas Chromatography (GC) can analyze gases or vaporizable samples but cannot determine the poorly volatile compounds or unstable compounds that are decomposed by heat.
GC analysis can be performed by reacting with a derivatizing reagent to produce a derivative with good volatility and thermal stability. In addition, highly sensitive analysis can be performed by derivatization suitable for the detection method.
FUJIFILM Wako provides various derivatizing reagents. They can be used not only as derivatizing reagents but also for organic syntheses.
| Abbr. | chemical name | Applicable functional group | Reaction type |
|---|---|---|---|
| AIM | N-acetylimidazole | catecholamine | acylation |
| BSA | N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide | hydroxy, carboxyl, amino, amide | silylation (TMS) |
| BSTFA | N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide | hydroxy, carboxyl, amino, amide | silylation (TMS) |
| CMTMS | 1,3-bis(chloromethyl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyldisilazane | steroid | silylation (DMS) |
| DMCS | dimethylchlorosilane | steroid | silylation (DMS) |
| HFBI | N-heptafluorobutyrylimidazole | Catecholamine | acylation |
| HMDS | 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexamethyldisilazane | alcohol, phenol, carboxyl, sugar | silylation (TMS) |
| MBTFA | N-methylbistrifluoroacetamide | primary and secondary amine , hydroxy, thiol, sugar | trifluoromethylation |
| MSTFA | N-methyl-N-trimethylsilyl Trifluoroacetamide | steroid, catecholamine | silylation (TMS) |
| TFAA | trifluoroacetic Anhydride | alcohol, amine | trifluoromethylation |
| TFAI | N-trifluoroacetylimidazole | catecholamine | acylation |
| TMCS | chlorotrimethylsilane | alcohol, phenol, carboxyl, sugar | silylation (TMS) |
| TMSA | N-trimethylsilylacetamide | sugar | silylation (TMS) |
| TMSDEA | N-(trimethylsilyl)diethylamine | amino acid | silylation (TMS) |
| TMSI | N-trimethylsilylimidazole | alcohol, phenol, carboxyl acid, steroid, hormone, nucleic acid | silylation (TMS) |
Trimethyl silylation
Trimethylsilylation (TMS) is the most commonly used silylation and is applicable to most compounds with active hydrogen.
Silylation is easy in the order of alcohol > phenol > carboxylic acid > amine > amide, in the order of primary > secondary > tertiary for alcohol, and primary > secondary for amine.
| Product code | Product name | CAS RN® | Pkg. size | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 130-17881 | N-methyl-N-trimethylsilyl trifluoroacetamide (MSTFA) | 24589-78-4 | 5 mL | 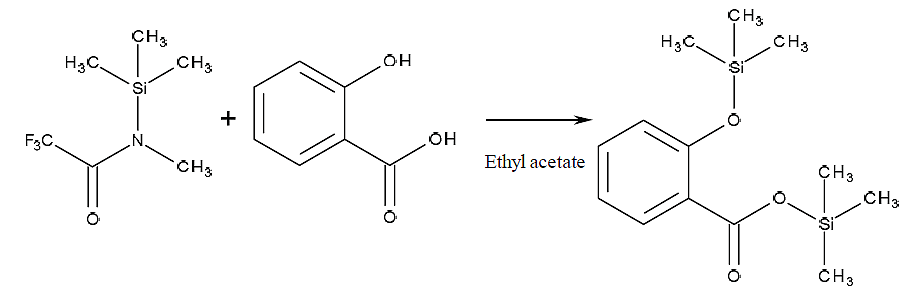 |
| 138-17882 | 25 mL |
Silylation
Silylation is a derivatization that reacts with hydroxy groups, mercapto groups, and amino groups to change poorly volatile substances to volatile ones and is used to inhibit tailing.
In GC/MS, moreover, the GC derivatizing reagent provides a mass spectrum that facilitates structural analysis and is often used to improve sensitivity and resolution. It is useful for derivatization of amides, nitrosamines, sugars, and steroids.
In addition, silylated derivatives are effective for most detection systems.
| Product code | Product name | CAS RN® | Pkg. size | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 025-18281 | N-(t-butyldimethylsilyl)-N-methyltrifluoromethyl acetamide (MTBSTFA) |
77377-52-7 | 5 mL | 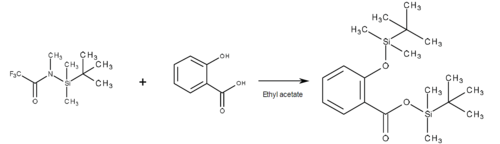 |
Acylation
This reagent introduces acyl groups into functional groups (hydroxy-, mercapto-, and amino groups) with active hydrogen to convert them into esters, thioesters, and amides. It weakens the polarity of functional groups and improves separation. It converts them to volatile compounds. Acyl groups containing halogen improve detection sensitivity in ECD.
| Product code | Product name | CAS RN® | Pkg. size | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 169-26301 | 2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorobenzoic anhydride | 15989-99-8 | 1 g | 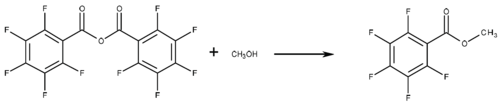 |
Esterification
Since esterification of carboxylic acid increases volatility and reduces polarity, GC analysis can be performed under mild conditions, and improvement of separation can be expected.
This reagent acts as an esterifying agent against aliphatic or aromatic carboxylic acids to easily form alkyl esters.
| Product code | Product name | CAS RN® | Pkg. size | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 139-18071 | O-methylhydroxylammonium chloride | 593-56-6 | 5 g | 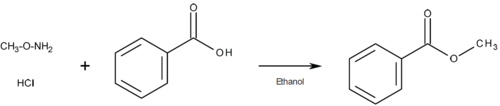 |
Other Derivatization
Ferroceneboronic acid is a useful derivatizing reagent, especially for GC-MS analysis. Alkylboronic acids react with difunctional compounds to form cyclic boronate and is used for GC analysis and GC-MS analysis.
| Product code | Product name | CAS RN® | Pkg. size | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 066-06223 | ferroceneboronic acid | 12152-94-2 | 1 g |  |
Product List
- Open All
- Close All
Silylation Reagents
Acylation Reagent
Esterification Reagent
Other Derivatization Reagent
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.
The prices are list prices in Japan.Please contact your local distributor for your retail price in your region.



