Anti Phocaeicola, Monoclonal Antibody (PV-L2B7-117K1)
- for Immunochemistry
- Manufacturer :
- FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation
- Storage Condition :
- Keep at -20 degrees C.
- Structural Formula
- Label
- Packing
|
Comparison
|
Product Number
|
Package Size
|
Price
|
Inventory
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
50uL
|
|
In stock in Japan |
Document
Product Overview
Developed by Dr. Jun Kunisawa and Dr. Ken Yoshii at the National Institutes of Biomedical Innovation, Health and Nutrition, Fujifilm Wako now offers monoclonal antibody against Phocaeicola vulgatus1) (formerly Bacteroides vulgatus). It is suitable for use in ELISA, flow cytometry, immunoprecipitation, and Western blotting, allowing for rapid, simple, and cost-effective detection of gut bacteria.
Antibody Information
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
|---|---|
| Antigen | Heat-treated Phocaeicola vulgatus |
| Host | Mouse |
| Formulation | 1 x D-PBS, 0.05% Sodium Azide |
| Conjugate | Unlabeled |
| Cross-reactivity | Phocaeicola vulgatus (DUF4988 domain-containing protein) |
| Application | ELISA (Direct/Sandwich) Flow Cytometry Immunoprecipitation Western Blotting |
Data
Quantification of Individual Gut Bacterial Species by Sandwich ELISA and Comparison with 16S rRNA Gene-Based NGS
Bacterial counts in three human fecal samples were measured using sandwich ELISA with combinations of anti-gut bacterial antibodies. Relative abundances obtained by sandwich ELISA were compared with those obtained from 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing via NGS1).
Combination of antibodies in ELISA
- (1) P. vulgatus
Capture Antibody: PV-L1A6-117K2
Detection Antibody: PV-L2B7-117K1 - (2) F. duncaniae
Capture Antibody: FD-S2D3-18K1
Detection Antibody: FD-L4F6-18K2 - (3) S. copri
Capture Antibody: SC-S10C3-49K1
Detection Antibody: SC-S10C3-49K1
Quantification of Gut Bacterial Counts by Sandwich ELISA
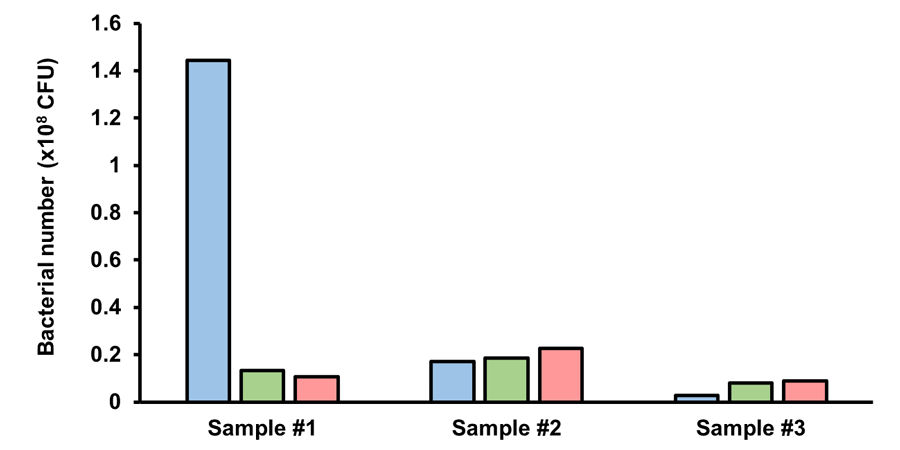
- Phocaeicola vulgatus
- Faecalibacterium duncaniae
- Segatella copri
Comparison with 16S rRNA Gene-Based NGS
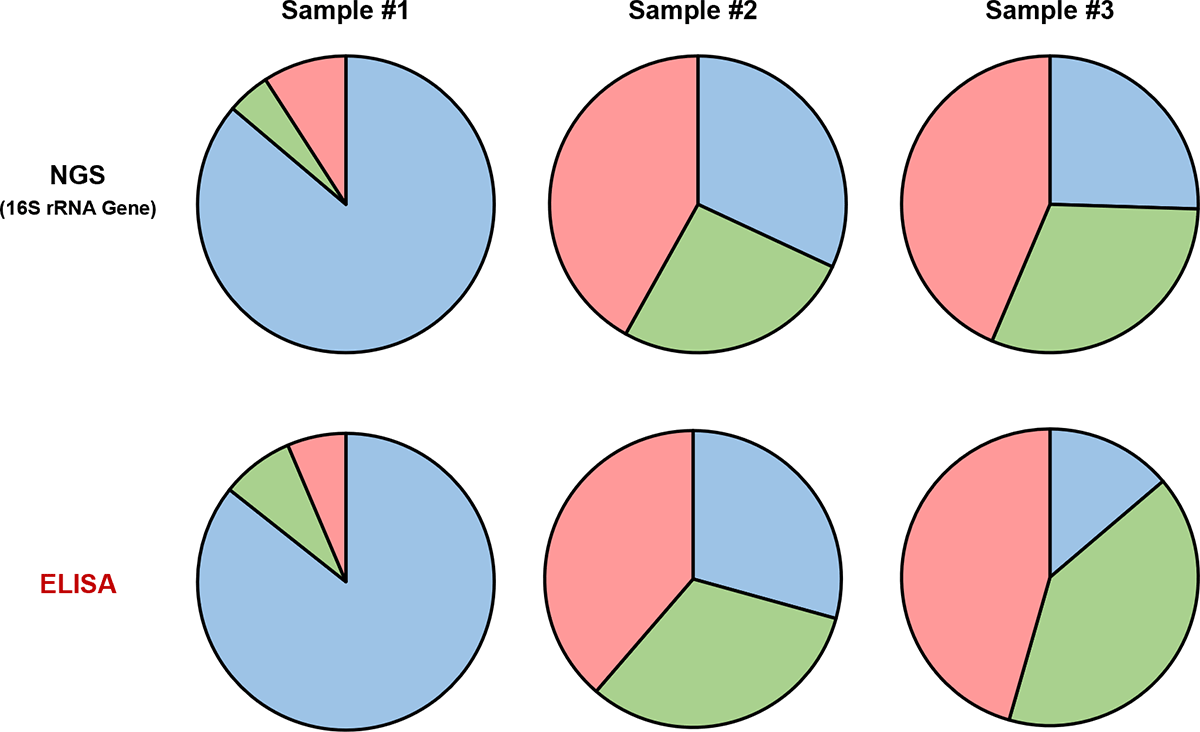
- Phocaeicola vulgatus
- Faecalibacterium duncaniae
- Segatella copri
ELISA
100 μL of a bacterial suspension was added to a 96-well microplate to coat the wells. The suspension was prepared either by diluting freeze-dried, heat-inactivated bacteria in PBS or by suspending them in B-PER solution followed by lysis with glass beads. After blocking and washing the antigen-coated plate, culture supernatants from individual hybridoma clones were added and incubated for 2 hours. Antibodies against gut bacteria bound to the antigens were detected using HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG1).
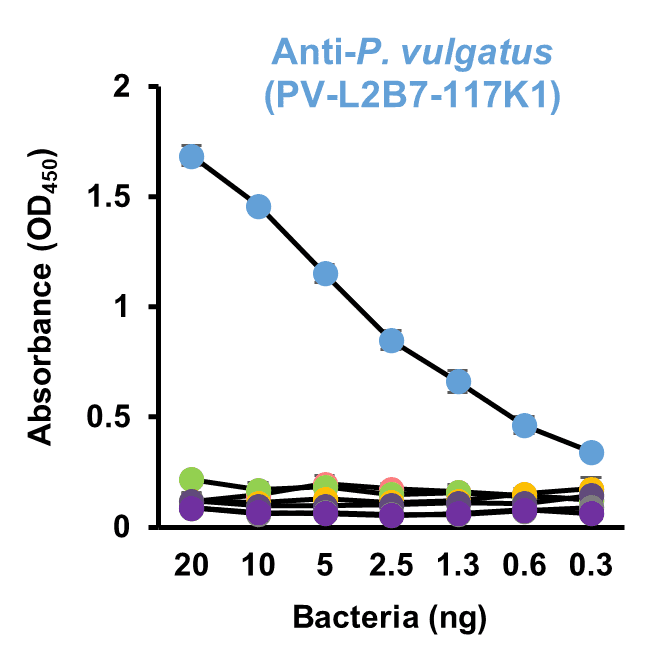
- P. vulgatus
- F. duncaniae
- S. copri
- B. pseudocatenulatum
- B. longum
- B. wexlerae
- A. muciniphila
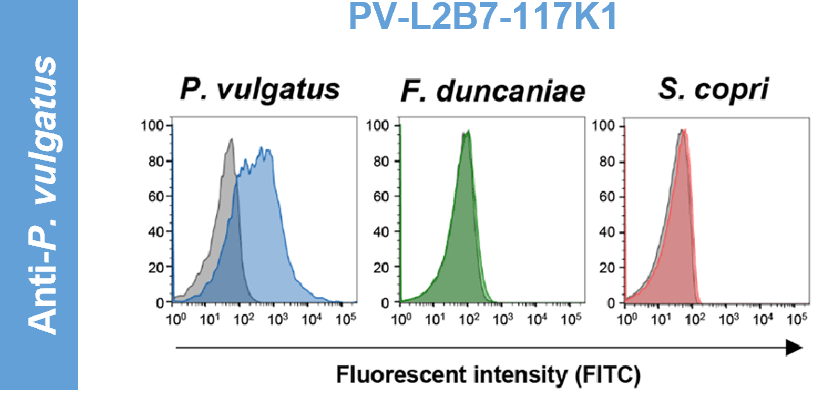
Flow Cytometry
After fixation with Farmer’s fixative (ethanol:acetic acid = 7:3), the bacteria were centrifuged at 13,040 x g for 2 minutes at 4 °C. Next, 100 μL of the bacterial suspension was mixed with 1 μg of anti-gut bacterial antibody in PBS-T containing 1% BSA and incubated on ice for 1 hour. After washing, FITC-conjugated anti-mouse IgG was added, and the sample was incubated for 30 minutes on ice in the dark. The stained bacteria were then washed and analyzed by flow cytometry1).
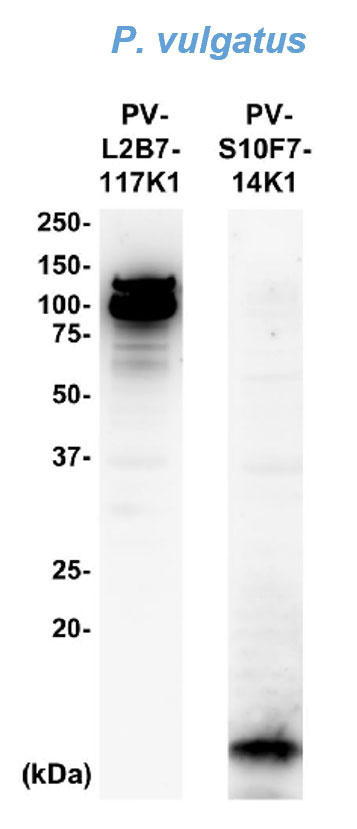
Western Blotting
Phocaeicola vulgatus JCM5826 was collected by centrifugation at 10,000 x g for 5 minutes. Two micrograms of protein were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and blocked. Immunodetection was performed using 25–50 ng/mL of anti-gut bacterial antibody and HRP-conjugated mouse IgG1).
References
- Yoshii, K. et al.: Sci. Rep., 15(1), 1(2025).
Establishment of enterotype-specific antibodies for various diagnostic systems
FAQ
About antibody
- Does this product react with Phocaeicola species other than Phocaeicola vulgatus?
- Cross-reactivity has only been confirmed for Phocaeicola vulgatus used in the immune response; cross-reactivity with other bacterial species within the same genus remains unknown.
Overview / Applications
Property
Manufacturer Information
Alias
- Anti Bacteroides, Monoclonal Antibody (PV-L2B7-117K1)
For research use or further manufacturing use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Product content may differ from the actual image due to minor specification changes etc.
If the revision of product standards and packaging standards has been made, there is a case where the actual product specifications and images are different.




